Items filtered by date: December 2014
My Xbox One Notes
There are some casting notes here: My Meta Quest 3 Notes | QuantumWarp
General
- Misc
- How to clear the cache on Xbox Series X | Digital Trends - Want to clear the cache on your Xbox Series X to help improve performance? Here's how the cache works, what it affects, and the ways to clear it on Series X.
- View the status of your game and app installations | Xbox Support
- YouTube app video is very small
- Run the screen calibration in settings. you don't need to change anything and once complete YouTube video size will be fixed.
- It indicates a value is missing and is restored using this method.
- How to fix "small screen" glitch on Xbox 1! (Still working 2023) - Sometimes on the Xbox one the display/resolution of the YouTube App will suddenly become messed up, and the directions that are on Xbox.com to fix it don’t work. This video should help to fix that glitch.
- Xbox How to Adjust Screen Size (Series X, Series S, One) - YouTube - How to change the screen aspect ratio and align TV on Xbox Series X, Xbox Series S, or Xbox One.
- Run the screen calibration in settings. you don't need to change anything and once complete YouTube video size will be fixed.
- You’re repeatedly prompted for your password when signing in on Xbox
- You’re repeatedly prompted for your password when signing in on Xbox | Xbox Support - If you’re repeatedly prompted to enter your password when you try to sign in on your Xbox One or Xbox Series X|S console, try the following solutions.
- Kodi - Enable SMB network shares as a source
- System --> Add-ons --> My add-ons --> All --> SMB support (libsmb2) --> Enable
- Now SMB shows up in the "Add video source" menu.
- If you cannot access settings
- Do a hard power cycle.
- How to restart or power cycle your Xbox console | Xbox Support - You can restart, perform a full power cycle, or physically disconnect your Xbox console to reboot it completely and fix many common issues. This process does not erase any of your games or data.
Networking
Port Forwarding
A network port lets your Xbox console communicate with the Xbox network servers and other Xbox consoles over the internet.
To let your Xbox console communicate with the Xbox network, you might need to open or forward ports, which means you'll be making a configuration change to your firewall or network hardware, such as a router. Port forwarding for Xbox is done on your router or other network hardware, not on the Xbox console itself.
Port forwarding is:
- not needed for all Xbox services
- only needed to allow for unsolicited traffic
If your router does not have UPnP enabled (or available) which just allows the Xbox to setup the port forward rules automatically, then you will manually need to configure your port forwarding.
Tutorials
- Xbox Port Forwarding: Guide - GadgetMates Help - This guide will explain what port forwarding is, why it matters for Xbox users, and how to set it up properly. Opening the right ports on your router can enhance your Xbox’s online experience, leading to smoother gameplay, less lag, and more stable connections.
- Troubleshoot NAT errors and multiplayer game issues | Xbox Support - Can your Xbox console connect to the Xbox network, but you can’t hear your friends online within a game or a party? Or are you unable to host or join a multiplayer game? If so, then you may be encountering an issue related to Network Address Translation (NAT).
- How to get Open NAT on Xbox Series X|S, Xbox One with port forwarding | Windows Central - Getting an Open Nat can vastly improve your Xbox experience. Microsoft's Xbox platform has a big multiplayer focus, and ensuring your network is properly set up for this can vastly improve your experience if you're struggling with strict NAT messages.
- Tweaking4All.com - pfSense 2.x - How to fix Strict NAT for XBox One
- A quick solution to change the annoying STRICT NAT, to OPEN NAT, on an XBox One (and possibly other consoles), when using pfSense as your firewall.
- STRICT NAT = This implies that you can join a multiplayer game and that you can chat … but you cannot host a multiplayer game. Not to mention all kinds of unexpected errors making live miserable.
- pfSense: Step by Step Guide to Multiple Xbox One's Open NAT + Play Together (2.3.x) | Digiex - This step by step guide will talk you through a working setup for allowing Multiple Xbox One's in the same network to get a fully Open NAT and be able to play together in the same games/parties all behind a pfSense Router/Firewall.
The Ports
| Port Number | Protocol | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 88 | UDP | Xbox Live connectivity | |
| 3074 | UDP/TCP | Xbox Live party chat and matchmaking | |
| 53 | UDP/TCP | Domain Name System (DNS) | Forwarding this will break local servers |
| 80 | TCP | Web traffic | Forwarding this will break local servers |
| 500 | UDP | Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) | |
| 3544 | UDP | Teredo tunneling | |
| 4500 | UDP | IPsec NAT Traversal |
- Network ports used by the Xbox network on the Xbox console | Xbox Support - Official list of required ports.
Testing
Extensible to test port forwarding you need to do the following things:
- Setup the port forwards to point to your PC.
- Run an app on the PC that exposes/responds on those ports
- From outside of your network, connect to these ports and see if you get an appropriate response.
- Once you have checked the port forwards work, re-point them to your Xbox.
Misc Diagnostic /Microsoft Network
- GitHub - microsoft/xbox-multiplayer-analysis-tool - Xbox Multiplayer Analysis Tool is a network traffic capturing tool to aid in the debugging of Xbox services issues and other network traffic from both a PC and Xbox development console.
- Xbox Status | Xbox Support - Check this page for details on the status of Xbox features and functionality.
- How to use Xbox Networking in Windows 10, to check your connection to Xbox Live | Digital Citizen - How to use the Xbox Networking tools from the Settings app or the Xbox app in Windows 10, to check the status of your internet connection and Xbox live gaming.
Open Ports (Apps)
- Simple Port Tester v.3.0.0 | PcWinTech.com™
- This port tester program will open the port on the system it is running on and listen for a connection from this site. So when the port tester program says the ports are open you can count that they are.
- This allows you to setup multiple ports at a time.
- When running it brings up an external site ready for you to test a port.
- Available as an installer or portable version.
- Easy to use but there is no stop button so you must close the app.
- MajorGeeks links
You can also use simple servers to give the same results. A bit more fiddly but a strong alternative method.
- HFS (HTTP File Server)
- Access your files directly from your disk via the web
- portable, GUI, HTTP on custom ports.
- MiniWeb HTTP server
- MiniWeb is a high-efficiency, cross-platform, small-footprint HTTP server implementation in C language. It implements GET and POST methods and works on multiple platforms ranging from server, desktop, game console and IoT hardware.
- last updated 2018
- Run on any port
miniweb.exe -r ./wwwroot -p 8080
- netcat 1.11 for Win32/Win64 - ancient netcat for Windows
- run this command to start a listener on port
12345nc -l -p 12345
- run this command to start a listener on port
- Powershell
- If you prefer no downloads, you can use PowerShell to create a simple TCP listener:
# Run in PowerShell as Administrator $listener = [System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener]8080; $listener.Start(); $client = $listener.AcceptTcpClient()
- Change
8080to your desired port. - You can then test by connecting to it from outside using
telnetornc.
- If you prefer no downloads, you can use PowerShell to create a simple TCP listener:
Check the ports are open on the PC (Apps)
- CurrPorts: Monitoring TCP/IP network connections on Windows
- CurrPorts displays the list of all currently opened TCP/IP and UDP ports on your local computer.
- This can be used to verify that the ports you have opened, are actually open.
Opened Port Testers (Online)
- GRC | ShieldsUP! — Internet Vulnerability Profiling - GRC Internet Security Detection System. Check ports and their status.
- Port Checker - Port Forwarding Tester - Port Checker is a free tool for checking open ports and to test Port Forwarding. PortChecker can also be used to diagnose router connectivity issues.
- Open Port Check Tool - Test Port Forwarding on Your Router - Port checker is a utility used to identify your external IP address and detect open ports on your connection. This tool is useful for finding out if your port forwarding is setup correctly or if your server applications are being blocked by a firewall.
- Port Forwarding Test Tools: 6 Best We Tested - Every web services must run on a port or else the service will be inaccessible.
- Open Port Check Tool -- Verify Port Forwarding on Your Router - A free open port check tool used to detect open ports on your connection. Test if port forwarding is correctly setup or if your port is being blocked by your firewall or ISP.
Opened Port Testers (Apps)
These must be run from outside of your network to be of any use in testing port forwarding.
- Advanced Port Scanner – free and fast port scanner - A free network scanner allowing you to quickly find open ports on network computers and retrieve versions of programs running on the detected ports. The program has a user-friendly interface and rich functionality.
- Zenmap - Official cross-platform Nmap Security Scanner GUI - Zenmap is the official cross-platform GUI for the Nmap Security Scanner. It is free and runs on Linux, Windows, Mac OS X, etc.
Opened Port Testers (Command Line)
These must be run from outside of your network to be of any use in testing port forwarding.
- Telenet
telnet your.public.ip 12345
Double NAT Detected
- Double NAT = An additional (or unexpected) network hop has been detected in the packet path.
- Strict NAT = UPnP is not enabled.
- Double NAT Detected
- The Xbox can be very twitchy about detecting this, so sometimes I wonder if there is actually Double NAT taking place.
- If all services are available in the Xbox network test, the this warning can be ignored as the Double NAT is not interfering with anything.
- Double NAT detection is not intrinsically bad, it is just the Xbox has detected an additional (or unexpected) network hop in the packet path.
- This additional NAT is most likely caused by an additional router or AP between the Xbox and the internet. (i.e. not all your devices are on the same subnet / You have daisy chained two routers)
- This is not caused by my Powerline adapters as I ruled this out by connecting directly to my router. Cheaper adapters can create an internally NAT network which can cause this error.
- pfSense Router (with NAT Reflection enabled)
- If running pfSense this detection "could" be caused by using NAT reflection
- You would only need to setup UPnP or port forwarding once and the router will take care of everything else.
- Detection is probably caused by NAT Reflection being present on port 80.
- I disabled NAT reflection on all of the additional port forwards (NAT) that were recommend by Microsoft to forward and this made no difference to the detection results.
- This is not caused by my pfSense router having multiple WAN Gateways. I disabled all but the WAN and still got the Double NAT detection.
- Even with Port forwarding or UPnP enables I was still getting the Double NAT issue.
- Diagnostics
- I ran packet capture on my pfSense router for the Xbox's IP and port 3074. When you see traffic here in both directions then the port forwarding is working correctly.
- I set up the port forwarding in pfSense first, but this might not be needed as the traffic from the Xbox is in response to initial packets from my Xbox on my network rather than being unsolicited.
- Expect to see traffic between your Xbox and a Microsoft IP address.
- I ran packet capture on my pfSense router for the Xbox's IP and port 3074. When you see traffic here in both directions then the port forwarding is working correctly.
- An Xbox can usually can open ports (port forward) automatically using UPnP but this has to be enabled on your router.
- Most residential routers have this on by default but commercial ones probably don't because of the security implications.
- If your Xbox network tests says NAT type = "Strict NAT" then this is a good indication that UPnP is disabled.
- Detecting Double NAT
- Use a hop plotter such as Tracert after reading the articles below.
- Double NAT. How can it be detected? (and why/how it should create issues?) - Super User
-
'Tracert' (Trace Route) command will show if you have a double NAT. e.g. tracert 8.8.8.8. You will see more than one hop with a private IP address. Note that this assumes small office / home networks where every router applies NAT. Corporate networks may have more hops and you'd need to do more testing to figure out which hops apply NAT.
- An example of something double NAT detectably breaks is UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) Port Forwarding. When a device on your network requests a temporary port forward rule from your router, it won't work right because the upstream router also needs to forward the port. The device will know something is wrong because the router replied that it granted to port open request, but the port still isn't open from the internet. The device can guess that you are in a double NAT situation.
- You can also get IP address range overlaps in double NAT situation. It could be impossible for the inner and outer network to communicate with each other because they use the same IP ranges and are thus indistinguishable. Internet may still work on the inner network depending on how smart the inner router is.
- The major reason double NAT is not desirable is devices in the outer network cannot initiate a connection to devices in the inner network. Actual routing (e.g. static routes) allows bidirectional communication.
-
- Detecting and Resolving Double Network Address Translation Issue | Intermedia Cloud Communications - This article explains when Double NAT could be an issue and what you can do to alleviate the issue.
Xbox Website
- You cannot view your games library on this site, it use to be a feature.
Xbox App (Android/Windows/Website)
General
- Xbox's PC app lists unplayable console & phone games—why? | Windows Central - Microsoft broke something on the back end of the Xbox app, but could it be a sign of things to come?
Check if your Xbox is present in the App
`Xbox App --> Library --> Consoles`
- This is not the most logical place to look for an attached Xbox, you would assume your Library is just for your games.
- If you know you have already added your Xbox at a prior time but it is not visible, then this is most likely a network issue such as Double NAT or a lack of `Port Forwarding`/`UPnP`. You should now test your Xbox network connectivity before trying anything else.
Cannot add my Xbox to the App
This can have a few causes:
- The Xbox network is down. You can check the here.
- The Xbox is already added and present.
- Network connectivity issues such as port forwarding are preventing communication.
- The Xbox is already added but not visible because of network connectivity issues.
- You cannot add the same Xbox twice to your App, it will always fail as if it cannot talk to it.
- What would be nice is if an error message came up saying you were trying to add the same Xbox twice.
XBOX 360 Emulator
- XBOX 360 Emulator - Keep asking for my Xbox password
- XBOX 360 Games on XBOX One Keeps Asking For Password - Microsoft Community
- ** Solution from Dan_774 ** ** works **
- I had this problem on my xbox one x and accidentally solved it. Here's how:
- Launch the 360 game. While in the 360 game, open the 360 menu by pressing select and start at the same time. Log in to your account. Select "remember me".
- Once logged in, open the 360 menu again and log out WHILE STAYING IN THE GAME.
- Open the 360 menu again and log in again. This time it shouldn't ask for your password.
- Now you can fully exit the game, relaunch it, and it should automatically sign you in to your 360 account.
- I did this for multiple accounts on my xbox one and it worked every time so I don't have to keep re-entering my password every time I want to play black ops 2 and any other 360 game. Hopefully it works for you, too.
- I had this problem on my xbox one x and accidentally solved it. Here's how:
- ** Solution from Dan_774 ** ** works **
- 360 games on series x never reminds my password, everything else works - Microsoft Community
- Dan_774 solution is on this page.
- Another suggestion:
- I figured it out! If you have multiple XBox Ones on your account, only the "HOME" Xbox will remember password and auto sign into xbox 360 games.
- You have to sign into your Microsoft Account on a trusted browser, then click on your profile on the top bar and go to settings to see all hardware associated with account.
- Click on your New XBox Device.
- This is good time to register with Microsoft with a click of a button BTW.
- There is no button to make a "HOME" device but there will be a button that states "This is not my Home Device" if it happens to be so.
- I sold my last xbox one and did not remove my device from account.
- Once I removed my older devices my new Xbox now remembers my XBox 360 Login and auto-sign ins. What a relief...
- I figured it out! If you have multiple XBox Ones on your account, only the "HOME" Xbox will remember password and auto sign into xbox 360 games.
- I keep getting logged out of Xbox Live playing backwards compatible games but only on the 360 not on the Xbox One. | Microsoft Community
- Your password is longer than 16 characters. 360s including the emulator on the Ones do not like passwords longer than 16 characters if your password is longer than 16 characters then you would need to change it to something smaller.
- You have two step verification turned on. Again the 360s including the emulator do not like two step verification so you would either need to turn it off or use your app password.
- You changed your gamer tag since the last time you downloaded your profile to the 360 Emulator/360 console.
- My password is too long to enter into my xbox 360 | Microsoft Community
- Basically it is a limitation to the 360 including the emulator on the One for backwards compatible games that it does not like passwords longer then 16 characters so if you are wanting to play games on your 360 just make change your password to something that is less then 16 characters.
- Enable 2Fa and generate an App password.
- XBOX 360 Games on XBOX One Keeps Asking For Password - Microsoft Community
- Passwords always incorrect
- Password always incorrect when signing into Xbox live for 360 games on Series X console | Reddit
- I found a fix. I turned off two step verification
- Yeah somewhere on the xbox / microsoft website there is some button under a "security" tab that says "generate app password" and the password it generates is what you enter for the Xbox 360 download-profile password.
- This thread also details steps including the password fix from Dan_774 but using an app password.
- App passwords can only be used if 2FA is on.
- In summary
- If you are using 2FA you need to use an App password.
- You can turn of 2FA.
- Password always incorrect when signing into Xbox live for 360 games on Series X console | Reddit
Purchases and Xbox.com
- Redeeming Codes
- To redeem a Xbox One code, use on of the following options:
- Goto to https://www.xbox.com/redeemcode
- On the Xbox One dashboard: Click on Gamertag --> Three balls --> Redeem Code
- If you get a code and it is for an Xbox 360 game, then you
- need to redeem it from the https://www.xbox.com/redeemcode
- you could maybe do it from a real Xbox 360.
- I do not know if you can do it from the 360 emulator on the Xbox One
- To redeem a Xbox One code, use on of the following options:
- View Digital Purchases
- Console: Settings --> Account Management --> Download History
- Xbox.com: Gamertag --> My Microsoft Account --> Order History
- Xbox.com: Gamertag --> Xbox Profile--> My Games ???
Controllers
Different Controller Models
- Xbox Wireless Controller (Model 1914)
- box Series X Wireless Controller (Model 1914) Repair Help: Learn How to Fix It Yourself. - The third revision of the classic Xbox Wireless Controller was released in November 2020, bundled with the Xbox Series X and Series S. This controller is backwards compatible with previous Xbox One consoles, and PCs.
- It has 3 buttons in the middle and a headphone jack.
- Xbox Wireless Controller | Xbox - Experience the modernized Xbox Wireless Controller, designed for enhanced comfort during gameplay. Stay on target with textured grip, seamlessly capture and share content.
- Xbox One Wireless Controller (Model 1708)
- Xbox One Wireless Controller (Model 1708) Repair Help: Learn How to Fix It Yourself. - Xbox One controller was introduced in 2016 with the launch of the Xbox One S and adds Bluetooth support for Windows 10/11.This controller fixes many of the design flaws found on the Model 1537/1697 controllers and is much more reliable. This controller has been replaced with the improved Model 1914 controller.
- This has a headphone jack
- Xbox Elite Wireless Controller Series 2 (Model 1797)
- Xbox Elite Wireless Controller Series 2 (Model 1797) Repair Help: Learn How to Fix It Yourself. - The Xbox Elite Wireless Controller Series 2 was released on November 4, 2019, and is compatible with the Xbox One, X, & S consoles as well as PCs running Windows 10/11.
Misc
- Microsoft Xbox Repair & Replacement Parts - Microsoft Store - Find genuine replacement parts to repair Xbox Wireless Controller and Xbox Elite Wireless Controller Series 2. Free standard shipping and returns.
- RKJXK Series | Potentiometer Type | Multi Control Devices | Products Search | Products & Technologies | Alps Alpine - Official website.
- How To Connect a wireless Xbox One controller to your console - YouTube | My Mate VINCE - How To' video shows you how to sync your Xbox One controller to your Xbox One. There are three ways that you can connect your controller.
Glossary
- Wiper
- This is the metal disc in a potentiometer that is rotated on the carbon track.
- Hall Effect Potentiometer / Hall Effect Thumbsticks
- These are potentiometers that are based on magnets rather than carbon tracks and a wiper. The benefit is that they do not have any moving parts that will wear out.
- Can Hall Effect Sensors Stop Drift Forever? - iFixit - Hall effect sensors are ideal for joysticks. Find out how Hall effect sensors work, where to find them, and why they’re the perfect antidote to joystick drift!
- Hall Effect Technology in Gaming Controllers - Learn how Hall Effect technology revolutionizes gaming controllers by providing precise control, reducing stick drift, and enhancing durability. Explore the future of gaming with advanced Hall Effect sensors.
- Everything you need to know about Hall Effect Sensing Joysticks & Trig – EasySMX
- In the world of interactive gaming, controllers are the crucial tools through which we enter and navigate virtual realms. Integral to these controllers are the joysticks and triggers, which have seen considerable evolution in their design and the technologies behind them. In this article, we delve into two significant technologies that power these components: Hall Effect sensing and potentiometer-based mechanisms, as seen in ALPS joysticks.
- Hall effect sensors don't play well with metallic parts iirc, like installing metal thumbsticks in a Xbox One controller could mess with the hall sensor triggers.
- Third party hall effect sensors replacement for xbox controller? | Microsoft Community
- Can use more power
- Xbox series controllers have a 10000Hz polling rate, but current Hall sensors are limited to 1000Hz.
- Do Hall Sensors make a difference in gameplay? | Reddit
- Hall sensors alone don't impact gameplay. They're simply a way to read the joystick. A more durable way than potentiometers, but alone they don't alter gameplay.
- Yes it does affect all non Shooters or 3D games. ALPS is far superior for metroidvanias fighting, racing, platformers in which you need perfect inputs for competitive play. HALL wont register diagonal inputs correctly (or register them at all) and most of the time you going to regret having one.
- Hall effect sensors do make a difference in gameplay. They have less of a chance to miss-input than potentiometers, and don't degrade. Having more reliable input will 100% make a difference in gameplay.
- My layman's explanation is that hall effect sensors are better than traditional carbon potentiometers because they're immune to PODE aka they don't wear down and cause misinputs.
- To keep it brief: carbon film potentiometers (the normal type found in GCCs) wear down over time, and they get less accurate. We call this "PODE" in the community. This has some positive gameplay effects, but if there is too much wear, it can have really really bad gameplay effects too.
- Hall effects sensors don't wear the same way, so once you set up your controller, it should be good to go for a much longer time.
- Jun Zeng's Hall Effect Sticks - PS5/Xbox Installation & Calibration - YouTube | VK's Channel
- These have a special board that will correct the jitter and calibrate the circularity test.
- @alexklaus2778
- One question: I also installed Hall Sticks on a XBox controller and noticed afterwards that the LT/RT Buttons also work with hall sensors. After testing it, I could see how the hall sensor in the sticks gets disturbed by the magnets on the trigger. For my normal Xbox controller I bought clicky buttons from extremerate and want to remove the magnet. You seem to only built in the hall sticks. How did you work around that problem? I guess the scuff you have there will work with the same hall technology for the LT/RT buttons.
- I do not see a proper solution there since installing the board and calibrating it with software means that it will be centered until I press the LT button (which has its hall sensor right under the sicks). That would cause the left stick to drift a little up or down.
- New V2.0 Hall Effect Modules - Now without Jitter! - YouTube | VK's Channel - Orange Module V2.0 (I bought mine from this seller it is also cheaper here) the price is for 1 unit.
- GuliKit - This company makes products with Hall Effect Sensors.
Thumbsticks: Potentiometers vs Hall Effect Sensors
Xbox controllers (most of them) come with thumbsticks that use potentiometers that change resistance so the controller knows how far you have moved the stick. This technology is well tested but the potentiometers wear out because the wiper is a piece of metal that is run against a carbon strip and because of the friction over time these will fail. Hall effect Sensors are a new technology that use magnets and as such there is no physical touching between surfaces so they do not wear out. Below I have done a table of the pros and cons of each of the technology whilst having my 1708 Xbox controller in mind, although most of the principles will be the same no matter what controller you use.
| Pros | Cons | |
| Potentiometer (POT) |
|
|
| Hall Sensor |
|
|
Conclusion
So in conclusion hall effect sensors are a good thing if decent sensors that do no suffer from jitter and that they will not interfere with the rest of your controller (i.e. triggers on the xbox controller) or you could get ones that come with an additional circuit board that prevents interference and jittering.
Using the standard potentiometers are what your controller was designed for and just swapping like for like is not a bad thing. If you keep wearing out the sticks out frequently then you should use hall sensors.
Tutorials
- Troubleshooting
- Xbox One Wireless Controller Model 1708 Troubleshooting - iFixit - How to fix common issues with the Xbox One Model 1708 and 1914 wireless controllers.
- My Xbox controller has connection issues after the last update | Xbox Support - The latest Xbox controller firmware update may affect Bluetooth connectivity and performance with some older non-Xbox devices. If your controller is having Bluetooth-related issues after a firmware update, you can choose to revert your controller to an earlier firmware version to correct the problem.
- Thumbstick Replacement
- Xbox One Wireless Controller Thumbstick Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide - This guide will assist you in replacing your thumbstick. If you have a rogue thumbstick, you have come to the right place.
- Misc
- Revert/Rollback/Downgrade Xbox Controller Firmware. There is a way to do this!!! (FULL guide with pics) - Microsoft Community
- How to Repair Xbox One Controller Triggers Like a Pro - YouTube | GetRefurbed - Welcome to our comprehensive Xbox One Controller Trigger Repair Guide! If you're tired of dealing with unresponsive or sticky triggers on your Xbox One controller, you're in the right place.
- Schematics
- XB1 Controller PCB Scans, Traces and Info - 1708 "Slim" | Acidmods
- Xbox One controllers/Xbox One Rapid fire Controllers | Acidmods - Other controllerPCB Scans, Traces and info.
- Xbox One Controller Circuit Board Layout | IOT Wiring Diagram - Diagrams, traces and other information.
- Xbox One - Search | Wiring Diagram And Schematics - Search Results for: xbox one
- Diagrama control Xbox One 1708 - YouTube | JCX
- A video of the schematics being made and a download link to the files aswell.
- Mediafire Download link of the schematics.
- A video of the schematics being made and a download link to the files aswell.
- Disassembly / Teardown
- Internal Aerial
- When removing the internal aerial be careful because the socket is very fragile
- iFixit images
- This is used for the Bluetooth.
- It is an I-PEX4 / MHF 4L socket and plug.
- Removal/Disconnection Methods
- Rotate the plug on the socket to free it up a little before you remove it. You can even rotate it when you pull it off.
- Desolder the wire on the other board, leaving the plug connected to the socket.
- use a proper removal tool
- MHF® 4L | I-PEX - MHF® 4L is the M.2 standard, mated height 1.2 mm, 1.4 mm, and 1.7 mm max., small form factor with high performance up to 12 GHz.
- How to Operate MHF® 4L Mating and Unmating Tool/ Micro RF Coaxial Connector | I-PEX - How to mate and unmate the MHF® 4L micro RF coaxial connector.
- MHF 4L Mating and Unmating Tool (I-PEX MHF4L 90609-001) Manual (PDF)
- 90609-0001 in Bag by I-PEX | Tooling and Accessories | Future Electronics - Buy I-PEX 90609-0001 in Bag. MHF4L PUSHING AND PULLING TOOL from Future Electronics
- Potentiometer (POT) / Hall Effect Sensors
- The standard potentiometers (POTs) are 10.3K Ohm
- I do not know why Hall Sensors have 2 different types on the stick.
- 1708
- Xbox One Wireless Controller Model 1708 Top Motherboard Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide - This guide will show you how to access and replace the top motherboard.
- How to Disassemble an XBOX ONE Controller - YouTube | How To Guys - Covers the 1708 model.
- Xbox One S Controller Teardown And Assembly - YouTube | TronicsFix - We disassemble and Xbox One S controller, have a look inside then reassemble it. I think this is a 1708.
- Xbox One S Controller (v3) (1708) Review - Teardown - Assembly - YouTube | sthetix - This video will show you how the new Xbox One controller V3 (the one with Bluetooth technology) looks. You can see the differences when compared to V2 controller.
- Xbox One S Controller Disassembly 2016 - YouTube | The Money Mentor - This is the new Xbox One S Controller fully disassembled.
- 1914
- How to Disassemble & Reassemble the Xbox Series X/S Controller - YouTube | MODDED WARFARE - How to completely disassemble and then reassemble an Xbox Series X/S Controller for repair, cleaning or modifications. This is the 1914 model.
- How to completely disassemble an Xbox Series X or Series S controller - YouTube | How-FixIT - Step-by-step guide to disassembling and assembling an Xbox Series X or Series S controller. DIY teardown instruction.
- Internal Aerial
Stick Drift
Testing
- Gamepad Tester - Check Controllers and Joysticks Online | Hardware Tester - Displays info about all gamepads connected to your computer. Check buttons, joystick axes, drift, and more. Works with all controllers and joysticks in a modern browser.
What Causes Stick Drift?
- this could stop stick drift, so why don't they use them? - YouTube | TinkerManMick - This explains why stick drift happens and how to fix it.
- Why Do Joysticks Drift? - YouTube | iFixitYourself - Sony isn't the only company to use off-the-shelf joystick modules, but, like Microsoft, they've made it difficult to repair this consumable component. Joysticks have a known life expectancy-it's listed right in a product sheet from the manufacturer. In this video, we head back inside a DualSense controller to see what is failing, and how.
Tutorials
- General
- How I FIXED my STICK DRIFT | Reddit
- Many different solutions on this page with explanations
- The quick and dirty diagnosis is to plug the controller into a windows pc, pull it up in the device manager and check the properties. That page will show you a real time display of what the sticks are reading for input.
- If you have a controller you don't use, replace the little plastic disks you find inside the light green housing
- Another long-term fix is to replace your controller or thumbsticks with a different kind of sensor, one that can’t wear out. A controller with Hall Effect thumbsticks works by using magnets and electrical conductors.
- How to Fix Stick Drift on Xbox One: Troubleshoot & Repairs
- This wikiHow article will go over troubleshooting steps and how to repair your controller.
- A video and many repair options.
- How to Fix Analog Drift on XBOX One or Elite Controller Series 1 (moving on its own, stopping) - YouTube | How To X
- QUICK AND TO THE POINT. The Xbox One controller can experience stick drift when one or more of the analog sticks have problems, causing characters in games to move on their own, or suddenly stop while sprinting. Usually it's because debris gets inside the analog stick, so cleaning mechanisms and sensors can help.
- This covers a lot of options including cleaning the potentiometer with alcohol.
- Here’s Why PS5 Joysticks Drift (and Why They’ll Only Get Worse) - iFixit
- Why are the PS5’s joysticks drifting? They use the same fallible hardware as most game controllers. Here’s what’s happening inside, and how we could fix it.
- A full teardown of a thumbstick and attempted fixes, including calibration, and why they only sometimes work.
- Snapback, potentiometer degradation and capacitor mod installations - This document both explains snapback and potentiometer issues for customers who want to order a controller or want to have me service their controller and serves as a reference for people looking to adjust their capacitance (scroll down to "finding the optimal capacitance" section). Apart from that, it's also hopefully a useful resource for people who want to understand controllers better.
- How I FIXED my STICK DRIFT | Reddit
- Replace Potentiometer Wiper only
- How to Repair Xbox One Analog Stick Input ( Stick Drift ) - XB1 - YouTube - How to repair Xbox One analog stick input. If your having issues with your character not walking in the direction you want or if the speed is inconsistent or lags we suggest trying to replace these analog stick sensor wheels before you buy a new XB1 controller. Often this will solve your analog stick issues.
- another stick drift fix - YouTube | TinkerManMick - Here is another method to fix stick drift for your Xbox Series X controller.
- Replace Potentiometer Only
- Xbox One Elite Controller (Model 1698) Joystick Potentiometer Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide
- XBOX Series X Controller Repair - Fake ALPS Joysticks?? - YouTube | Buy it Fix it
- This shows up close a failed potentiometer housing with the carbon rails/tracks.
- Tthe values are probably out because he has not calibrated the sticks.
- You can buy genuine parts on RS components.
- Full Stick Replacement
- ModFreakz® - How To Solder Xbox One Analog Joystick In Place - YouTube
- This video shows how to solder an analog joystick into a Xbox One controller.
- Shows a close up of an original thumbstick after it has been removed.
- How to Replace Xbox One Controller Analog Joystick - Fix Stick Drift & More - YouTube | SOSS GAMING - In this video you will learn how to test your controller, take the controller apart, remove the analog joystick, install and replace the joystick with soldering iron, use a multi-meter to measure the potentiometers, and manually calibrate the joystick.
- How to Replace Xbox One Controller Analog Joystick - NEW METHOD - Fix Stick Drift, Broken, & Loose - YouTube | SOSS GAMING
- This video explains why calibration is needed when swapping parts.
- This video shows you how to calibrate the thumbsticks by manually altering the position of the potentiometers by using their pins.
- This also shows just swapping out the wiper here, but it is not very effective.
- Xbox Series X/S Wireless Controller Joystick Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide - Follow this guide to replace a broken or drifting joystick (aka thumbstick or analog stick) for the Xbox Series X/S wireless controller.
- Xbox Series X Wireless Controller (Model 1914) Joystick Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide - This guide will show you how to replace the joystick on your Xbox Series X Wireless Controller (Model 1914) and fix stick drift.
- Xbox One Controller Fixed! Installing & Calibrating Hall Effect Sticks - YouTube | FixIt All Workshop
- How to replace Xbox One controller sticks with Hall effect sensors.
- Since the new Hall effect sensors are adjustable, I did manually adjust and calibrate them to the dead center—a time-consuming process but very useful since the Xbox One controller lacks a software calibration tool.
- ModFreakz® - How To Solder Xbox One Analog Joystick In Place - YouTube
Fixes
- Update controller firmware
- This probably will not fix anything, but it certainly will not harm.
- Software Calibration (Window Only)
- This method is only temporary and will only work on Windows.
- How to Replace Xbox One Controller Analog Joystick - NEW METHOD - Fix Stick Drift, Broken, & Loose - YouTube | SOSS GAMING
- Software Calibration (Xbox Accessories App)
- You should try software calibration before any other method if it is available to you.
- See section below.
- Modified Software Calibration (Xbox Accessories App)
- Xbox controller calibration method - YouTube | The PhotoTechy
- This is where you do not follow the calibration wizard exactly to try and mitigate the drift.
- I do not know if there is any merit in this method.
- Xbox controller calibration method - YouTube | The PhotoTechy
- Blow out the thumbsticks with air
- This only works some of the time but is worth a go.
- Clean the potentiometers (Wiper and Carbon Track) with Isopropanol alcohol.
- This worked for me and is my recommended method.
- This should not need a recalibration as you are using the original parts.
- Replace the affected potentiometer's Wiper
- Sometime this can work if cleaning does not.
- This method requires recalibration.
- NB: You can try several wipers to see if you get one that does not require calibration because it is the correct value, but this could be time consuming and might not work.
- Replace the affected potentiometer on the thumbstick
- This means you do not have to desolder the whole stick.
- This method requires recalibration.
- NB: You can use a multimeter to get potentiometers that are correct. See this tutorial for more information. How to Replace Xbox One Controller Analog Joystick - Fix Stick Drift & More - YouTube | SOSS GAMING
- Replace the thumbstick with a new one
- This method requires recalibration.
- Hardware Calibration
- If software calibration is not available there are several hardware methods avaliable to complete this process.
- See section below.
Stick Calibration Methods
Over time the resistance values in a potentiometers change over time (unless you are using hall effect ones) and so re-calibration can fix the problem but also when you swap parts in your thumbsticks these might not have the perfect values and again calibration is required.
- Xbox Accessories App (Windows and Xbox)
- This currently only works for:
- Xbox Wireless Controller (Model 1914)
- Elite 2 (model 1917)
- You might have to plug the controller in via the USB to get all options in the app.
- The Elite controller also uses this app.
- PC XBOX App does not show a calibration option | Microsoft Community - This shows in images shows only the 1914 can be calibrated with software.
- How To Recalibrate Xbox One Contoller [Quick Guide] - Tech4Gamers - Is your Xbox One controllers' calibration offset? Learn how to successfully recalibrate your controller with us.
- Using the Xbox Accessories thumbstick recalibration tool | Xbox Support - If you're experiencing minor issues with the thumbsticks on your controller, or if you are performing a self-repair of your controller and need to recalibrate the thumbsticks, you can use a self-calibration tool in the Xbox Accessories app.
- Latest Xbox Alpha Channel Update Adds Thumbstick Calibration Tool for Series Wireless and Elite 2 Controllers - XboxEra
- As part of Microsoft’s regular cadence of updates for Xbox consoles, the latest Alpha channel update includes a new feature for Xbox Series Wireless and Elite 2 controllers that allows players to calibrate their thumbsticks if they have repaired the circuit boards on the controller or to simply resolve minor thumbstick issues.
- The option will not appear for older Xbox One controllers (controllers without the share button).
- Xbox Series X/S Controller Joystick Module Replacement and Calibration - YouTube | StickFix - Removes and replaces thumbstick and then calibrates with the Xbox calibration software
- This currently only works for:
- Hall Effect Sticks / Potentiometer
- Ypu can just upgrade your potentiometers to hall effect, you do not have to swap the stick section.
- These potentiometer/sticks can be adjusted after they have been fitted.
- Xbox One Controller Fixed! Installing & Calibrating Hall Effect Sticks - YouTube | FixIt All Workshop - Hall sensors can be adjusted manually using adjustment holes.
- How To Calibrate Orange Hall Effect Analog For PS5/Dualsense Controllers!! Tutorial - YouTube | Layhss
- How To Calibrate ALL Hall Effect Analog Sticks on PS5 DualSense & PS4 Controllers! EASY Drift Fix! - YouTube | Gears and Tech - Installation of Hall Effect Sticks is complete, now its time to calibrate the sticks. Let me show you the most correct way to fix drift and centering.
- HALL EFFECT ANALOGS for PS5 & XBOX | Are they any good? - YouTube | Uber Micro Repairs - Shows the guy calibrating the hall sensors with the holes on them.
- Manually altering the position of the potentiometers by using their pins
- This is done by bending the pins of the potentiometer and/or altering the position of these pins in the PCB (which requires a soldering iron).
- How to Replace Xbox One Controller Analog Joystick - NEW METHOD - Fix Stick Drift, Broken, & Loose - YouTube | SOSS GAMING @ 825s - See this new methods in action.
- Drift Fix Adapter / Drift Repair Board
- This is a tiny circuit board that you solder onto the back of the controller’s circuit board, behind the thumbstick. It has two potentiometers that allow you to compensate for the loss of resistance in the thumb stick’s own potentiometers.
- These are used to add an easy calibration method but as such can also fix stick drift.
- You can buy these on AliExpress
- How to Fix Joystick Drift Permanently! - YouTube
- FINALLY! PERMANENTLY FIX JOYSTICK DRIFT for PS4, PS5, XBOX One, and Series X Controllers! New mod from Helder Finally Fixes Joystick Drift!
- One of the most frustrating issues with modern controllers is that they’ll eventually get joystick drift. This issue essentially makes the controller unusable. Up until now, there have only been ways to band-aid the problem but those are just temporary. We FINALLY have a permanent fix for Joystick Drift! Let’s take a closer look!
- Drift Fix Analog Stick Fix PCB Mod | Acidmods
- Has pictures
- These are not drift proof like people want them to be.
- These only meant for you to be able to re-calibrate the center.
- If the carbon filter is too far gone on the stick pots then you're still going to have noticeable drift and only a replacement can fix.
- I have the top ones but not using them because even slight calibration for example on right make analog not able to go fully left. Maybe other versions are better but that top one isn?t worth any money. I read somewhere that 10k ohm trimmers can be use for better results but never tried.
- The higher the value used the less impact is has current wise on the circuit. Remember there are 4 POTs in there that all use the same power rail. So 4 x 10k in parallel is really a single 2.5k load on there, but you toss in 4 more 10k and now it's a 1.25k load and now it is using twice as much current. Using a higher value, like 1M, it will still change the voltages of it, which is what the MCU is measuring to 'see' where the stick is, but current wise you've changed it from a 2.5k load to a 2.475k load, not a big enough difference to really matter.
- Placing it in series is far more work as you would have to place it on the correct side, or both sides and use twice as many parts, and it would really stuff up the divider. Unless you used some trimpots with more turns that you'd want to turn so you could dial in that very minute value, whereas tossing them on there in parallel is quick and easy, and unless the stick is really way off it's not noticeable, and if it is way off then trying another stick or POT should be done first before trying to dial it back in with a parallel one.
Notes
- General
- How can I calibrate the thumbsticks? - Xbox One Wireless Controller 1697 - iFixit - I replaced the thumbsticks on my 1697 model with new hall effect based thumbsticks. Is it possible to calibrate the thumb sticks? The controller firmware seems to have internal stored calibration values of old ALPS potentiometer thumbsticks. Unfortunately the new ones are slightly off center and have different full-scale deflection ratio.
- DIY Xbox Controller Repairs Just Became Much More Appealing - iFixit
- Microsoft’s new recalibration tool means that it’s actually possible for a normal human with basic soldering skills to replace their controller thumbsticks.
- Hall Potentiometers and Drift Fix Adapter are also mentioned.
- Xbox Accessories App
- Can be found
- Xbox: The Xbox Accessories app comes pre-installed on Xbox consoles. Press the Xbox button to open the guide, select My games & apps > See all > Apps, and then choose Xbox Accessories.
- Windows: To open the Xbox Accessories app on Windows, press the Start button , type Xbox Accessories or choose it from the list, and then sign in. If the app isn’t installed on your PC, get it here.
- Adjusting the controller stick settings in the Xbox Accessories app | Xbox Support - You can adjust sensitivity settings for the left and right sticks on your Xbox controller using the Xbox Accessories app to customize gameplay to your own personal need or style. This functionality is supported for the Xbox Elite Wireless Controller Series 2 and analog joysticks connected to the left or right USB ports of Xbox Adaptive Controllers.
- How to optimise your Xbox Elite Controller for better gaming | GamesRadar+ - Six tips and tricks to get the most accurate controller experience possible with Microsoft's luxury peripheral
- The Xbox February Update is Starting to Roll Out - Xbox Wire - Use touch controls in Xbox remote play, adjust thumbstick sensitivity for Xbox Wireless Controllers, and more with Xbox’s February Update. This also mentions New thumbstick recalibration tool for Xbox Wireless Controllers (Model 1914).
- Can be found
Controller Sensitivity
- Controller is hypersensitive on Xbox Home Screen / Dashboard
- This is caused by stick drift on your controller.
- I would suggest plugging it into a PC and checking the feedback from the controller.
- Problem with dashboard sensitivity | Reddit
- OoomaThurman
- i had this yesterday, i just unplugged the unit for a while and it resolved it. Reset / hard reboot did nothing to fix it. Unplugged for about 5 mins and came back to it. Might have just been a lucky reset though :-/
- Misanthrope-X
- You could check to see if your controller has a firmware update in the accessories app.
- Your second issue sounds like stick drift but the right stick doesn't have any function on the home screen so that shouldn't impact it there.
- The best you can do for stick drift is take the controller apart and clean the stick area with isopropyl alcohol but that would probably just be a temporary fix.
- MistbornSynok
- It’s caused by the stick drift, I had this issue before.
- GEDROCKL33
- Having this issue currently as well the right stick moving on its own. Which i have a friend that works with GS he put it on their controller tester for Trade ins and the Right stick was perfectly Zeroed.
- I have done a unpair repair, Hard shut off with Xbox button and left on D-Pad until the controller shut off havent done a Clear Cache reset yet but will try that first.
- Edit!!! Did a Reset Cache clear on the system and havent had any issues so far since. Link to what i did is here How to clear the cache on Xbox Series X | Digital Trends As a note i did the power cycle your xbox series X and the clear Blu Ray Cache. I did not do the reset console. Unsure if its a permanent fix but so far this has worked for me.
- OoomaThurman
- Can I adjust my Xbox Controller's sensitivity? - Quora
- If we were talking about using an Xbox One Elite controller then the answer would be "yes!"[1] . Standard Xbox One controllers don't seem to have the ability to non-invasively adjust the Trigger range[2] — which is what you're really asking about.
- All non-invasive customizations to Xbox One controllers require the Xbox Accessories app[3]. In your case, go to the Microsoft Store app on your PC and download Accessories app, then plug in your controller using a USB cable. Last time I checked this didn't work if you tried to do it using the Wireless Adapter. You'll see what you can configure and customize there.
- Having said this, the whole reason why the Elite exists is because Microsoft wanted to give non-professional players the experience of using a highly customized controller. The implication there is that it is possible to invasively modify the controller to your heart's content. How to do that? As far as I know at minute this is the only way, while each game it's different and you would need different settings.
- Each game in the settings options have the sensitivity options where you can work it out this.
- No you can not change the sensitivity in xbox one settings. Maybe in a particular game but have not got any in which you can change. So there is not pretty much customization you can do about it.
D-PAD Button Repair
- Easiest way to fix the D-pad on an Xbox controller - works on Series S, Series X and One controllers - YouTube
- This video shows how you can repair a none working D-Pad on an Xbox One, Xbox Series S & Xbox Series X controller.
- The D-Pad, also called the directional pad uses a conductive film for the buttons.
- This film is known to go bad, which causes the D-Pad to stop working.
- NB: Do not put the sticky film on top of a towel where you get loads of filth if you are going to reuse
- NB: I would use a pen to mark on the board where the outside of the plastic film sits to get a perfect fit upon re-fitting.
Use an Xbox 360 Controller on Xbox One
- How to Use an Xbox 360 Controller on Xbox One: 5 Steps
- Do you wish you could use your old Xbox 360 controller on your Xbox One or Xbox One X and S?
- While you can't directly connect an Xbox 360 controller to your Xbox One, it is possible to use an Xbox 360 controller with the Xbox One using a Windows computer.
- This wikiHow teaches you how to connect your XBox 360 controller to your Windows 10 PC and stream your Xbox One games to the XBox app on Windows 10.
- To do this, you will need an Xbox One, a Windows 10 PC, and a wired XBox 360 controller, or a wireless XBox 360 controller with a wireless adapter.
- How To Use An Xbox 360 Controller On Xbox One | Yoodley - If your Xbox One controller is broken, or if you want to connect two controllers for multiplayer purposes, you have come to the right place. This guide explains how you can connect your wired or wireless Xbox 360 controller to Xbox one and play multiplayer or other split-screen games.
- How to use a Xbox 360 controller on the Xbox One (5) - YouTube | My Mate VINCE
- This quick video shows you how to use a wired and wireless Xbox 360 controller on the Xbox One.
- This does require a 3rd party dongle.
Console Disassembly
- Schematics
- Case / Teardown
- How to Reassemble Your Xbox One Easily #Shorts - YouTube - How to Reassemble Your Xbox One easily. Putting your Xbox One back together can be a real pain. This video will show you how to do it a lot easier. (Gen 1 / Black)
- How to Open an Xbox One Console - YouTube - How to take apart an Xbox One console for cleaning, repair, hard drive upgrade or modifications. (Gen 1 / Black)
- How to Reassemble Your Xbox One Easily #Shorts - YouTube - How to Reassemble Your Xbox One easily. Putting your Xbox One back together can be a real pain. This video will show you how to do it a lot easier. (Gen 1 / Black)
- DVD Drive
- How To: Replace the Optical Drive in your XBox One! - YouTube | iFixit - Unless your buying all your games and movies online, you’re going to need your optical drive. It can be a huge annoyance when that thing stops working. So today i’m going to show you how to replace the optical drive in your XBox One! (Gen 1 / Black)
- FILTHY Xbox One S BROKEN Disc Drive | Cleaning and Repair - YouTube | Coffee and Guitars - I got this Xbox One for $20 locally. It turns on but doesn't read the disc. Let's tear it apart and see what's up!
- How To: Replace the Optical Drive in your XBox One! - YouTube | iFixit - Unless your buying all your games and movies online, you’re going to need your optical drive. It can be a huge annoyance when that thing stops working. So today i’m going to show you how to replace the optical drive in your XBox One! (Gen 1 / Black)
- Hard Drive
- Xbox One S Hard Drive Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide
- If you want to replace the hard drive with one that has a larger capacity, this guide will teach you how to replace the hard drive step by step.
- This only covers the physical swapping.
- Microsoft Xbox One S Hard Drive HDD Replacement | Repair Tutorial - YouTube | Joe's Gaming & Electronics
- Microsoft Xbox One X Software Hard Drive Replacement | Repair Tutorial - YouTube | Joe's Gaming & Electronics
- Xbox One Hard Drive Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide - Follow this guide to remove the hard drive from your Xbox One, and follow it in reverse to install a new drive. (Gen 1 / Black)
- Xbox One S Hard Drive Replacement - iFixit Repair Guide
Hard Drive upgrades and repairs
General
- Xbox One Internal Hard Drive Replacement - Playlist - YouTube | XFiX
- Got hard drive issues, no problem, well it's a problem. Let's fix it!
- An extensive list covering different issues related to hard drives.
Formatting and partitioning of the new drive and optionally transferring your data
There are several steps to swapping your harddrive depending on whether you want to move your data across. some of these tutorials assume you have stripped your Xbox apart and can access both hard drvies.
- Tutorials
- Microsoft Xbox One Hard Drive HDD Formatting Software Reinstall | Repair Tutorial - YouTube | Joe's Gaming & Electronics
- This is the tutorial I followed.
- Xbox One Internal Hard Drive Upgrade or Repair: Build any size drive that works on any console | GBAtemp.net - The Independent Video Game Community - This is a set of scripts that allow you to create a standard/official 2TB, 1TB, or 500GB internal hard drive that works on any Xbox One, Xbox One S, or Xbox One X console and can be reset and remain at that appropriate size. In effect, all Xbox One consoles are potentially 2TB consoles.
- Xbox One Windows and Linux Internal Hard Drive Partitioning Script - Updates | GBAtemp.net - The Independent Video Game Community
- Top Xbox One Hard Drive Upgrades: Boost Your Gaming Storage | Aomei - Check out this post for practical ways to make Xbox One hard drive upgrades easily - perform Xbox One internal hard drive or SSD upgrade and use external drive.
- XBOX One Hard Drive Partitioning | CD247 - How To Partition An XBOX One Hard Drive. Essential Information on how to replace a faulty XBOX One hard drive properly, or upgrade to a lager drive.
- How To Correctly Partition Your XBOX One Hard Drive For A Replacement Or Upgrade - YouTube | CD247 Repair Centre
- If you've got a faulty XBOX One hard drive, or are upgrading to a 1TB or 2TB drive, here's how to do it. This applies for HDD's, and also for Solid State Hard Drives, the process is the same.
- We are using an XBOX One S, but the process is the same for all models. The OSU update procedure for the original XBOX One is slightly different, so see my website if you have the Original model.
- If you've got a faulty XBOX One hard drive, or are upgrading to a 1TB or 2TB drive, here's how to do it. This applies for HDD's, and also for Solid State Hard Drives, the process is the same.
- Microsoft Xbox One Hard Drive HDD Formatting Software Reinstall | Repair Tutorial - YouTube | Joe's Gaming & Electronics
- Offline Update (repairs and new drives)
- Perform an offline system update | Xbox Support - The Xbox Offline System Update (OSU) process allows you to update your console by downloading a file to a USB flash drive and then installing that file directly onto your Xbox Series X|S or Xbox One console.
- Microsoft Xbox One X Offline Update E101 E106 E100 E200 E305 E208 Error Update | Repair Tutorial - YouTube | Joe's Gaming & Electronics - In this video, our technician shows how to remove and replace the hard drive on an Xbox One X and do an offline update. When we experience these error codes below we are able to repair the console 85% of the time. The HDD will be formatted and ready to install new software.
- 2024 How to Upgrade your Xbox One X and Xbox One S to SSD Drive. WITHOUT Scripts and Software! - YouTube | Electronics&Computers
DVD Drive not reading Discs
- Disc Trick
- Xbox One NOT READING DISC FIX! How to get your Xbox to READ disk AGAIN 2020 - YouTube | YXLtheMAN
- Is your Xbox One not reading your games or movies? Try this, As I show you how to fix it.
- Hold the disc while it is trying to pull it in for a moment and then push it in.
- This is not a permanent fix but more a work around if you are desperate.
- Is your Xbox One not reading your games or movies? Try this, As I show you how to fix it.
- XBOX One Disc NOT Reading - TRY THIS FIX FIRST - YouTube | CD247 Repair Centre
- This works for all XBOX One models. If your XBOX One disc isn't spinning, and therefore doesn't load, try this simple fix FIRST.
- Very often, the disc drive mechanism needs to reset. The amount of consoles I see where this will get the drive started again, is huge.
- Hold the disc as shown, and let the drive try and pull the game inside. Keep holding for a second (BUT NOT TOO LONG) and then let go, so that the disc is pulled inside.
- Xbox One NOT READING DISC FIX! How to get your Xbox to READ disk AGAIN 2020 - YouTube | YXLtheMAN
- Clean the input rollers
- Xbox One disc drive fix - YouTube | MB Outbound
- for all those who's consoles are giving you that "we cannot read this disc" error message, this is what I did to fix mine.
- The rollers that pull the disc in were cleaned and this seemed to fix his issue.
- Xbox One disc drive fix - YouTube | MB Outbound
- Swapping the Laser
- When you are swapping the laser, buy the laser on a deck as the lasers are hard to get aligned properly.
- xbox one not reading disks, but has a new laser - Xbox One - iFixit
- Q: hi, my xbox one stopped reading disks, after determining it was the laser i have replaced it, however even with the new laser it’s still not reading disks, it spins up briefly and the laser illuminates for a second but then there is nothing, like the drive goes dead, what am i doing wrong? - Xbox One
- A:
- Was the laser replaced with a replacement laser only or with the laser caddy? If it’s without the laser caddy they are really hard to align level properly.
- It’s most likely an alignment problem.
- xbox one not reading disks, but has a new laser - Xbox One - iFixit
- XBOX One (Original) DISC DRIVE Not Working? Here's The FIX - YouTube | CD247 Repair Centre
- If your Original XBOX One console isn't reading discs, has got stuck, or is making a noise, then you need to watch this video.
- I will get you to try some easy fixes first, but if all else fails, you will have to replace your laser. I'll show you how.
- How To REPLACE Your XBOX One (Original) LASER - In Real Time - YouTube | CD247 Repair Centre - I show you how to replace your Xbox One (Original) blu ray laser unit, in real time.
- How To REPLACE ANY Xbox One Laser - The COMPLETE GUIDE!! - YouTube | CD247 Repair Centre
- In this video I'll talk you through the various XBOX One laser fixes.
- All the different version of Xbox one use the same laser.
- Easiest to buy a laser on a deck.
- How to Replace your XBOX One X Laser - Won't Read Discs - Step By Step Tutorial - YouTube | CD247 Repair Centre - This video will show you how to replace the laser deck in your XBOX One X console.
- Xbox One X Won't Read Discs - Original, X & S Models - Laser Replacement - YouTube | TronicsFix - Xbox One X laser replacement can be a difficult fix. This repair video can be used to replace the laser in your Xbox One S and original consoles as well.
- SOLVED: Why won't my Xbox read disk even after replacement laser lens - Xbox - iFixit
- Optical lasers have an anti static point on the circuit board that needs to be desoldered for the laser to function. If have already removed it you have a defective laser or incorrect model for you drive.
- When you are swapping the laser, buy the laser on a deck as the lasers are hard to get aligned properly.
My Microscope Notes
This is list of my microscope kit and collection of my related notes.
Kit List
- TV with HDMI
- You need something to put the picture on.
- Microscope Base and Stand (25mm Pillar)
- This is a basic base and stand and I bought it because I could not afford a full double boom arm which should be easier to use.
- I choose 25mm pillar size because I did not think I needed a 32mm due to the work I was doing. I am still not sure what is best.
- 76mm Ring Holder Big Size Heavy Duty Adjustable Boom Large Stereo Arm Table Stand For Lab Industry Stereo Microscope Camera - AliExpress
- Connecting Objective: DIA 76mm
- Connecting Pillar: DIA 25mm
- Stand Size: 38cm x 26cm x 34c
- Stereo Microscope Limit Fix Position Ring Holder (25mm)
- This is put on the stands pillar and prevents the microscope falling down the column when you adjusting the stands position. There is also the added advantage that you can then free rotate the microscope horizontally.
- This is put on the stands pillar and prevents the microscope falling down the column when you adjusting the stands position. There is also the added advantage that you can then free rotate the microscope horizontally.
- Stereo Microscope Focusing Bracket 76mm to 50mm Microscope Adapter Ring
- Most booms and microscope stands have a holder for a traditional stereoscopic microscope which uses a 76mm holder, this adapter allows you to use a normal microscope with a diameter of 50mm on these booms and stands.
- KOPPACE Stereo Microscope Focusing Bracket Lens Interface 76mm to 50mm Microscope Adapter Ring - AliExpress
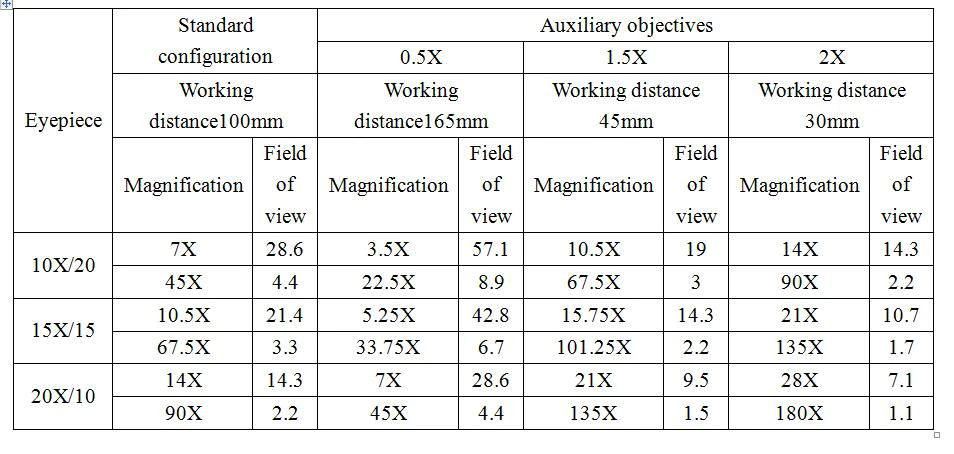
- The Microscope (180x)
- I bought the 180x but I don't know if this is too powerfil
- Adjustable 180X 120X 300X 200X 130X Zoom C mount Lens 0.7X~4.5X Magnification 25mm For HDMI USB Industry Video Microscope Camera - AliExpress
- 180x Features:
- Working distance: 100mm-150mm
- Zoom c-mount Lens
- 0.5X/1X/0.35X C-mount adapter
- zoom ratios: 6.5:1
- Objective Magnification Power by 0.6 - 4.5X(about 10 - 120X 180X or 300X on the display)
- Size: 168mm(L) * 50mm(DIA)
- 180x Features:
- I bought the 180x but I don't know if this is too powerfil
- Barlow Objective Lenses (0.5x, 0.75x, 1.0x)
- You should make sure the microscopes main lens is covered at all times to prevent it getting dirty or damaged, the 1.0x solves this issue without changing magnification (i.e. protection only).
- 0.75X 0.5X 2.0X 0.35X 1X Barlow Auxiliary Objective Glass Lens For 200X 180X 300X C MOUNT Lens Industry Video Microscope Camera - AliExpress
- Microscope Camera (Mechanic RX-510)
- Mechanic 4500 Million HD Microscope Camera RX-450 RX-510 HDMI Input Digital Simultaneous Microscope Camera for Phone Repair - AliExpress
- Specs
- Item name: 5100 million HD Microscope Camera
- Product Model: RX-510
- Colour: Red
- HDMI: 1920 X 1080@60FPS
- Video Output: 4K@25FPS 1080P@60FPS
- TF Card: Max 64G
- original Sony sensor / 4K video output / 5X zoom / ultra-high resolution image
- C-Mount fitting
- Package List
- 1pcs x Microscope Camera
- 1pcs x C to CS Mount Adapter
- 1pcs x lens cap
- 1pcs x Remote Control
- 1pcs x Type B Square Port USB Cable
- 1pcs x Chinese/English Manual
- I bought mine with a power supply.
- Mechanic Website (.com)
- Mechanic Website (.hk) - This is not a great site to navigate. I am not sure if this is their official site.
- Mechanic Facebook
- Specs
- Mechanic 4500 Million HD Microscope Camera RX-450 RX-510 HDMI Input Digital Simultaneous Microscope Camera for Phone Repair - AliExpress
- C to CS Mount Adapter
- This is an adaptor mount which allows the use of C-Mount lenses on to a CS-mount CCTV camera body.
- This adaptor ring is used in conjunction with specific C-Mount ring adaptors for various mirror less camera bodies.
- The distance from the reference surface to the focal point of the C-mount is 17.562 mm, and the focal length of the CS is 12.5 mm..
- If you are installing a C mount lens to a CS mount camera, you will need a lens converter. This kind of converter is called C-CS ring.
- This adds 5mm extra back focus to correct the position of the camera to the focal point.
- Ring Light
- A ring light is required to make sure you get a good image. 6500k is as close as you can get to natural light.
- Adjustable 6500K 5500K 144 LED Ring Light illuminator Lamp Fo Industry Stereo Microscope Lens Camera Magnifier 110V-240V Adapter - AliExpress
- Biology Stereo Microscope 23.2mm eyepiece to C-Mount adapter
- Allows me to mount my microscope camera onto my Bressler biological microscope by providing a 25mm C-Mount on top of a standard microscope eyepiece holder/tube which has an internal diameter of 23.mm.
- CMOS CCD USB HDMI Industrial Video Camera Adapter Electronic Eyepiece Microscope 23.2mm to C Mount For Biological Microscope - AliExpress
- The thread is a standard C-MOUNT for docking any C-MOUNT industrial camera or electronic eyepiece to the Biology Stereo Microscope.
- Eyepiece tube diameter of 23.2mm
Notes
- The Microscope Connections
- The eyepiece:
- C-Mount
- The Barlow Lens end:
- This is the screw thread and diameter standard for my microscope.
- 1-3/4" (42mm) Mounting Thread
- M48x0.75
- The eyepiece:
- C-Mount/ CS-Mount
- C and CS share the same connection threads
- Inner Diameter: 25.4mm / M28
- K3PGP - Experimenters Corner - Difference between C and CS mount
- The physical difference is the CS mount lens is designed to be mounted ~5mm closer to the image sensor than a C mount lens. (C-mount lenses are designed to be mounted 17.526mm in front of the image sensor vs. 12.5mm for CS-mount.)
- You can always use a C mount lens on a CS mount camera by using a 5mm spacer ring (many cameras now have C/CS selectable adjustment screws or rings).
- C-Mount | OptoWiki Knowledge Base - Standardized interface for the mounting of lenses, described in ISO 10935 (1996-12) Optics and optical instruments – Microscopes – Interface Type C
- CS-Mount | OptoWiki Knowledge Base - Standardized interface for the mounting of lenses, described in ISO 10935 (1996-12) Optics and optical instruments – Microscopes – Interface Type CS
- C and CS share the same connection threads
- Barlow Lens
- Barlow lens - Wikipedia
- Barlow Lens - Microscope.com
- A Barlow lens is a diverging lens that alters the focal length of a microscope and, therefore, the field of view.
- The most common type of Barlow lens is the Reducing Barlow.
- A Reducing Barlow reduces the magnification power of the microscope, but has the advantage of increasing the field of view and the working distance between the objective and the specimen.
- Reducing Barlows are typically 0.3x, 0.5x and 0.75x although other powers are available.
- 0.5x
- Working Distance: Increases
- Field of View: Doubles
- Magnification: Halves
- Buying Guides
- The B&H Microscope Buying Guide | B&H eXplora - Discover everything you need to know about how to buy your first or next microcope that best suites your needs.
misc
Washed out colours on my Dell U2414H monitor
I have written these instruction while trying to diagnose and fix washed out colours on my Dell U2414H monitor attached to my Dell E6540 laptop which uses the Intel HD Graphics 4600 GPU however the solutions and logic will apply to al lot of setups.
Things that can affect Colours on a monitor
- OS can affect colour?
- Graphics Card
- Windows Colour Profile
- Bad Panel / Panel Quality
- Driver
- EDID profile
- Angle of viewing
- Cable quality
Solutions
Some of these options might not realise unless you restart your PC.
- Calibration (settings can be changed at the monitor and through Windows)
- Run the Windows calibration tool (in particular, increasing Gamma)
Use an Online Gamma Calibration Tool
- Run the Windows calibration tool (in particular, increasing Gamma)
- Windows
- check the brightness in the Action Center (bottom right of screen where screen snip is)
- This will only affect the inbuilt panel
- Make sure `Night light` is not enabled.
- Make sure no 3rd party screen brightness utilities are running.
- Disable accessibility colour filters
- Make sure the monitor is set to native resolution and the correct refresh rate.
- check the brightness in the Action Center (bottom right of screen where screen snip is)
- Intel / nVidia / AMD Utility
- Ccreate a custom resolution in 1080p
- Hardware
- Use HDMI and put to full colour range
- Use external USB graphics card
- Use another graphics card (not so easy in a laptop)
- Try different HDMI cables
- The HDMI signal is especially susceptible to cheap cables.
- I won't buy another monitor without this port | Make Use Of
- HDMI 2.0 maxes out at 18Gbps, and 4K with HDR will eat most of that bandwidth alive—flickering, washed-out colors, dropped signals. HDMI 2.1 bumps that to 48Gbps, but the packaging on most cables doesn't make the distinction obvious—so you end up swapping cables and squinting at your screen.
- Laptop display panels have a hardware brightness control, look at this, but should be tied to action centre brightness setting.
- Check the monitor is being correctly detected.
- Graphics Card
- use the `Intel HD Graphics Control Panel` to alter the colour and gamma (or the nVidia/AMD equivalent)
- nVidia cards only: This can be rectified for both DisplayPort and HDMI by creating a custom resolution with a 59.999Hz refresh rate. This will be treated by any application* as 60Hz but uses the correct Full Range RGB 0-255 colour signal. The process for setting this up is shown in the video below.
- Dell U2414H monitor
- Make sure it's device driver is installed and does not display as "Generic PnP Monitor" in device manage
- Install the ICC profile for the Dell U2414H monitor. You will find this in the driver package.
- Check the monitor's viewing angle. Depending on how you look at it the picture can look bad.
- Check the monitors physical settings (colour, gamma, brightness, contrast, etc...). There is no harm in having a play as you can always put them back.
- If you have several monitors of the same model, there can be differences between the revisions.
- Your monitor is old and failing. Get a new one.
- Try all of the ports (miniDP, DP, HDMI) and see if you get a better picture through one over the others.
- Daisy chaining the DP ports should not cause any issue, but no harm i trying a single monitor on its own.
- Try Display Port v1.2
- Try your monitor with a known good laptop or PC to test to rule out the computer.
- Configure the monitor via `EDID` which I assume will require `DDC/CI` to be enabled. This monitor might not be EDID capable.
- Enable DisplayPort 1.2
- This might not be compatible with your devices and can cause the monitor to no longer recognise an input (not permanently though)
- It might make the picture better.
Dell U2414H monitor settings
These are a reference for my monitors but if you have a Dell U2414H you might as well use them.
- Custom Colour:
- R:100,
- G:98
- B:990
- Brightness: 100
- Contrast: 75
- DisplayPort: v1.2 (optional)
Research
- Windows Calibration
- General Calibration
- How to Calibrate Your Monitor Color in Windows 10 - Windows 10's built-in color calibration settings help you improve your monitors color accuracy. This article shows you how to find it and set it up.
- How to Color Calibrate Your Monitor | Windows Learning Center - Learn how to calibrate your monitor’s display colors with Windows 11. Get tips on how to have a better online shopping experience with color calibration.
- 4 Ways to Fix Washed out Colors After Windows 11 Update - Guiding Tech
- Does your monitor screen look washed out after a recent Windows update? Here are the top ways to fix washed out colors on Windows.
- Methods include Disable Color Filters in Accessibility Settings.
- Calibrate Display Color, Brightness, and Contrast in Windows 11 Tutorial | Windows 11 Forum - This tutorial will show you how to calibrate the color, brightness, and contrast of a display in Windows 10 and Windows 11.
- How to calibrate display to fix warm colors on Windows 11 - Pureinfotech - If you notice significant warm yellowish colors on the screen, you could resolve this problem calibrating the display on Windows 11.
- Color management settings in Windows - Microsoft Support - The Windows color management settings page (located in Settings > System > Display > Color profile) enables users to add or remove color profiles, set default color profiles for the connected displays, as well as access display calibration and enable automatic color management.
- How To Do Color Calibration? - Steps to manually calibrate screen color in Windows
- Monitor Looks Washed Out or Fading - Why & How to Fix It - Tech News Today - If the colors on your monitor are too bright, or the contrast seems out of place, your monitor is probably washed out or fading.
- How to Calibrate Your Monitor in Windows 10 and Fix Washed out Colors - WinBuzzer
- Washed out colors? We show you how to calibrate your monitor in Windows 10 via the in-built color calibration tool.
- Out of the factory, monitors and laptop screens can present washed out colors, a shift in RGB tones, and various other issues. Other times, the ambient lighting of the room can affect the visuals of your display and make it hard to see. As such, it's often worthwhile to calibrate your monitor in Windows 10, and we're going to show you how.
- Gamma Calibration
- How To Change Windows 11/10 Gamma Settings - In this article, we’ll show you how to change your Windows 11/10 gamma settings and improve your monitor’s color output.
- How to Change the Gamma in Windows 10 - If you’re wondering how to change the gamma on Windows 10 and customize other color calibration settings, look no further. In this article, we’ll show you what you can do to get the most accurate colors on your Windows 10.
- [Fix] Too Much Brightness, Whiteness and Gamma Level in Windows 10 and 11 Display – AskVG - If you notice extra or too much brightness or whiteness in the display of your Windows 10 or Windows 11 device, this article will help you in fixing the issue and reducing the whiteness level in your PC monitor or laptop screen.
- Misc
- How to clear the Display Profile entry? Solved - Windows 10 Forums - A few months ago I had to calibrate a very old monitor using a Spyder and calibration software and since then that monitor has died. I removed the calibration software but somehow the "profile" i had created seems sticky. Can't delete it. It may not have any impact on performance but I would like to tidy things up and delete this entry. Anyone know how?
- [Guide] How to Use Built-in ClearType Text Tuner in Windows? – AskVG - ClearType text is usually used on LCD monitors and Laptop screens. It provides smooth and clear display on your screen.
- [DPI Scaling Fix] Bold, Blurry or Hard to Read Font Problem in Windows 8.1 / 10 – AskVG - Many Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 users are facing a strange problem in which the fonts on screen look weird. The screen text becomes very hard to read. The text looks blurry like you are having an incorrect screen resolution or a faulty graphics card.
- General Calibration
- Intel 4600 HD GPU / Intel HD Graphics Control Panel Calibration
- Best settings to fix washed out colors in Intel HD Graphics Control Panel? | Reddit
- You need to set the quantization range to full range both under Display > General Settings or under Video > Color Enhancement > Input Range, where you have to click Use Driver Settings first.
- HDMI tend to default to RGB limited mode, which is what non-HDR televisions use, but it's not suitable for computer displays.
- Fix your laptop's color and brightness with Graphics Command Center | PCWorld - Fix Windows 10 auto-brightness and color problems with this hidden Intel app.
- Potential fix for Intel graphics washed out colours (non native HDMI displays) | Reddit
- When I tried to change the resolution of my monitor to something else I realised that my monitor was using the full colour range. It was only in the case of the default 1080p resolution that it would show washed out colours.
- The solution was to create a custom resolution in 1080p
- windows 10 - External monitor is washed out with Intel HD Graphics - Super User
- This is what worked in my case. My monitor was being incorrectly detected as a HDTV with limited range and adding a custom resolution with "CVT-RB" timing fixed it.
- How To Geek may have the answer! Essentially HDMI sometimes defaults to RGB Limited. You need to go into your graphics card control panel and change it to RGB Full. On Intel cards it's at the bottom of the General tab according to HTG's instructions.
- The technical difference is that full range RGB uses full 8 bit range from integer value 0 to 255 where 0 is black and 255 is white. Limited range RGB transmits the image with 8 bit integers but all values 0-35 result in black and all values 235-255 result in white. As a result, the image is actually using only integer values 35-235 meaning you get better compability with old displays but lose about 22% of all possible colors due less effective bits available for the signal.
- If GPU and display are both compatible, you always want full range RGB support.
- Some technical information here.
- How to Avoid Washed Out Colors When Using HDMI on Your PC - Black colors may look washed out and gray if you connect your PC to its display via an HDMI cable, and it's not your display's fault.
- Quantization Range Option Is Not Visible in the Intel® Graphics
- Describes expected behavior of the Quantization Range option that’s found on the Intel® Graphics Control Panel and the Intel® Graphics Command Center depending on video connection type.
- With the most recent drivers (xx.xx.100.xxxx and newer), the Quantization Range option will only be visible if the video output on your computer is native HDMI. Using a DisplayPort (DP) video output or adapters such as DP-to-HDMI or USB Type-C to-HDMI will cause the option to disappear.
- Quantization Range Option in the Intel® Graphics Control Panel or... - Expected behavior of the Quantization Range option that’s found on the Intel® Graphics Control Panel depending on video connection type.
- Best settings to fix washed out colors in Intel HD Graphics Control Panel? | Reddit
- 3rd Party Calibration add Tools
- LCD monitor test images - Welcome to the Lagom LCD monitor test pages. With the test images on these pages, you can easily adjust the settings of your monitor to get the best possible picture quality.
- Best free Monitor Calibration Tools for Windows 11/10 - Learn how to calibrate your monitor using these free Color or Monitor calibration tools for your Windows 11/10 PC. Good for Photographers or Gaming.
- 10 Best Monitor Calibration Tools for Windows in 2022 - To calibrate your monitor, you’ll need calibration software, special calibration gadgets, or a combination of both. Let’s review software and hardware to find the ideal calibration tool for your monitor.
- Best Free Monitor Calibration Software Windows 10 - TechWiser - You can always buy a hardware colorimeter but, if you have zero dollars to spend, here is some free software that will get the job done.
- Gamma calibration - Lagom LCD test
- This is a gamma calibration test image. The gamma defines how the luminance (the amount of light) on the screen depends on the 8-bit RGB values. As of 2007, computer monitors are supposed to adhere the sRGB standard, which is very similar to a gamma value of 2.2.
- Screen Brightness Tools (ie night light)
- 10 Best Monitor Brightness Control Software - Windows 10/11 come with a brightness control, but most people want something better. That's why this article will list the best screen brightness software.
- Lightbulb: open source F.Lux alternative for Windows - gHacks Tech News - Lightbulb is an open source program for Windows that provides you with options to reduce blue light automatically as the day passes by.
- Monitor Color Calibration Software: 5 Best To Use in 2024
- The 5 best display color calibration software programs for Windows PCs are Calibrize, QuickGamma, W4ZT, and CalMAN ColorMatch
- You also have the option to choose between RGB or EDID RGB. In case you don’t know, EDID RGB helps you to gain values from an external display. That way, you can connect your laptop to an external display and color calibrate it directly.
- Dell U241H Monitor
- Dell U2414H Review | PC Monitors
- A review of the Dell U2414H, a 23.8 inch AH-IPS member of the UltraSharp family with exceptionally thin bezels.
- This can be rectified for both DisplayPort and HDMI by creating a custom resolution with a 59.999Hz refresh rate. This will be treated by any application* as 60Hz but uses the correct Full Range RGB 0-255 colour signal. The process for setting this up is shown in the video below.
- Dell U2414H Review - TFTCentral - Dell's UltraSharp range always attracts quite a lot of attention and they always seem to do a good job of updating their screens to offer buyers something a bit new and different each time they do.
- U2414H Banding using sRGB preset. | DELL Technologies
- Q: My monitor is exhibiting banding with the sRGB preset. It doesn't do this on the Standard preset, but I would like to use the sRGB preset since that's the one that was factory calibrated. Is there anything I can do to correct this?
- A:
- Factory default does not over write calibrations. I would reset and check all modes.
- Install the driver from the File Library. The driver includes the INF, ICM (ICC), CAT files.
- Calibrating Dell U2410 and U2414H using Colormunki Display | DisplayCAL
- Hi! I'm new to display calibration and bought and X-Rite Colormunki Display for calibration and profiling of my Dell U2410 and U2414h.
- I followed an advice from some guys in the Dell forum and used the factory menu for OSD adjustment of the white point (because usually SRGB preset doesn’t offer RGB sliders).
- Dell U2414H Review | PC Monitors
- Misc
- If you turn all the brightness up full and a pure white page does not get any brighter then this is the maximum whiteness that the monitor will show white. If the white looks off colour at this point, then it is a limitation of the monitor.
- sRGB - Wikipedia - sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) colour space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web.
- DisplayPort - Wikipedia - DisplayPort (DP) is a proprietary[a] digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA).
- DISPLAYPORT 1.2, DISPLAYPORT 1.4, DISPLAYPORT 2.0 and DISPLAYPORT 2.1 - To help you understand the evolution and the differences between DP standards, today’s article will walk you through the differences between DisplayPort 1.2, DisplayPort 1.4, DisplayPort 2.0, and DisplayPort 2.1.
- GitHub - dylanraga/win11hdr-srgb-to-gamma2.2-icm - Transform Windows 11's virtual SDR-in-HDR curve from piecewise sRGB to Gamma 2.2
Transferring Music Tracks from Sony MiniDiscs
There are a few ways to recover music from Sony Minidiscs and these will vary between devices:
- Digital download
- Digitally without loss.
- This will be the actual audio file 'as-is' from the disk. (aea)
- Tracks will be split into individual files.
- Analogue
- Output via the 3.5mm jack.
- This is a universal method.
- There will be no track data.
- SPDIF / Optical / Coax
- Digital with minimal loss
- There will be no track data.
This article is dedicated towards digitally downloading tracks direct from the Walkman with no sound quality loss.
My Kit
- Hardware
- Windows 11 Laptop
- Sony Portable Minidisc Recorder MZ-N710 (NET MD Walkman)
- USB cable (USB A to Mini-B)
- Edge browser (Google Chrome can be used)
- Software
Dump the Music Tracks from your MiniDiscs
TL:DR
- If you just want to dump all of your miniDiscs then I would use: Method 3 (Archive Disc)
- This will download the TOC, track information in a CSV file, and all of the tracks in one operation.
Setup
- Connect device to the computer
- Using the USB A to Mini-B cable.
- Install Zadiag
- Short instructions
- Connect your MZ-N710 via the USB cable.
- Download Zadig
- Run the Zdiag installer
- Click install
- Reboot windows
- GitHub - asivery/webminidisc
- The Windows USB stack requires a driver to be installed to communicate with any USB device. The bad news is that there are no official Windows 10 drivers for NetMD devices. The good news is that we don't need it! We can just use a generic driver like WinUSB to access the device.
- You can find installation instruction here, but the easiest way to install is to use Zadig.
- Short instructions
- In Edge Browser
- Open https://web.minidisc.wiki/
- This is "Web MiniDisc Pro" and is a fork of the original but can also download tracks digitally.
- Click `CONNECT`
- Select Netman MD
- Open https://web.minidisc.wiki/
- Safety
- Make sure all your discs have write protect enabled to protect you from mistakes.
- Make sure all your discs have write protect enabled to protect you from mistakes.
- Insert your disc
- Simply put your first disc into the MZ-N710
- You will now see all of your tracks
Download the Tracks
You should now be at this screen with your tracks showing.
Method 1 (Single Track - via Main UI)
- Click on the 3 dots and select
Enable Homebrew Mode Ripping in Main UI
- Select all of the tracks you want
- Clicking the top track, hold Shift and select the last track, this will select them all.
- Click "Download"
- We don't want to convert them here, we want the RAW data.
- The track(s) will now download as .aea files labelled with their track number, and name (if present).
Method 2 (Single Track - via TOC)
- Enter Homebrew Mode
- Click on the 3 dots and select
Enter Homebrew Mode
- Read the warning and click "YES, I KNOW WHAT I AM DOING"
- Important information
- You are about to enter the homebrew mode.
- The features accessible through this mode aren't part of the NetMD specification and have not been developed by Sony.
- The developers of netmd‑exploits / netmd‑js are not responsible for any damage done to the discs, data and / or players.
- From this point on, the software assumes you know what you are doing and will not ask for confirmations or try to prevent damage.
- Important information
- Click on the 3 dots and select
- Homebrew Mode explained
- You will be now present with a some tables representing Tracks and the TOC
- See: Homebrew mode [MiniDisc Wiki]
- The "Track Junction Map" has one track per sector thing
- Track 0 is not a track, it possibly is the TOC.
- You can only download one track at a time.
- Not all tracks are named
- The unit must be power cycled between each disk (i think) to clear the TOC which also happens when you swap the disc.
- If you press the Shift key the track names should be displayed but I never got this to work, maybe my tracks did not haven names on them.
- Some things to keep in mind:
- After exiting homebrew mode, the player needs to be reset by taking out the batteries. TOC changes won't be applied otherwise. This is important for Type-R devices in particular.
- Don't enter the homebrew mode if there are any TOC Edits queued up.
- If any tracks / fragments / cells / timestamps are removed / added you will need to update the "Other TOC Values", otherwise the changes won't be applied or the disc will become corrupted.
- Digital transferring of tracks via USB only works if the track can be played by the player. If you create an invalid track and trigger a download, it will crash.
- After creating a track, please reset the player before downloading it. The players keep a second copy of the TOC, which this software cannot alter.
- If the track download is stuck on 'Seeking...' it means the track is corrupted. If you are sure the track is valid and can be played on the unit, please report it as a bug.
- This mode is still very unstable. If you find any bugs, please report them by creating an issue on this project's github page or by messaging the developers on the Minidisc.wiki Discord server.
- Download the track
- Select the 'Position Sector' tab.
- Click on a sector in "Track Junction Map"
- With 'Shift' pressed down, the ToC tiles show their numbers instead of descriptions
- Select the ToC tile with the number of the track you want to download on the Track Junction Map
- If your device supports it, there should be a download button below the tables, which you should click.
- The track will now download as an .aea file labelled with it's track number, and name (if present).
Method 3 (Archive Disc)
This is the best and most efficient way to archive your discs.
- Enter Homebrew Mode
- Read notes from Method 2
- Archive the Disc
- Click on the 3 dots and select
Toolbox --> Archive Disc
- The TOC will be downloaded as a
toc_.bin - The track and disk information will be downloaded as a CSV file.
- All the tracks will now download, one after the other each as an .aea file labelled with it's track number, and name (if present).
- The TOC will be downloaded as a
- Click on the 3 dots and select
Swapping Disc
- Disc swapping detection (not tested)
- There is an option to disable disc swapping detection. this could be useful but would require manual relaod of TOC
- I have not used this
- This is only avainable in Homebrew mode.
- Found here: Homebrew Menu --> Toolbox --> Disable disc swap detection
- Manual Method
- Stop the disk spinning before ejecting
- On my MZ-N710 if I hold the
CANCEL/CHGbutton this will stop the disc spinning and allow you to swap the disc without restarting "Web MiniDisc Pro" but this does not always work.
- On my MZ-N710 if I hold the
- You might need to restart "Web MiniDisc Pro".
- Repeat the download method you choose.
- Stop the disk spinning before ejecting
Convert the AEA files to something useful
In this section I will show you how to take the tracks that you dumped from each disc,
- and put them into 1 file. The container we will use is
MKA. This makes it much easier to manger your disks. Of course this extra step is optional.
OR - a useable format
Single-file albums, Generate multi-track files, Parallel or Sequential?
This section goes over some of the basics of how different formats handle your tracks.
- General
- To have a single audio file with multiple sequential tracks, you need to use a file format that supports CUE sheets or has an equivalent built-in method for marking track points. This is exactly how commercial music CDs work. The audio is a single, continuous stream, but the CUE sheet acts as a table of contents, telling the player where each track begins and ends.
- This approach is different from a multi-track container like MP4, where the tracks exist in parallel and the user can switch between them. In your case, the playback is seamless, and the "tracks" are just markers within the file.
- MKV, MKA, MP4 Containers
- These can store multiple separate tracks, but these will be played in parallel accompanying the video stream. This allows for the videos to have audio in different languages, eg English, Italian and German.
- You can multiplex multiple sound files together as one audio track in a container and use chapter markers to allow "Track selection". This is not exactly the same as choosing a track on a CD but is is close enough
- These containers do NOT supports embedded CUE sheets.
- Key Concepts
- Single Audio File:
- The main file contains all the audio data for every track, one after the other.
- It's one long, continuous audio stream.
- Track Markers:
- These are pieces of metadata embedded in the file or stored in a separate CUE sheet file.
- They don't contain any audio data themselves; they simply indicate the start time of each song or "track" within the single audio file.
- aka Chapters
- CUE Sheet (.cue):
- This is a plain text file that contains the metadata for the audio CD, including artist, album, and, most importantly, the start times for each track.
- The CUE sheet is typically placed in the same folder as the single audio file (often a .WAV or .FLAC file).
- When you open the CUE sheet file in a media player, it will read the metadata and present the single audio file as a list of separate tracks, allowing you to skip, shuffle, or play a specific song just as you would with individual files.
- Single Audio File:
- Chapters vs Tracks
- Chapters are time pointers on a file with limited metadata such as a title. They can be embedded in a file such a MKV/MKA or present in an external CUE file. The term chapter has come from DVDs where extensively they were Videos and not audio only like CDs.
- Tracks are individual files, with full file header and meta information. Ypu might be able to ad thee in to a single file to behanve like CD.
- Tracks and Chapters are not the same thing yet depending how you playback your media they can appear to do the same job.
- FLAC and WavePack
- These are single files that supports embedded CUE sheets allowing for multiple tracks in one file.
Getting Files Setup
- Once you have dumped all of your discs, each disc's AEA files should be in their own folder, within a parent folder as shown. This will make managing and transcoding them much easier.
C:\dumpedmusic\ C:\dumpedmusic\1\01. No title.aea C:\dumpedmusic\1\02. No title.aea C:\dumpedmusic\1\03. No title.aea C:\dumpedmusic\2\01. No title.aea C:\dumpedmusic\2\02. No title.aea C:\dumpedmusic\2\03. No title.aea C:\dumpedmusic\flacoutput\ .....
- Extract the FFmpeg binaries (..\bin\ffprobe.exe, ffplay.exe, ffmpeg.exe) to C:\dumpedmusic\
Convert all AEA files to FLAC
- My AEA files (998 files, 29 folders) 3.46GB --> 10.3GB FLAC files
AEA is not supported in the MKV container so we need to change the format of the files. FLAC is a lossless codec so is a good one to go with even thought there are a few considerations (size and no strict support). If you do not want to use FLAC the next best codec to go for is the OPUS codec which is heavily supported and is better than MP3. There are no issues with OPUS codec but it is a lossey codec.
- Open PowerShell
- Navigate to
C:\dumpedmusic\ - Run the PowerShell script below which will create an individual FLAC file from each AEA and put it in the same folder
Get-ChildItem -Filter *.aea -Recurse | ForEach-Object { ffmpeg -i $_.FullName -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "$($_.DirectoryName)\$($_.BaseName).flac" }- While running some basic information will be shown.
- All
FLACfiles will be overwritten if present, but yourAEAfiles will be untouched.
- Right click on the parent folder
C:\dumpedmusic\and select Agent Ransack - Now search for File name:
*.aea - Select all of the results and delete them
- You are now left with each of the disc folders only containing
.flacfiles.
Finalise the Format
Single FLAC file (Embeded CUE)
You can combine multiple FLAC files into a single, continuous file using a few methods, with the best choice depending on your preference for a visual interface or a command-line tool. The most common and effective method is to create a single FLAC file with a CUE sheet. This preserves the original tracklist and metadata while keeping the audio as one file.
This is the simplest method for most people. An audio editor with multi-track support allows you to arrange the files visually before exporting.
foobar2000
While primarily a media player, foobar2000 has powerful conversion and file management tools.
- Download the FLAC Tools
- FLAC - Downloads
- FLAC for Windows (the file flac-X.Y.Z-win.zip contains both command-line tools and libaries, in 32 and 64 bit).
- Install the FLAC Tools
- Extract to a folder of your choice.
- Adding flac.exe to your system PATH is optional.
- Open foobar2000 and select your files
- Add all the individual FLAC tracks to your foobar2000 playlist.
- Select all the files, right-click, and choose `Convert -> ...`
- In the `Converter Setup`
- Output format: FLAC level 5 (this is default)
- Destination: Generate multi-track files,
No title- Default:
[%album artist% - ]%album% - All tracks with the same formatted name will be put into the same file.
- Not 100% what this means, it might be for aother automations, i just selected all my files and hit convert but the files did share sequenced names i.e.: 1.flac, 2.flac etc...
- If the output format has native support for multiple tracks in one file (e.g. Ogg and MP4 containers), the converter will use this. Otherwise the converter will generate an accompanying cue sheet file (.cue) for each multi-track file.
- All internal track titles will be labelled,
No titlebecause the files you are converting do not have any metadata (i.e. title) we can use, so the output file's name will be used instead. - Title Formatting Syntax Reference - Foobar2000 | jmhauchard - All variables are explained here.
- Default:
- Processing:
- nothing to do here
- Other
- nothing to do here
- Click `Convert`
- Please select destination folder
- Select where you want to output the file
- Please locate flac.exe
- if you do not have flac.exe in your path and have not told foovar2000 where it is then you will get this popup.
- Locate and select flac.exe.
- Conversion will now run
- This will create a single FLAC file with an embedded CUE file that identifies the tracks and stores their metadata.
- Fix the Filename
- The file will be named
No title.flacso you should rename this to the disc's number eg:1.flac
- The file will be named
Adding Metadata into the FLAC file
- Use AIMP: Advanced Tag Editor
- This editor comes with the AIMP player and is super easy to use.
- It supports all available fields
Multiplex FLAC files into a MKA container
We will now use MKVToolNix to combine the tracks into one MKA file with chapters signifying the tracks.
- Open MKVToolNix
- Add Track 1
- Right click in the
Source Fileswindow, click "Add files". - Select your Track 1.
- Click "Open".
- Right click in the
- Add all of the other tracks for the disc.
- Right click on the file you have just added (Track 1) in the
Source Fileswindow and select 'Append Files'. - Select track 2, hold shift and then click on the last track to select them all. It is important to select them in the order required.
- They can now be added in one go, instead of one by one (unless you want too !!)
- Click "Open"
- Right click on the file you have just added (Track 1) in the
- Output Tab
- Miscellaneous --> Additional options:
--engage append_and_split_flac- You can also click on the button to the right to add this switch.
- This allows use to merge FLAC files. See notes for more information.
- Chapters --> Generating chapters:
One chapter for each appended file- For each track add, this sets chapter markers for it.
- Chapters --> Generating chapters:
Chapter <NUM:2>- This is the default setting and will output chapters names in the format:
Chapter 03
- This is the default setting and will output chapters names in the format:
- Miscellaneous --> Additional options:
- Set the output location and file name.
- eg: C:\dumpedmusic\flacoutput\disc1.mka
- MKA should already be set as the filename
- Recently used folders can be selected by using the favourites button to the right.
- --generate-chapters-name-template | mkvmerge -- Merge multimedia streams into a Matroska file - This sets the name template for chapter names generated by the option --generate-chapters. If the option is not used then default 'Chapter <NUM:2>' will be used.
- Now to run click on 'Start multiplexing'
- This software will now create a single MKV file with chapters using the FLAC files.
Adding Metadata into the MKA file
We have now created our disc files but the tracks have no information, we will fix that in this section.
Once you have opened your file in MKVToolNix you can swap between the Header editor and Chapter editor without have to close and reopen the same file.
- Headers
- Open MKVToolNix
- Select `Header editor`
- There is extra meta data here that you can set but I am not sure what is needed.
- Maybe add a name for the file like
80's Rockin theTitlefield. - Be careful in here as you might break stuff.
- Save
- Header editor --> Save
- Chapters
- Open MKVToolNix
- Select `Chapter editor`
- Click on `Open supported chapter file format`
- Open your
MKAdisc file. - Select a Chapter
- NB: Chapter and Track name are interchangeable as they do the same thing.
- Edit the
Namefield to something useful like:Track 01 - Status Quo - Lonely NightStatus Quo - Lonely Night
- Edit each chapter as required.
- Save
- Chapter editor --> Save
Folder with Separate Tracks
Software
Playback
So you have the files, how do you play them back. for the most part it is simple but I just want to put some notes here to allow the easy use of track/chapter selection on the various programs I have used and got working. Most of the player I have come across do not allow you to get a list of chapters up on screen easily or at all.
This table is shows how various media players can handle single-album files and chapters/tracks.
| Player | Chapter Markers | Chapters Skippable | Chapter Information Panel |
Overall Disc Time Position |
Notes |
| Audio Video Players | |||||
| VLC |
|
|
|
|
|
| PotPlayer |
|
|
|
|
|
| Kodi |
|
|
|
|
|
| SMPlayer |
|
|
|
|
|
| mpv |
|
|
|
|
|
| 5KPlayer |
|
|
|
|
|
| Audio Only Players | |||||
| AIMP |
|
|
|
|
|
| Clementine |
|
|
|
|
|
| MediaMonkey |
|
|
|
|
|
| MusicBee |
|
|
|
|
|
| foobar2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Audacious |
|
|
|
|
|
| Amarok |
|
|
|
|
|
Editing Metadata, Tags and CUE Files
- MKVToolNix
- Only for MKA and MKV
- This is a feature of the main program.
- Mp3tag
- the universal Tag Editor (ID3v2, MP4, OGG, FLAC, ...)
- Mp3tag is a powerful and easy-to-use tool to edit metadata of audio files.
- Kid3 - Audio Tagger
- If you want to easily tag multiple MP3, Ogg/Vorbis, FLAC, Monkey’s Audio, MPC, MP4/AAC, MP2, Opus, Speex, TrueAudio, WavPack, WMA/WMV, WAV and AIFF files (e.g. full albums) without typing the same information again and again and have control over both ID3v1 and ID3v2 tags, then Kid3 is the program you are looking for.
- foobar2000
- This is a feature of the main program.
- Foobar2000 Tagging ~ Fixing Swapped Artist | Title Tag Info | The Audio File - Do you have albums where the artist's names are in the track title field, and the title of the track is in the artist name field?
- AIMP: Advanced Tag Editor
- This is a feature of the main program.
- Edit a single file with all the music tracks and cue file in chapters editor?
- So it seems it is not possible to just drag the song (from the playlist) in this case (with single files without cue it is) to the Advanced Tag Editor to open it in the Chaptors editor be edited?
- Yes, it impossible. Because playlist displays cue-items, not the file.
- MediaInfo
- This is a feature of the main program.
- FFmpeg
- This is a feature of the main program.
- MetadataTouch
- Paid, not just for AV media files
- VLC
- This is a feature of the main program.
- Only file level Metadata can be edited, it does nto support chapters.
- Tools --> Menu --> Media Information
- The "General" and "Extra Metadata" tabs allow you to edit or add a wide variety of tags to the container.
- Also can be done by:
- Right click on any item in a playlist
- Select Information
- Edit the data as required
- Click save
- Audacious
- This is a feature of the main program.
- MusicBrainz Picard
- A cross-platform music tagger written in Python, powered by the MusicBrainz database.
- WonderFox HD Video Converter Factory Pro
- Wondershare UniConverter
- Lists
- 17 Best Metadata Editors in 2025 - Here are the best metadata editors that allow you to edit metadata associated with different types of files, such as videos, audio files, photos, and PDFs.
- Best Free Video Metadata Editor software for Windows PC | TheWindowsClub - Here, I will mention six options to free video metadata editor software for Windows 11/10. These software are used to view, edit, add, or remove video metadata. Let’s check these out!
- CUE files
- CUE File Specs
- CUETools - CUETools
- CUETools is a tool for lossless audio/CUE sheet format conversion. The goal is to make sure the album image is preserved accurately.
- A lossless disc image must be lossless not only in preserving contents of the audio tracks, but also in preserving gaps and CUE sheet contents. Many applications lose vital information upon conversion, and don't support all possible CUE sheet styles. For example, foobar2000 loses disc pre-gap information when converting an album image, and doesn't support gaps appended (noncompliant) CUE sheets.
- Cuegenerator
- A small online utility which facilitates creating cue files from track lists
File Splitting / Extracting
- Software
- Medieval CUE Splitter (Windows)
- CUE Splitter is a freeware tool that splits a single big audio file, mostly an album or a compilation, into the relative independent audio tracks, using the informations stored in its associated .CUE file; without decoding/re-encoding the data stream!!!
- CUETools - CUETools
- foobar2000
- mkvextract
- gMKVExtractGUI gMKVExtractGUI | SourceForge - A GUI for mkvextract utility (part of MKVToolNix) which incorporates most (if not all) functionality of mkvextract and mkvinfo utilities.
- Sheck's Software » MKVCleaver - A front end (GUI) for MKVExtract.exe (from MKVToolNix package by Moritz Bunkus) which extracts data from MKV files.
- Flacon - Audio File Encoder
- Flacon extracts individual tracks from one big audio file containing the entire album of music and saves them as separate audio files.
- Supported input formats: WAV, FLAC, APE, WavPack, True Audio (TTA)
- Supported out formats: FLAC, WAV, WavPack, AAC, OGG or MP3
- Linux and Mac ony.
- Medieval CUE Splitter (Windows)
- Tutorials
- Top 3 CUE FLAC Splitters to Separate FLAC into Tracks - Looking for a reliable CUE FLAC splitter for cutting a large FLAC audio file into multiple tracks? This post will introduce different FLAC splitters to separate FLAC with/without CUE.
Joiners / Single Album Files
These software will join multiple files into a single files, not containers.
- VLC
- This will need some search for but it is done by the command line.
- Example (untested)
"C:\PROGRAMFILES\VideoLAN\VLC\vlc.exe" -vv 1.mp3 2.mp3 --sout-keep --sout=#gather:transcode{acodec=mp3,ab=128}:standard{access=file,mux=dummy,dst=combinedout.mp3}
- Audacity
- Requires a lot of work to build a track
- foobar2000
- Foobar2000: 1 FLAC Image File From Multiple Tracks (Embedded CUE File) - YouTube | Better Anime & VGM Soundtrack Ripping
- Shows how to use the "Generate Multi-Track Files" Convert Feature to create a single FLAC image that contains all the tracks and can still be played separately using Foobar2000 or any other software supporting embedded CUE.
- Also show how to embed multiple artwork as well as EAC accurip log and EAC CUE file into the metadata tags.
- This allows for a complete archive of any album that is just 1 single file.
- Foobar2000: 1 FLAC Image File From Multiple Tracks (Embedded CUE File) - YouTube | Better Anime & VGM Soundtrack Ripping
- Lists
- 15 Best Free Video Joiners for PC – TechCult - 10+ Best Free Video Joiner for Windows 10 PC: Wondershare Filmora, VirtualDub, Clideo, Movica, WinX Free Video Converter, Adobe Spark & more.
Converters
- MKVToolNix
- Only for MKA and MKV
- This is a feature of the main program.
- VLC
- FFmpeg
- WonderFox HD Video Converter Factory Pro
- Wondershare UniConverter
- foobar2000
- fre:ac
- fre:ac is a free audio converter and CD ripper with support for various popular formats and encoders. It converts freely between MP3, M4A/AAC, FLAC, WMA, Opus, Ogg Vorbis, Speex, Monkey's Audio (APE), WavPack, WAV and other formats.
- Not been updated in a while.
- How can I make a FLAC+cue from multiple FLAC files?
- Load FLAC files and under file list enable "Create cue sheet" and "Encode to a single file" checkboxes.
- Under "Selected encoder" field choose FLAC.
- From "Encode" menu select "Start encoding" and choose output file.
- CD Rippers
- Exact Audio Copy
- Exact Audio Copy is a so called audio grabber for audio CDs using standard CD and DVD-ROM drives. The main differences between EAC and most other audio grabbers are :
- It is free (for non-commercial purposes)
- It works with a technology, which reads audio CDs almost perfectly. If there are any errors that can’t be corrected, it will tell you on which time position the (possible) distortion occurred, so you could easily control it with e.g. the media player
- In-depth Guide to Ripping Perfect FLAC files from CD - Exact Audio Copy (EAC) V1.8 (100% Logs) - YouTube | sharky
- This guide covers how to rip perfect .flac tracks from your CDs as well as a working CUE sheet, a m3u file for the album and a .log file that will score 100%...
- EAC (Exact Audio Copy) Beginners Guide - Accurate CD Archival - YouTube | Studio 3B Rocks
- This EAC (Exact Audio Copy) guide is the basic steps you will need to archive your Music CD collection into FLAC files so you can save them forever, and stream them with your favorite program for years to come.
- Exact Audio Copy is a so called audio grabber for audio CDs using standard CD and DVD-ROM drives. The main differences between EAC and most other audio grabbers are :
- CUERipper - CUETools
- CUERipper is a utility for extracting digital audio from CDs, an open-source alternative to EAC.
- It has a lot fewer configuration options, so is somewhat easier to use, and is included in CUETools package.
- Exact Audio Copy
Notes
- General
- Welcome to /r/MiniDisc - read me first! | Reddit - Hi MD friends, this community is getting big and I wanted to spend a few minutes welcoming newcomers to the community and showing off our rules and resources.
- NetMD & USB connectivity [MiniDisc Wiki]
- NetMD & USB connectivity NetMD is the USB interface that was used for transferring audio to a MiniDisc via a computer.
- Most NetMD recorders used USB Mini-B to connect to a PC. Some used full size USB Type-B, and others used a proprietary connector.
- A PC would then copy audio to the disc using software, usually SonicStage or Simple Burner.
- Remember MiniDisc? Here's How You Can Still Use It in 2020 - Old media has a way of becoming popular again (vinyl, anyone?). So, can we expect a resurgence of the MiniDisc?
- MINIDISC: A BEGINNER'S GUIDE – DELTAMEDIA INTL INC
- Introduced by Sony in 1991, the MiniDisc is a convenient recording medium that is removable, low cost and near-CD quality. This article will reveal the pros and cons of the MiniDisc format, and will explain its features.
- Background story and history of the technology including the ATRAC codec
- Web MiniDisc / Web MiniDisc Pro
- GitHub - asivery/webminidisc:
- Upload your Music to NetMD and HiMD MiniDisc devices thanks to WebUSB and WASM
- Differences between Web Minidisc and Web Minidisc Pro
- Web MiniDisc Pro was forked from the original Web MiniDisc to provide a more advanced workflow for interacting with NetMD devices.
- https://web.minidisc.wiki/is the new webapp. Web MiniDisc Pro = Brings NetMD Devices to the Web
- Web MiniDisc Pro - Brings NetMD Devices to the Web
- Bring back to life your old NetMD MiniDisc player. Upload music to MiniDisc from the Browser.
- the new version of the webapp.
- Web MiniDisc Pro - It is a complete replacement for Sony's SonicStage and Simple Burner software. It is considered the flagship NetMD software project.
- Web MiniDisc - Brings NetMD Devices to the Web
- Bring back to life your old NetMD MiniDisc player. Upload music to MiniDisc from the Browser.
- This is the original version of the webapp.
- The Web MiniDisc Application - Use your old NetMD device in the browser - Get control of your MiniDisc device thanks to WebUSB and WASM
- Some of the last MiniDisc players, branded as NetMD units, were equipped with a USB port that allowed for recording music onto the device by using the infamously SonicStage software (Windows only, of course). When Sony abandoned the MiniDisc, that software was left unmaintained and, nowadays, it can’t run outside virtual machines or without using dangerously unsigned drivers.
- I’ve been lucky enough to find my old MZ-N710
- The Web MiniDisc Application - YouTube | Stefano Brilli - A short demo of how the Web MiniDisc application works.The GitHub project also contains a few instructions to make the app work fine if you're on Windows or Linux.
- Web Minidisc Update: ToC Cloning and ATRAC download via USB on Type-S Sony NetMD portables | Reddit
- I'm very happy to announce a new version of Web Minidisc Pro. It's now possible to transfer tracks via USB back to the computer from Sony Type-S portables.
- To enable this new functionality, you must check the "Factory Mode Ripping In Main UI" switch in the ellipsis menu.
- After enabling that functionality, the 'Record' button gets replaced by the 'Download' button. If a warning shows up, saying that the current version is not supported, please use the full factory mode to download the RAM and ROM, then contact me.
- It can definitely rewrite the TOC of an errored disc, but if the disc itself is damaged, the data just won't persist, so it will go back to its old, errored self.
- Has instructions on fixing a disc's TOC
- Worked with my MZ-N710 today
- You can convert them in vlc media player if you need to, under media /convert. Vlc also does batch conversion as well.
- AEA files are supported by VLC you can convert them/batch convert them directly from vlc media player under Media/convert/save. (to mp3 should you want to).
- It won't be possible with the MDS-S500. The button to enter the factory mode won't even be displayed. This works only on portables because of how they're built (the CPU and the USB controller are one chip, this is not the case in bookshelf systems / decks).
- Sony made a tool to convert from ATRAC to MP3: https://www.sony.com/electronics/support/downloads/W0002971
- Managing tracks [MiniDisc Wiki]
- Web MiniDisc Pro has two ways to copy tracks on a MD back to the PC: recording and downloading. The Sony MZ-RH1 also allows downloads similar to the exploits method below.
- If many options are disabled, the disc may be write-protected. Check the write-protect tab on the disc (open = writable; closed = protected).
- Ignore vs Skip?
- Bad Sector - Web Minidisc Pro | Reddit
- asivery
- Skip this sector discards this sector's data, and jumps to the next one.
- Ignore writes the corrupted data to the output file you'll download.
- NeoG_
- Skip = Delete corrupted data , audio will jump slightly as part has been removed. Track length is slightly shortened.
- Ignore = Keep corrupted data, audio will act unpredictably while going over the corrupted data such as making glitchy sounds, Track length is preserved.
- asivery
- Bad Sector - Web Minidisc Pro | Reddit
- Web Minidisc Pro - Atracdenc vs Remote Atrac encoder, which gives best quality ? | Reddit
- This is for transferring music to the device
- I also read this on the web minidisc pro guide page :
- "SP mode does not need any encoder as the ATRAC processing is performed by the recorder. This also means SP mode records much slower than LP modes."
- So I guess choosing the Remote Atrac Encoder, doesn't change anything quality wise, when you choose SP mode ?
- The remote encoder uses Sony's propriety ATRAC3 encoder from the PSP SDK and has a much higher output quality when compared to atracdenc.
- And indeed, the remote encoder does not impact SP (ATRAC1) audio.
- GitHub - asivery/webminidisc:
- Other Sites
- Minidisc Community Portal - The MiniDisc Community Portal
- Minidisc Repair & Technical | Facebook Group - You want your minidisc repair yourself? Exchange technical information and repair damaged minidisc devices, a community designed to share your expertise and stories.
- Buying Guide
- MiniDisc Buyer's Guide [MiniDisc Wiki] - MiniDisc Buyer's Guide This page is intended to be a compliment to the Getting Started guide, with more details about particular generations of machine, decks, and “gotchas” - for someone new to the MD format, please check the Getting Started guide first. What do you need?
- All NetMD devices [MiniDisc Wiki] - All NetMD devices Page / USB Capable players
- Sony MZ-RH1 / MZ-M200 [MiniDisc Wiki]
- Sony MZ-RH1 / MZ-M200 The last portable MiniDisc recorder produced by Sony.
- When originally released, it was the only device capable of transferring recordings made on standard MiniDiscs back to a computer. However, this functionality is now available to all USB-equipped HiMD portables as well as a number of NetMD portables thanks to the WebMiniDisc project. A list of the NetMD portables which support this feature can be found Here
- Devices that support Homebrew features [MiniDisc Wiki]
- This page lists Type-S and Type-R portables from Sony (as well as direct clones) that support the netmd-exploits as described on the Web Minidisc Pro guide.
- The exploits for Type-S devices are older and more thoroughly tested. The exploits for Type-R devices currently operate slower and there may still be errors to work out, and not all functions are available.
- As of this writing, ripping performance is roughly: - Type-R devices will rip at roughly half of real-time, for SP audio. - Type-S devices will rip at roughly 4x real-time, for SP audio.
- Hardware
- Write Protect
- MINIDISC WRITE-PROTECT SWITCH - YouTube
- Check the write-protect tab on the disc (open = writable; closed = protected)
- Open mean the tab is there, closed the tab is pushed in so there is a gap/hole.
- An easy to read diagram

- Write Protect
- Sony MZ-N710
- Buy a `Sony MZ-N710`
- MZ-NF810 same as MZ-710 but with radio tuner.
- The Italian programmer who originally wrote this software used his MZ-710.
- Sony MZ-N710 [MiniDisc Wiki] - Sony MZ-N710 Compact and durable NetMD recorder, with its only significant downside being a reliance on gumsticks for internal power, not AA batteries. Works perfectly in both Web MiniDisc and SonicStage. Identical to the MZ-NF810, with the exception of lacking a TV tuner.
- Sony RM-MC33EL [MiniDisc Wiki] - The remote.
- Buy a `Sony MZ-N710`
- Copying MiniDiscs to PC
- Copying MiniDiscs to PC [MiniDisc Wiki]
- This guide covers real time audio transfer from a MiniDisc to a PC for archival.
- Be aware that the most common USB sound card with SPDIF input, the C-Media CM6206, does not accept inputs with a SCMS copy protection signal.
- Optical and Coaxial digital signals can be converted with an inexpensive adapter.
- Transferring MiniDisc recordings via USB tutorial (Web MiniDisc Pro) - YouTube
- This method of transferring MiniDiscs is faster than realtime, and seemingly as close to the original recording as one can get.
- Didn't see a tutorial on this so I figured I might as well make one in case this helps someone.
- Covers Method 1, Method 3
- Use Web MiniDisc Pro to transfer audio files from two NetMD Walkmans. - YouTube
- We have a MZ-N910 and we're given a MZ-N510 Sony MD Walkman. Let's use the Web MiniDisc Pro project to extract audio files digitally from these.
- Covers Method 1
- Platinum-MD - Platinum MD - Minidisc + NetMD Upload
- This project aims to make uploading audio files to NetMD players seamless and automatic.
- This has not been updated in a while.
- Avasiable for windows, Linux and Mac
- Copying MiniDiscs to PC [MiniDisc Wiki]
ATTRAC / AEA Format Information
- General
- AEA files are supported by VLC you can convert them/batch convert them directly from vlc media player under Media/convert/save. (to mp3 should you want to).
- The music/tracks on the minidisc are stored in
ATRAC1digital format and when dumped, the file type isAEA.
- File information
- AEA File - What is a .aea file and how do I open it? - Learn about .AEA files and view a list of programs that open them.
- An AEA file contains audio data encoded in the ATRAC1 format, which is a data compression format developed by Sony. It stores audio most likely dumped from a MiniDisc (MD), which is an optical disc similar to a compact disc (CD) that can be played with various MD players.
- AEA files are not common, since MDs were introduced back in 1992 and overshadowed by CDs. You will most likely never encounter an AEA file unless you dump audio from an MD you own. You may also receive an AEA file from a friend sharing music dumped from one of his MDs.
- The ATRAC1 format is a variation of the ATRAC format, which stands for Adaptive TRansform Acoustic Coding. Besides being used in MDs, the format was also utilized in the Sony Dynamic Digital Sound (SDDS) theater sound system in the 1990s.
- AEA File - What is a .aea file and how do I open it? - Learn about .AEA files and view a list of programs that open them.
- CODEC Information
- ATRAC: Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding for MiniDisc | minidisc.org
- Compression of 16-bit 44.1 kHz stereo audio into less than 1/5 of the original data rate with minimal reduction in sound quality.
- 16-bit 44.1 kHz = (16/44.1)
- .AEA File Codec Info Question... | Reddit
- DCT based audio formats don't really have a bit depth, so VLC decodes them all to 32-bit PCM internally. Newer versions of VLC identify this as "decoded bit depth" and report the original bit depth if available, but I suspect for atrac files it is not available, and only the sample rate is.
- I'm still looking for the most viable way of converting ".aea" files extracted with WebMiniDisc Pro, and although ffmpg is a good option I have the doubt about wich are the best settings for the conversion to WAV or FLAC, since in the VLC info about the ".aea" file, it says that the bit depth is 32 bits wich I find too high but altough the source is only 16 bit I don't want to convert to 16 bit as I would be cutting information from the original minidisc file... so is trully 32 bit the depth of the minidisc files (SP)?
- VLC worked fine for converting multiple at once but otherwise I used Audacity. For some reason VLC wouldn't play some of the tracks but Audacity does. You can use a software called SPEK to see if information is lost during conversion.
- The AEA files should be 16/44.1.
- The decoding is happening with the open source ATRAC1 decoder in ffmpeg/VLC and is itself passable but still not quite as good as if you'd played the audio on a minidisc machine and recorded it onto your computer.
- I haven't tested converting the AEAs to anything yet but I'd say if the result is any greater than 320 kilobits per second, something is lying along the way. The SP format is only 292kbit/sec and ATRAC isn't that miraculous.
- An alternative ATRAC decoder (and encoder...) exists in the form of "atracdenc" here: https://github.com/dcherednik/atracdenc
- I'd just go with converting to a very common lossy format once now (320 kbps MP3 if you want to overdo it, but 128/192 is probably "just fine", and if it's spoken word only - not music - even less than that should be plenty - YMMV) for everyday use and easy accessibility, and keep the AEA files for long-time archival (you can always turn the AEA files into WAV/FLAC using ffmpeg).
- ffmpeg's source code won't go away that fast, so there will always be the possibility of converting later (assuming the AEA files are smaller than a corresponding FLAC file, so you can save storage space by hanging onto the AEA files + ffmpeg instead of just FLAC). Also, VLC will most likely "forever" be able to play back AEA files on the fly.
- Analyse the
.aeafile withFFmpeg(Useffprobe) to see the properties:ffprobe input.aea [aea @ 000001bb2aec5e40] Estimating duration from bitrate, this may be inaccurate Input #0, aea, from 'input.aea': Duration: 00:05:02.25, bitrate: 292 kb/s Stream #0:0: Audio: atrac1, 44100 Hz, stereo, fltp, 292 kb/s or ffmpeg -i input.aea [aea @ 00000225f2775cc0] Estimating duration from bitrate, this may be inaccurate Input #0, aea, from 'input.aea': Duration: 00:05:02.25, bitrate: 292 kb/s Stream #0:0: Audio: atrac1, 44100 Hz, stereo, fltp, 292 kb/s At least one output file must be specified
ffmpeg -iappears to do the same thing asffprobe, however it expects an output file and will give the information but also an error.
- Analyse the
.flacfile withFFmpeg(Useffprobe) to see the properties:ffprobe input.flac Input #0, flac, from 'input.flac': Metadata: encoder : Lavf62.4.101 Duration: 00:05:02.08, start: 0.000000, bitrate: 1001 kb/s Stream #0:0: Audio: flac, 44100 Hz, stereo, s16
- ATRAC: Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding for MiniDisc | minidisc.org
Converting ATTRAC/.AEA
- Guides
- Converting ATRAC files to other formats [MiniDisc Wiki]
- Converting ATRAC files to other formats with FFMPEG.
- This will keep all the audio information in the WAV file as is. To create FLAC files with better tag and error correction support, use this command instead:
for f in *.aea; do ffmpeg -i "$f" -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "${f%.aea}.flac"; done- My PowerShell script for Windows was based off this.
- There are Windows and Linux scripts here.
- Convert ATRAC3 Plus to ATRAC1 · Issue #9 · dcherednik/atracdenc · GitHub
- Q: Is not possible yet. It's only possible to decode Atrac1, not Atrac 3 or Atrac 3 Plus.
- A: You can decode ATRAC3PLUS by FFMPEG to PCM and than encode PCM to ATRAC1. The result will be same.
- The New Year present ))
- I added support of reading from stdin for windows and POSIX. So now it should be possible make a pipe from ffmpeg to atracdenc. Example:
ffmpeg -i input_audio_file_supported_by_ffmpeg -f au - | atracdenc -e atrac1 -i - -o out.aea
- https://github.com/dcherednik/atracdenc/releases/tag/0.0.2
- For Windows Win32 Api based reader is used. Limitation: only AU(SND) 16bit 44100Hz stereo/mono input stream supported.
- I added support of reading from stdin for windows and POSIX. So now it should be possible make a pipe from ffmpeg to atracdenc. Example:
- Is there a fool's guide to the new NetMD backup exploits? | Reddit
- With that in mind, here's an easy way to convert AEA files to something else:
- If these are LP2 or LP4 recordings, you can achieve Sony-quality conversions on your computer by renaming the AEA files to OMA and using ATRACtool.
- Important to note: the aea files are ATRAC and not lossless to begin with. They are however the original data on the disc and thus the highest quality rip possible.
- It's also important to note that the files are ATRAC, and there are differing qualities of ATRAC decoders. In particular, Sony made significant improvements to the ATRAC decoding on Type-S machines.
- So, whilst if you archive the raw ATRAC data, you are getting a bit-for-bit copy of what's on the disc, however in order to play the files, they need to be converted to raw PCM at some stage of the process. Playing back these files using software decoding may result in reduced sound quality versus playing them back through a Type-S player and recording the bitstream with a lossless codec.
- I'd hazard a guess and say that a Type-S MiniDisc player has a more advanced ATRAC decoder than VLC. Many (all?) currently available software decoders are based on reverse engineering the ATRAC spec. Sony never publicly released detailed technical information on how ATRAC works, nor what improvements they made to the encoder and decoder over the years, particularly the improvements made to the decoder in Type-S machines.
- Type-R, that came out before Type-S, had a more efficient encoder - it used more processing power to optimise the allocation of bits to more "important" sounds. Discs recorded on a Type-R machine will sound better, even on older equipment, than discs recorded on older machines. Then Type-S came out, this rolled in the encoding improvements of Type-R and added decoding improvements. This could take older ATRAC data and somehow do a better job of decoding it, as well as use the Type-R improvements when recording.
- VLC Converting Guide - Is there a fool's guide to the new NetMD backup exploits? | Reddit
- There's been some discussion about the merits of ATRAC ripping versus recording the optical audio output of a deck. My apologies for contributing to the noise on that. Whenever this ocmes up I consider it important to mention there's different options with different trade-offs in terms of quality.
- Although on technicality this isn't fully correct, everyone who says ATRAC ripping is the best possible method is right that it's the fastest, most convenient, and cheapest method and typically good enough. But not always -- we've had a couple people come by who had recordings where getting every last bit of quality that existed in the recordings was important and for them, ripped ATRAC files wasn't the answer.
- Guide using VLC is given.
- Trying ATRAC1 in software way? | Reddit - Some technical information about using FFmpeg, foobar2000, atracdenc, traconv.
- Convert AEA to MP3 - Easily Convert AEA ATRAC1 Audio Files - YouTube
- Have some old AEA audio files lying around and want to convert them to the more common MP3 format? This video shows you how to convert AEA ATRAC1 audio files to MP3 effortlessly.
- WonderFox / VideoConvertoryFactory Advert.
- How to Convert AEA (ATRAC1 Audio) to MP3?
- Have some old AEA audio files lying around and want to convert them to the more common MP3 format? This post shows you how to convert AEA ATRAC1 audio files to MP3 effortlessly.
- WonderFox / VideoConvertoryFactory Advert.
- Converting ATRAC files to other formats [MiniDisc Wiki]
- Tools (ATRAC)
- Sony
- MP3 Conversion Tool (Y0015367) | Sony Asia - A tool to convert from ATRAC (v1.0.1.12270) (2008-01-30), needs SonicStage.
- MP3 Conversion Tool (W0002971) | Sony USA - A tool to convert from ATRAC (v1.0.00.06210) (2007-08-29), needs SonicStage.
- MP3 Conversion Tool (Z0005236) | Sony UK - A tool to convert from ATRAC (v1.0.1.12270) (2007-08-29), needs SonicStage.
- SonicStage Digital Archive : Sony Corporation | Internet Archive
- This is the SonicStage Digital Archive.
- These files are provided for users who are in the need to sync their Minidisc recorders with a Windows-based PC, to mix high-quality tracks using DSD, or simply for those who are interested on how this software evolved during its lifespan.
- GitHub - dcherednik/atracdenc
- Dirty implementation of ATRAC1, ATRAC3 encoder.
- This is an encoder and decoder.
- GitHub - XyLe-GBP/ATRACTool-Reloaded
- GUI-based and Open source ATRAC3 / ATRAC3+ / ATRAC9 Converter. - XyLe-GBP/ATRACTool-Reloaded
- Utility tool to convert Sony's ATRAC3/ATRAC3plus/ATRAC9(.AT3/.AT9) to Wave(.WAV) sound. or Or convert Wave sound to Sony's ATRAC3/ATRAC3plus/ATRAC9.
- ATRAC3 and ATRAC3plus are mainly used for PSP and PS3, while ATRAC9 is used for PSVita and PS4.
- atracdenc - OpenSource ATRAC1 ATRAC3 Encoder | code.mastervirt.ru
- ATRAC Decoder Encoder
- It is free LGPL implementation of ATRAC1, ATRAC3 encoders.
- Linux based utility
- This is a copy of GitHub - dcherednik/atracdenc
- GitHub - MiniDisc-wiki/atrac-utils - General utilities for working with ATRAC files.
- Sony
- Tools (Other)
- BatchEncoder (Audio Conversion GUI)
- An audio files conversion software.
- It supports most of popular audio file formats including lossy and lossless compression.
- The program is very simple to use. BatchEncoder is basically GUI front-end for command-line tools.
- All it does is create background processes and pass arguments to it with options set in presets/format menu and additionally adds input and output file paths.
- For specific options for each format use help available for command-line tools.
- Audacity ®
- Audacity is the world's most popular audio editing and recording app. Edit, mix, and enhance your audio tracks with the power of Audacity.
- This uses FFmpeg under the hood.
- Merging multiple audio files into one single file using Audacity : CRST Support - This guide will walk you through the process of merging multiple audio files into one using Audacity, a free and open-source audio editing software. This method is useful for combining recordings, music tracks, or other audio clips into a single file.
- MKVToolNix
- Description
- MKVToolNix is a set of tools to create, alter and inspect Matroska & WebM files under Windows, macOS, Linux and other Unices. It is the de-facto reference implementation of a Matroska multiplexer.
- MKVToolNix consists of the following command-line tools and GUI:
mkvmerge- is a tool to create Matroska & WebM files from other formats.
- used for merging or multiple files into one MKV file, or to rewrap a single file into an MKV file. In this process you can also select which tracks from which files you want.
mkvinfo- allows one to get information about the tracks in Matroska & WebM files.
- It just reads out all the metadata and contents of an MKV file.
mkvextract- can extract tracks from Matroska & WebM files to other formats.
- used to extract individual tracks from an MKV file into separate different non-MKV files.
mkvpropedit- can edit properties such as header and chapter information or attachments without remuxing.
- Just modifies the properties and metadata of an MKV file without remuxing or rewrapping the whole thing.
MKVToolNix GUI- sits on top of the commands
- an easy-to-use program making the functionality of those command-line tools available as a GUI.
- What it does: Designed for Matroska containers (MKV/MKA), it lets you easily mux (combine) multiple audio files into a single MKA container without re-encoding.
- Official Sites
- mbunkus/mkvtoolnix (Codeberg.org) - Creating and working with Matroska files
- MKVToolNix community & help forum - helping others use & understand MKVToolNix to its fullest potential.
- mkvmerge | MKVToolNix Docs - Merge multimedia streams into a Matroska file.
- Wiki - mbunkus/mkvtoolnix - Codeberg.org - Creating and working with Matroska files
- FAQ - mbunkus/mkvtoolnix - Codeberg.org - Creating and working with Matroska files
- Making a .MKA with many tracks (like a CD) - Need some help and clarification - Help - MKVToolNix community & help forum
- ATRAC is not supported. FLAC is supported, but appending FLAC files is currently disabled by default. You can enable it manually. Please see this FAQ entry for details & instructions.
- A lot of people append FLAC with mkvmerge with the options given in the FAQ entry. For most of them playback works fine. However, this depends on the player.
- The sentence you quoted should probably read something like this:
- "So basically in order to support appending and splitting FLAC tracks properly and be widely compatible with other devices I would have to implement my own FLAC decoder, something I’m not willing to do."
- FLAC is the only audio format for which this is a problem in mkvmerge.
- And again, please read about adding vs appending, as “only the first track plays” is the usual symptom for when you add all files instead of appending the second & all following files, causing content of all files to be laid out in parallel instead of in sequence.
- mbunkus
- Personally I use Opus for everything. For my personal audio I usually encode at 140 or so, but please look elsewhere for evidence-backed info on which bitrates to use for it. It’s been a while since I looked into it.
- Generally it depends on the devices you want to play your stuff on. Most software players support Opus, and I don’t think there’s really one that supports Matroska but not Opus. Hardware players are obviously a different topic.
- If I don't use
FLAC, and I cannot useAEA, what si the next best codec to use =OPUS
- Adding files vs. Appending files vs. adding as additional parts - mbunkus/mkvtoolnix - Codeberg.org
mkvmergecan lay out content either in parallel or sequentially:- Parallel: when you have three files that are laid out in parallel, the content of all three files will be played simultaneously.
- Sequentially: when you have three files that are laid out sequentially, all of the content of file 1 is played first followed by all of the content of file 2 and finally followed by all the content of file 3.
- "Appending files" vs "adding as additional parts"
- If you ever run across media files which have been split somewhere in the middle with a program like WinSplit (meaning they've been split at an arbitrary position), then the second part won't have a full set of headers.
- In such cases mkvmerge can treat those two parts as if they were only one file.
- This is what the »add as additional parts« option does.
- My thoughts:
- Append files = Normal track use.
- Adding as additional parts = For single files that have been split without each getting their own header or certain media like DVD VOB files.
- Appending & splitting FLAC audio tracks not supported - mbunkus/mkvtoolnix - Codeberg.org
- FLAC audio tracks cannot be appended or split with
mkvmerge. Versions up to and including v44 did not actually emit error messages; however, the result was that the resulting FLAC tracks were invalid and could often not be played. - Starting with version 45
mkvmergewill refuse to append or split FLAC audio tracks and emit an error message instead. - Starting with version 47, the old behavior can be restored by adding
--engage append_and_split_flactomkvmerge's command-line options (in the GUI: multiplexer → "Output" tab → "Miscellaneous" → "Additional options"). Please note that this will result in broken tracks: the official FLAC tools will not be able to decode them and seeking will not work as expected.
- FLAC audio tracks cannot be appended or split with
- Muxing | The Wiki - Muxing files with MKVToolNix
- Description
- GUI for mkvextract
- GitHub - Gpower2/gMKVExtractGUI
- A GUI in C# for mkvextract (MKVToolNix).
gMKVExtractGUIis a powerful and intuitive Graphical User Interface (GUI) built in C# .NET 4.0 for the essentialmkvextractutility, which is part of the MKVToolNix suite. It aims to provide a user-friendly wrapper that incorporates most (if not all) of the functionality of bothmkvextractandmkvinfo.
- Sheck's Software » MKVCleaver
- A front end (GUI) for MKVExtract.exe
- Extract data from multiple MKV files with minimum effort form the user.
- Enables the user to manipulate the extraction process on per file basis or as a whole.
- Provides information about each file to allow the user to make the best decision about the extraction setup.
- Provides a visual interface to MKVExtract.exe and allows to drag & drop files, manipulate extracted filenames based on a user’s criteria, session recovery after a crash or an error, changing of extraction options without messing around with the command line, extraction error tracking…
- GitHub - Gpower2/gMKVExtractGUI
- Batch Multiplexing (mkmerge)
- GitHub - akai10tsuki/mkvbatchmultiplex
- Batch multiplex video files using MKVToolnix generated command line
- A program is for processing mkvmerge command line and use it as a template to apply the multiplex instructions to all the files found in the directory.
- mkvbatchmultiplex Documentation | ReadTheDoccs - No meta description
- GitHub - akai10tsuki/mkvbatchmultiplex
- BatchEncoder (Audio Conversion GUI)
Other Codec/ Container and Tools
Audio Containers
TL;DR
- Local Files: MKV
- Web: WebM
- MKV (Matroska)
- MKA File - What is an .mka file and how do I open it? - Learn about .MKA files and view a list of programs that open them.
- In-Depth Understanding of MKA: What is MKA and How to Convert MKA - If you want to know how to handle MKA files better, click here. We offer a collection of MKA-related knowledge to guide you in dealing easily.
- Can I safely rename mkv to mka? - Help - MKVToolNix community & help forum - Is safe to rename a .mkv file that only contains audio and nothing else to .mka?
- From Matroska’s point of view the file name extensions don’t matter at all. Content-wise they’re the same type of file, carrying the same type of structure inside.
- The only difference you might encounter is if a piece of software uses different code paths depending on the file name & extension instead of looking at its content. I don’t know of any program that treats .mkv & .mka differently, but I thought I’d mention it.
- MKV Format: How It Works and How It Compares to MP4 - Learn about the Matroska Multimedia Container (MKV) format, its history, design, and technical structure, and how it compares to the popular MP4 format.
- While best known as a video container, the MKV format is an incredibly versatile and powerful container for audio as well. It is a completely open-source format that can hold virtually any number of audio, video, and subtitle tracks. This makes it a great choice for projects that need multiple, distinct audio streams within a single file. For example, you could have a high-quality main track, a lower-quality commentary track, and a different language track, all in one MKV file.
- Matroska is an audio/video container, often found with the .mkv extension. It is also the basis of the WebM container.
- MKA
- MKV and MKA are exactly the same file, they just have different files extension to show their use, but this is not mandatory.
- The MKA extension is used to show the user it is audio only.
- WebM
- WebM - Wikipedia - The WebM container is based on a profile of Matroska. WebM initially supported VP8 video and Vorbis audio streams. In 2013, it was updated to accommodate VP9 video and Opus audio. It also supports the AV1 codec.
- M4A (MPEG-4 Audio)
- M4A File - What is an .m4a file and how do I open it? - Learn about .M4A files and view a list of programs that open them.
- This is a popular container format, often associated with Apple's ecosystem (iTunes, Apple Music). M4A files can contain different audio codecs, like AAC or Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC). They also support metadata, chapter markers, and in some cases, multiple audio streams. Audiobooks, for instance, are often packaged in the M4B format (a variation of M4A) which allows for bookmarking and chapter skipping.
- M4A can be used to hold mulitple tracks but is difficult to use.
- MKV vs WebM
- MKV vs. WebM - What's the Difference? | This vs. That - What's the difference between MKV and WebM? MKV and WebM are both popular video container formats that are widely used for storing and playing multimedia content.
- mkv vs webm - Bing Search - Here’s a comparison of MKV vs WebM:
- MKV (Matroska):
- Supports a wide range of audio and video codecs, making it versatile for high-quality video storage.
- Ideal for storing movies and TV shows due to its ability to hold multiple audio tracks and subtitles.
- Generally larger file sizes compared to WebM, which may not be suitable for web streaming.
- WebM:
- Specifically designed for web use, optimized for streaming and lower file sizes.
- Supports VP8/VP9 video codecs and Vorbis/Opus audio codecs, making it efficient for online video.
- Less versatile than MKV, as it is primarily used for web applications and may not support as many features.
- In summary, MKV is better for high-quality video storage, while WebM is optimized for web streaming and lower file sizes.
- MKV (Matroska):
- MKV vs WEBM: Which One Should You Choose?
- What distinguishes MKV from WEBM? You may find a thorough comparison between the video formats MKV vs. WEBM here, along with MKV to WEBM conversion tools.
- It is possible to think of the WebM container format as a simplified version of the MKV format. The lack of support for other codecs is WebM's primary issue. It is only compatible with free codecs, such as VP8 and VP9, among others.
- In MKV vs WEBM, WEBM files can also be stored in MKV format. However, not every MKV file can be converted to WEBM format.
- WebM, a constrained variant of MKV, is supported by several web browsers. The permitted video codecs are the main limitation. Only the open and free VP8 and VP9 codecs are used for the WebM video. Between MKV vs WEBM, all MKV files were WebM files, although not every MKV file is WebM-compliant.
- OGG
- Ogg - Wikipedia
- Ogg is a digital multimedia container format designed to provide for efficient streaming and manipulation of digital multimedia. It is maintained by the Xiph.Org Foundation and is free and open, unrestricted by software patents.[
- Ogg - Wikipedia
Audio Codecs
TL;DR
- Lossless Audio: FLAC
- Lossey Audio: Opus (maybe @140bps)
- Video:
- H.264 (defacto standard)
- H.265 (better than H.264 but not everything can read this)
- AV1 (this is open source and is becoming the new standard but it is still relative new)
- General
- MP3, AAC, WAV, FLAC: all the audio file formats explained | What Hi-Fi?
- Do you know your OGG from your ALAC?
- Digital music comes in many different formats – almost everyone knows MP3 thanks to Napster at the end of the last century, but what about OGG, AIFF, MQA or DSD? Confused? Don't worry, we're here to help you chart a course through this alphabet soup.
- Here we'll break down what these file formats are, what makes them different from their alternatives and why that matters. We'll also spell out which qualify as hi-res audio.
- MP3s encoded at 128kbps will incur more sound loss than those encoded at 320kbps (kilobits per second, where each “bit” is essentially a “piece” of the song). Now that storage is so much cheaper, we'd avoid 128kbps at all costs, though 320kbps MP3s still have their purpose if your storage is limited – and they remain a standard on download stores.
- Which audio format is the best? - Live Sound Blog
- Find out which audio format is the best for quality, storage, and compatibility. Compare MP3, AAC, FLAC, WAV, and more to make the right choice!
- Casual Listening: MP3 (320kbps) or AAC
- Best Audio File Formats: Which One Should You Use? | Headphonesty - A comprehensive guide to understanding the different audio file formats and who they are for.
- Comparison of video container formats - Wikipedia - These tables compare features of multimedia container formats, most often used for storing or streaming digital video or digital audio content.
- Audio File Formats at a Glance: How to Choose the Right One - WAV? MP3? AIFF? Find out what the most common audio file formats are, how they differ and which format serves best for your purposes.
- MP3, AAC, WAV, FLAC: all the audio file formats explained | What Hi-Fi?
- MP3
- This is the original gold standard and is still heavily used to day, even with it's limitations.
- It does not support multiple tracks.
- It has a max bitrate of 320kps
- FLAC
- General
- FLAC is a lossless format, meaning it compresses the audio without any loss of quality. Because it's a very popular and open-source format, many audio players and rippers (like Exact Audio Copy or CUETools) have built-in support for embedding and reading cue sheets from FLAC files. This allows for gapless playback of albums that have continuous music, while still providing the ability to skip to specific tracks.
- Supports embedded CUE sheets.
- FLAC - FAQ
- A free, open source codec for lossless audio compression and decompression.
- FLAC stands for Free Lossless Audio Codec, an audio format similar to MP3, but lossless, meaning that audio is compressed in FLAC without any loss in quality.
- audio - Converting m4a (alac) to flac using ffmpeg, output is lower quality? - Super User
- Don't pay heed to the bitrate shown for the output during conversion - that is germane only when the encoder's rate control method targets a bitrate. The FLAC encoder doesn't. Run ffprobe on the output file after it has been generated. It will show the actual encoded bitrate.
- FLAC is a lossless codec, so irrespective of the bitrate obtained, it will be lossless i.e. of identical quality, relative to the source.
s16ands16prefer to the sample formats generated by ffmpeg's decoder for these formats.s16pmeans the decoded samples are signed 16-bit integers, with each channel in a separate plane i.e.C1 C1 C1 C1andC2 C2 C2 C2whereas ins16, they are stored interleaved asC1 C2 C1 C2 C1 C2 C1 C2. To clarify, this is the layout and format of the uncompressed output produced by the decoder. The actual data in the files is coded (hence the term encoded).- There is a PowerShell script with explanations simiiar to mine.
- FLAC compression options unclear: --exhaustive-model-search, --qlp-coeff-precision-search - Sound Design Stack Exchange
- They give a small improvement to the compression at the cost of encoding time.
- A table of the different compression switches and there different outcomes.
- Codecs - XiphWiki - This wiki describes our free and open protocols and softwar and covers the main codecs.
- FLAC Compression Levels Explained and Compared - BoomSpeaker
- In this article, we explain FLAC compression levels and help you choose the best option for your needs.
- FLAC 5 is the default compression level for a good reason. This level of compression is the optimal balance between file size reduction and playback performance.
- Tools
- GitHub - Ardakilic/flac-to-16bit-converter
- A cross-platform command-line tool that converts Hi-Res FLAC files to 16-bit FLAC files with a sample rate of 44.1kHz or 48kHz. Written in Go for excellent performance and cross-platform compatibility.
- Top 5 FLAC Mergers to Merge FLAC Files in a Breeze - This post introduces five simple FLAC Mergers to merge FLAC files into one. Keep reading and learn how to perform the job with your FLAC files.
- FLAC frontend
- FLAC Frontend is a convenient way for Windows users not used to working with command lines to use the official FLAC tools.
- It accepts WAVE, W64, AIFF and RAW files for encoding and outputs FLAC or OGG-FLAC files.
- It is able to decode FLAC files, test them, fingerprint them and re-encode them.
- It has drag-and-drop support too.
- GitHub - Ardakilic/flac-to-16bit-converter
- General
- Opus
- Opus (audio format) - Wikipedia
- Opus supports constant and variable bitrate encoding
- Opus packets are not self-delimiting, but are designed to be used inside a container of some sort which supplies the decoder with each packet's length.
- Still in active development.
- Opus (audio format) - Wikipedia
- WavPack
- While WavPack is an excellent and highly-regarded audio format, it is not as popular or as widely supported as FLAC. FLAC has become the de facto standard for lossless audio compression.
- WavPack Audio Compression
- WavPack is a completely open audio compression format providing lossless, high-quality lossy, and a unique hybrid compression mode. For version 5.0.0, several new file formats and lossless DSD audio compression were added, making WavPack a universal audio archiving solution.
- In the default lossless mode WavPack acts just like a 7-Zip compressor for audio files, including the preservation of all the headers and metadata, so the restored files are identical to the original. Unlike MP3 or WMA encoding which can affect the sound quality, not a single bit of the original information is lost, so there's no chance of audible degradation. The compression ratio depends on the source material, but generally is between 30% and 70%.
- ** Large List of Players **
- WavPack - Wikipedia
- WavPack is a free and open-source lossless audio compression format and application implementing the format. It is unique in the way that it supports hybrid audio compression alongside normal compression which is similar to how FLAC works. It also supports compressing a wide variety of lossless formats, including various variants of PCM and also DSD as used in SACDs, together with its support for surround audio.
- Supports embedded CUE sheets.
- WavPack explained - What is WavPack? WavPack is a free and open-source lossless audio compression format and application implementing the format.
- WavPack - Hydrogenaudio Knowledgebase
Audio Players (ADTRAC support)
- Windows Programs that can Natively Open Atrac3plus files - Grab Your Music (GYM) - Sony Insider Forums
- Just testing out various programs in Windows 10 and I have found these results from trying to playback Atrac3plus. The .oma files were encoded in 352kbps protected and not protected.
- Windows Media Player Classic: Protected YES Unprotected YES
- Vegas Pro 15: Protected YES Unprotected YES
- Audacity with FFmpeg installed: Protected YES Unprotected YES
- Foobar2000: Protected NO Unprotected NO (heard it works with a plugin, havent tried)
- VLC (heard it works like mpc but havent tried.)
- Winamp 5: Protected NO Unprotected NO
- Chrome: doesnt try to open it
- Steam: Doesnt pick up the file
- Sound Forge (part of Vegas now although you can probably lay your hands on it) does understand ALL ATRAC formats provided the files are not protected/encrypted. It's also quite reliable at converting from one to another, although making a NEW files always has to be .aa3 (which can then subsequently renamed .oma). For some reason it edits .oma files perfectly.
- Found a better way to get atrac3plus working in foobar2000. Just needs this plugin: vgmstream and it doesnt need further setting up
- Just testing out various programs in Windows 10 and I have found these results from trying to playback Atrac3plus. The .oma files were encoded in 352kbps protected and not protected.
- foobar2000 - An advanced freeware audio player.
Forums
- HydrogenAudio - The audio technology enthusiast's resource
- VideoHelp Forum - This forum will help you with all your video and audio questions!
Troubleshooting
- Question: says "no disc" - possible solutions? | Reddit
- Some suggestions such as try another player.
- Information on the technology
- MiniDisc Community Page: links - Repair links, tips and tricks.
- HowTo: Recover damaged MiniDisc (TOC Error) - YouTube | RedDragonUKTech
- This video will show how to make a minidisc that has had it's Table Of Contents (TOC) damaged by a faulty recorder.
- This doesn't recover physically damaged discs nor will it recover your data.
- It simply makes the disc usable again.
Divi Contact form will not send if using a free email address
Background
This article is based on the server running cPanel/WHM, the website CMS is WordPress with Divi as it's template, but the logic will most likely apply to a lot of other platforms.
Issue
I have a contact form that will not send the emails when the submitted details contain a free email address even though the contact form says the message was sent.
The failed emails do not appear in "Track Delivery" in cPanel so I have nothing to inspect and figure out what is going on.
If you do not manage your emails locally then an emails that are sent but are bounced will be returned to the server defined in the MX entry.
Cause
- Outbound emails are being scanned for SPAM by SpamAssassan (spamd).
- The email in the `Email Address` field on a Divi contact form is used by default for the
<reply-to>header. - Emails with freemail addresses present in the header score extra SPAM points.
- Because of the extra points caused by having freemail addresses present, the emails are scored just above the SPAM score threshold and they become flagged as SPAM.
- Flagged emails are modified and then delivered to the
systemmailbox in cPanel, they are never passed to the MTA (Exim).
- The modification and redirects are performed by
spamd. - cPanel "Track Delivery" shows transactions by Exim, but because the email never gets to Exim, there will be no record of the delivery or transport of the email.
- A modified email in the
systemmailbox might look something similar to this:
### Title ### Mail failure - rejected by local scanning code ### Message Body ### A message that you sent was rejected by the local scanning code that checks incoming messages on this system. The following error was given: This message was classified as SPAM and may not be delivered ------ This is a copy of your message, including all the headers. ------ .....
- The modification and redirects are performed by
Solutions
These are some solutions an workarounds, pick which ever best suits your needs, which ever you pick you should monitor the situation for a while to make sure the changes you implement are working as expected.
Use SMTP plugin for WordPress
- Using this method reduces the outbound SPAM score massively
- Requires you to setup an email account for every website. Do not use the cPanel system account for emails as this is a security risk.
- Your server does not need to handle email for the domain for you to be able to create an email account locally and send from it as normal, however I do recommend you make sure the SPF record is correctly set and that DKIM is not going to be an issue.
- My recommended plugin is: FluentSMTP | WordPress.org
Remove the Freemail address from the email header
- When using Divi, the email address on a contact form is used by default as the reply address Moving the client's email address to the content only would most likely reduce the SPAM score below 5 and therefore all the email to be sent.
- In Divi you would use Message Patterns to alter the content of the email.
Increase the outbound SPAM score threshold
- This change would be global
- WHM --> Exim Configuration Manager --> Basic Editor --> Apache SpamAssassin Options -->
- Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on the Apache SpamAssassin™ internal spam_score setting: Off
- Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on defined Apache SpamAssassin™ score: 8.5
- Do not forward mail to external recipients if it matches the Apache SpamAssassin™ internal spam_score setting: Off
- Do not forward mail to external recipients based on the defined Apache SpamAssassin™ score: 8.5
NB: 8.5 = Default Threshold + PHP_SCRIPT + KAM_COUK
Disable outbound SPAM scanning
- This change would be global.
- This is not the preferred method as there is not outbound SPAM checking which can allow abuse.
- WHM --> Exim Configuration Manager --> Basic Editor --> Apache SpamAssassin Options -->
- Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on the Apache SpamAssassin™ internal spam_score setting: Off
- Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on defined Apache SpamAssassin™ score: Disabled
- Do not forward mail to external recipients if it matches the Apache SpamAssassin™ internal spam_score setting: Off
- Do not forward mail to external recipients based on the defined Apache SpamAssassin™ score: Disabled
Disable certain SpamAssassin tests
You can reduce the SPAM score by disabling or cancelling out certain tests, but this requires a lot more time to setup.
Notes
WordPress - Email subsystem
- mail()
- The
mail()function on returns True or False. - An Essential Guide to PHP mail() Function By Examples - This tutorial shows you how to use the PHP mail() function to send email messages in plain text and HTML formats.
- The
- Email Logging
- A Simple Guide to WordPress Email Logging - MailPoet - Wondering what emails WordPress sends and how to log them? In this guide, we'll take you through how to set up WordPress email logging.
- How to Fix Could Not Instantiate Mail Function in WordPress - In this guide, we’ll show you how to fix could not instantiate mail function error in WordPress, ensuring your emails fly out without a hitch!
- Code Walk through
## wordpress/wp-includes/PHPMailer/PHPMailer.php 'instantiate' => 'Could not instantiate mail function.', --> mailPassthru($to, $subject, $body, $header, $params) --> $result = @mail($to, $subject, $body, $header, $params); --> mail() # This is a wrapper for sendmail --> sendmail # cpanel sendmail is blocking gmail addresses --> sendmail returns true or false
WHM - Settings
- General
- How to Adjust Spam Assassin Rule Scoring Serverwide – cPanel - Spam Assassin determines whether or not a message is spam based on the message's final calculated spam score. The overall score is calculated by testing the message against various rules, each assigning a sub-score, and then summing the sub-scores. If you find that specific Spam assassin rules are weighted too heavily or are not weighted enough, you may use the procedure in this guide to change them.
- Apache SpamAssassin™ Options - Exim Configuration Manager Basic Editor | cPanel & WHM Documentation
- Select the Basic Editor tab in the Exim Configuration Manager interface to modify your server's Exim configuration settings.
- This particular section explains all of the Apache options.
- Tutorial
- Spam Filtering on cPanel: Everything You Need To Know About SpamAssassin | cPanel - Spam is a huge challenge for anyone who hosts email, even though users only see a tiny fraction of the spam they’re sent. Most unwanted messages never reach inboxes, but an incredible 54 percent of all email traffic is spam, and that’s down from 70 percent a decade ago.
- cPanel / WHM | SPAMAssassin and cPanel | VPSBlocks Support - This tutorial describes how to use the SpamAssassin tool in cPanel to reduce the amount of unwanted e-mail.
- SpamAssassin’s internal spam_score
- Is calculated by summing the scores of various matched rules.
- This is not the SPAM threshold, but just the score that SpamAssassin assigns to the email after all of the tests.
- How to Configure SpamAssassin in cPanel – PhilmoreHost
- Configuring your internal SpamAssassin score threshold = Specify a score under Apache SpamAssassin bounce spam score threshold. ?
- cPanel Tutorial Series 6: using email - TransIP - This is the sixth part of our cPanel Tutorial Series.
- Apache SpamAssassin ™ reject spam score threshold
- Incoming messages that are designated as spam are stopped instead of subjects being rewritten (see Filters), or the mail is moved to your spam box. You will never see messages that meet these criteria in your mail. If you use this option, we advise you to use a fairly generous score so only messages that are definitely spam are stopped, for example with a score of 10-11.
- Apache SpamAssassin ™ bounce spam score threshold
- Sends a bounce email to the sender of spam when mail reaches the set score. This can work positively and negatively: a conscious spammer knows that you are using a filter and will try to find something to work around it, but someone with an infected computer / server will find out more quickly that he or she has an infected computer / server thanks to a bounce message.
- Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on the Apache SpamAssassin ™ internal spam_score setting
- Scans all outgoing messages from your VPS and stops all messages that reach the set spam score (default 5).
This is a very useful option that we highly recommend. For example, suppose you created cPanel accounts for your customers and they host their own sites but never update them, then there is a plausible chance that sooner or later a vulnerability will be found, and a domain will start sending spam. Thanks to this option, you get rid of that spam, so your VPS does not get a bad IP reputation.
- Scans all outgoing messages from your VPS and stops all messages that reach the set spam score (default 5).
- Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on defined Apache SpamAssassin ™ score
- This option does the same as the previous one, but this allows you to determine the spam score upon which SpamAssassin takes action when outgoing mail is recognized as spam.
- Do not forward mail to external recipients if it matches the Apache SpamAssassin ™ internal spam_score setting
- Mail that is addressed to your VPS and which is redirected is also scanned by SpamAssassin and stopped if it is marked as spam.
- Do not forward mail to external recipients based on the defined Apache SpamAssassin ™ score
- Same as the previous option but allows you to set a score yourself.
- Score
- By default, SpamAssassin marks mail as spam when it reaches a score of 5. This base value can only be adjusted via command line using the following commands:
sudo nano /etc/mail/spamassassin/local.cf
- The particular rule to alter is:
# Set the threshold at which a message is considered spam (default: 5.0) # # required_score 5.0
- By default, SpamAssassin marks mail as spam when it reaches a score of 5. This base value can only be adjusted via command line using the following commands:
- Apache SpamAssassin ™ reject spam score threshold
- acl_not_smtp and acl_smtp_data
- Both acl_not_smtp and acl_smtp_data can count towards the Apache SpamAssassin™ internal spam_score setting, depending on how your Exim configuration is set up.
- There is no proper documentation from cPanel for these options.
- Ypu can expose the underlying code in the GUI by using the 'Advanced Editor'.
- acl_not_smtp:
- outgoing_spam_scan (Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on the Apache SpamAssassin™ internal spam_score setting)
- This refers to Exim's Access Control Lists (ACLs) that apply to non-SMTP email submissions, such as mail sent from local scripts or PHP applications. This is often used to set rules for handling outbound mail generated by websites, contact forms, or local applications.
- Purpose: To control and filter outgoing email messages that are not sent via SMTP, such as web apps or local daemons.
- Advanced Settings (Under Advanced editor):
warn condition = ${if forany{<, $recipients}{!match_domain{${domain:$item}}{:+relay_domains}}} set acl_m_outbound_recipient = 1 warn condition = $acl_m_outbound_recipient condition = ${if <={$message_size}{1000K}} condition = ${if !eq{$originator_uid}{0}} condition = ${perl{spamd_is_available}} set acl_m_spam_scan_enabled = 1 deny condition = $acl_m_outbound_recipient condition = $acl_m_spam_scan_enabled spam = cpaneleximscanner/defer_ok message = This message was classified as SPAM and may not be delivered log_message = "SpamAssassin as cpaneleximscanner detected OUTGOING not smtp message as spam ($spam_score)" warn condition = $acl_m_outbound_recipient condition = $acl_m_spam_scan_enabled log_message = "S
- acl_smtp_data:
- outgoing_spam_scan (Scan outgoing messages for spam and reject based on the Apache SpamAssassin™ internal spam_score setting)
- Purpose: The acl_smtp_data ACL is used to inspect the content of the email before it's accepted for delivery. It is commonly employed for tasks such as:
- Spam Filtering: Checking the email content against spam filters (like SpamAssassin).
- Virus Scanning: Scanning the email for malware or viruses.
- Attachment Filtering: Restricting certain types of file attachments or scanning them.
- Rate Limiting or Message Size Checking: Ensuring that message sizes adhere to server limits.
- Custom Message Rejection: Applying custom rules to reject messages that contain specific content or violate policies.
- Advanced Settings (Under Advanced editor):
warn condition = $acl_m_outbound_recipient condition = ${if <={$message_size}{1000K}} condition = ${if !eq{$acl_c_authenticated_local_user}{root}} condition = ${if !match{$authenticated_id}{\N^__cpanel__service__auth__[^+%:@]+$\N}} condition = ${perl{spamd_is_available}} set acl_m_spam_scan_enabled = 1 deny condition = $acl_m_outbound_recipient condition = $acl_m_spam_scan_enabled spam = ${if eq{$acl_m1}{}{cpaneleximscanner}{$acl_m1}}/defer_ok message = This message was classified as SPAM and may not be delivered log_message = "SpamAssassin as ${if eq{$acl_m1}{}{cpaneleximscanner}{$acl_m1}} detected OUTGOING smtp message as spam ($spam_score)" warn condition = $acl_m_outbound_recipient condition = $acl_m_spam_scan_enabled log_message = "SpamAssassin as ${if eq{$acl_m1}{}{cpaneleximscanner}{$acl_m1}} detected OUTGOING smtp message as NOT spam ($spam_score)"
WHM - Outbound Filtering
- I am not sure if it uses the per user/cPanel custom rules (as appropriate) for calculating the spam_score when outbound filtering, I cant see why it doesn't though.
- When an email has been forwarded after being scanned for SPAM it will have an additional header with it's score.
- How to configure Spam Assassin to scan outgoing mail. – cPanel - This article covers configuring outgoing mail to be scanned by Spam Assassin.
- Enable Outgoing Spam Filtering Using SpamAssassin - eukhost - This guide explains how to enable Outgoing Spam Filtering Using SpamAssassin.
- Configure SpamAssassin to block outgoing form mail – cPanel
- There are actually two assigned spam scores, one when you receive the email locally and one that is assigned to it when it's scanned outbound.
- In this case Spam Score: X-Spam-Score: 100 refers to the score assigned on delivery to the server.
- The score that is being assigned to the server when it is sent is the Outgoing Spam Score which in this case is below the threshold of 2: X-Outgoing-Spam-Status: No, score=1.7 So with a spam score of 1.7 SpamAssassin isn't seeing this email as spam and sends it.
- How-To Prevent Exim From Forwarding Spam – cPanel - This article covers configuring Exim to not forward mail based on the message's Apache SpamAssassin™ Spam score.
SpamAssassin - Example rules that can be triggered
To find the rules, search for them in the following format: describe KAM_DMARC_STATUS
PHP_SCRIPT 2.5 - Sent by PHP script- spamassassin/rulesrc/sandbox/jhardin/20_misc_testing.cf - line 2897 · apache/spamassassin · GitHub
- phpmailer - SpamAssassin flags our PHP Emailer for being a PHP_SCRIPT (-2.499) - Stack Overflow
- Every email that is sent to a server with SpamAssassin gets -2.499 score because of the PHP_SCRIPT flag which has the description of Sent by PHP script
- The interesting thing is emails sent with WP SMTP Mail plugin via WordPress do not get flagged for this SpamAssassin rule even though WP SMTP Mail also uses PhpMailer
FREEMAIL_FORGED_REPLYTO 0.1 - Freemail in Reply-To, but not FromKAM_COUK 0.85 - Scoring .co.uk emails higher due to poor registry security.KAM_DMARC_STATUS 0.01 - Test Rule for DKIM or SPF Failure with Strict AlignmentT_SCC_BODY_TEXT_LINE- = number of lines in email ?
- /var/lib/spamassassin/3.004006/updates_spamassassin_org/
- spamassassin - What is SCC_BODY_URI_ONLY rule in spam assassin? - Stack Overflow - I am facing this issue SCC_BODY_URI_ONLY with my email when checked with SPAM ASSASSIN,Does anybody know about this rule. There is no great deal of documentation around it.
- meta T_SCC_BODY_TEXT_LINE __SCC_BODY_TEXT_LINE_FULL - __SCC_SUBJECT_HAS_NON_SPACE (72_active.cf)
- This will be to do with the length of the mail
- T_SCC_BODY_TEXT_LINE | Apache Mail Archives
- What is the purpose of the rule named T_SCC_BODY_TEXT_LINE? On my servers, it hits nearly every spam and ham email.
URIBL_BLOCKED small - ADMINISTRATOR NOTICE: The query to URIBL was blocked. See http://wiki.apache.org/spamassassin/DnsBlocklists\#dnsbl-block for more information.
SpamAssassin - Managing rules
- General
- WritingRules - SPAMASSASSIN - Apache Software Foundation
- This is a straightforward guide to writing your own add-on rules for SpamAssassin. This was originally written by MattKettler.
## Default rules, but these will be replaced upon upgrade /usr/share/spamassassin ## Rules seem to be here /etc/mail/spamassassin/
- This is a straightforward guide to writing your own add-on rules for SpamAssassin. This was originally written by MattKettler.
- CustomRulesets - SPAMASSASSIN - Apache Software Foundation - Listed below are several custom rulesets that are available as "drop in" .cf files. To use these rules, just place the file in
/etc/mail/spamassassin(if you use spamD, be sure to restart). - SpamAssassin Score Explained | Mailtrap Blog - The SpamAssassin score is a great indication of the quality of your emails. We explain how to interpret its results and improve upon them.
- WritingRules - SPAMASSASSIN - Apache Software Foundation
- KAM Ruleset
- This is not part of the Spamassassin base code.
- The is a 3rd party ruleset that is included with cPanel/WHM and is on by default.
- In cPanel/WHM:
/etc/mail/spamassassin/KAM.cf - KAM Ruleset | The McGrail Foundation
- The KAM Ruleset is a set of Apache SpamAssassin rules developed and used on our systems.
- This ruleset has been in active use and development since May 2004 and provides a significant boost to the performance and efficacy of a stock installation of Apache SpamAssassin.
- KAM Ruleset Channel | The McGrail Foundation - The McGrail Foundation Home Page
SpamAssassin - What rules caused an email to get flagged?
- Exim Mail Log - Example Entry
Sep 1 13:56:08 srv spamd[414141]: spamd: connection from localhost [127.0.0.1]:43490 to port 783, fd 6 Sep 1 13:56:08 srv spamd[414141]: spamd: setuid to cpaneleximscanner succeeded Sep 1 13:56:08 srv spamd[414141]: generic: trusted_networks doesn't contain internal_networks entry '0/0' Sep 1 13:56:08 srv spamd[414141]: spamd: checking message <XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXZldVRrQX6dyBuRHk9yR9jnJNGRM@www.example.co.uk> for cpaneleximscanner:992 Sep 1 13:56:18 srv spamd[414141]: spamd: identified spam (5.9/5.0) for cpaneleximscanner:992 in 10.3 seconds, 3794 bytes. Sep 1 13:56:18 srv spamd[414141]: spamd: result: Y 5 - FREEMAIL_FORGED_REPLYTO,KAM_COUK,KAM_DMARC_STATUS,PHP_SCRIPT,T_SCC_BODY_TEXT_LINE,URIBL_BLOCKED scantime=10.3,size=3794,user=cpaneleximscanner,uid=992,required_score=5.0,rhost=localhost,raddr=127.0.0.1,rport=43490,mid=<XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXZldVRrQX6dyBuRHk9yR9jnJNGRM@www.example.co.uk>,autolearn=no autolearn_force=no,shortcircuit=no
- spam - Where can i find explanation of a SpamAssasin scores like SPOOFED_FREEMAIL? - Server Fault
## This adds the score /var/lib/spamassassin/3.004006/updates_spamassassin_org/20_freemail.cf ## This is the list of the Freemail domains /var/lib/spamassassin/3.004006/updates_spamassassin_org/20_freemail_domains.cf ## An old list /var/lib/spamassassin/3.004006/updates_spamassassin_org/20_freemail_mailcom_domains.cf
- How to find the descriptions of SpamAssassin rules to help understand why a message was marked as spam – cPanel - If you find that SpamAssassin is marking messages as Spam when it should not be, or that SpamAssassin is not marking messages as spam when it should be, you can use the following procedure to find out what rules were applied to a message and review the description of the applied rules for additional context.
- How can I check why SpamAssassin applied a particular score? – cPanel - Some email messages are flagged or rejected as spam, but I'm not sure why. Can I check how SpamAssassin is applying this score?
- How to find SpamAssassin scan results – cPanel -When SpamAssassin scans an email the results are saved to the
/var/log/maillogfile. This can be used to determine what rules are being triggered by the message./usr/local/cpanel/logs/spamd_error_log
SpamAssassin - Here’s a breakdown of how this score is calculated:
I got this from my VPS provider:
SpamAssassin’s internal spam score is calculated by summing the scores of various matched rules.
- Rule-Based System
- SpamAssassin uses a large set of predefined rules to analyze various parts of an email, including:
- Email headers (e.g., suspicious sender domains, mismatched or forged headers).
- Message body content (e.g., words commonly associated with spam, HTML content, or embedded links).
- Attachments (e.g., dangerous file types, large attachment sizes).
- Blacklists (e.g., checking if the sender's IP address or domain is on a spam blacklist).
- Each rule is assigned a specific score, positive or negative, depending on how indicative it is of spam. These scores are predefined, but you can customize them in SpamAssassin’s configuration files.
- Positive score: Increases the likelihood that the message is spam.
- Negative score: Decreases the likelihood that the message is spam (e.g., messages from trusted sources might get a negative score).
- SpamAssassin uses a large set of predefined rules to analyze various parts of an email, including:
- Cumulative Scoring
- When SpamAssassin scans an email, it applies multiple rules. The total spam score is the sum of all the individual rule scores that match the email.
- Example:
Rule Description Score HTML_MESSAGE Email contains HTML 1.0 BAYES_99 Bayesian filter suggests 99% spam probability 3.5 RCVD_IN_SPAMHAUS Sender's IP is in the Spamhaus blacklist 2.0 DKIM_VALID Email has a valid DKIM signature -1.0 Total Score 5.5
- In this example, the email’s total spam score is 5.5.
- Spam Threshold
- The total score is compared to the spam threshold configured in cPanel/WHM. The default threshold is usually 5.0. If the total score exceeds this threshold, the message is flagged as spam.
- Spam Threshold of 5.0: If an email’s score exceeds 5.0, it is considered spam.
- Spam Threshold of 7.0: If the threshold is set to 7.0, only messages with a spam score higher than 7.0 will be flagged as spam.
- You can adjust the spam threshold score in the SpamAssassin configuration settings to make the filter more or less aggressive.
- The total score is compared to the spam threshold configured in cPanel/WHM. The default threshold is usually 5.0. If the total score exceeds this threshold, the message is flagged as spam.
- Bayesian Filtering (Adaptive Learning)
- SpamAssassin also uses a Bayesian filter, which is a machine-learning technique that adapts to the types of emails received over time. When trained with both spam and non-spam emails, this filter becomes more accurate in determining whether an email is spam by calculating the probability based on previously learned patterns.
- The Bayesian filter assigns probabilities to words or phrases, which contribute to the overall spam score.
- SpamAssassin rules like BAYES_50 (50% spam probability) or BAYES_99 (99% spam probability) are examples of how this filter impacts the overall score.
- SpamAssassin also uses a Bayesian filter, which is a machine-learning technique that adapts to the types of emails received over time. When trained with both spam and non-spam emails, this filter becomes more accurate in determining whether an email is spam by calculating the probability based on previously learned patterns.
- Custom Rules and Scoring
- You can also create custom rules and assign them specific scores. This allows you to adapt SpamAssassin to your organization’s needs by:
- Increasing the score of certain patterns (e.g., emails with specific attachments).
- Decreasing the score for emails from trusted domains or senders.
- You can also create custom rules and assign them specific scores. This allows you to adapt SpamAssassin to your organization’s needs by:
- Adjusting the Spam Score Multiplier
- In cPanel and WHM, the spam score is multiplied by 10 for internal use. For example, if you set a spam score threshold of 5.0 in WHM, it will show up as 50 in log files and email headers.
- For instance, if you see the following in an email header, It corresponds to a score of 4.0 (since 40 divided by 10 is 4.0), which is below the default spam threshold of 5.0, so the email wouldn’t be flagged as spam.
X-Spam-Score: 40
My Meta Quest Notes
These are a collection of my notes for the Meta Quest 3
General
- Official Sites
- General
- Meta – Shop VR headsets & Smart glasses | Meta Store - Discover Meta's revolutionary technology from virtual reality to social experiences. Shop Meta Quest, Ray-Ban Stories and VR accessories.
- Meta Store - Buy your games and Apps here.
- Meta Quest software update | Meta Store
- With the Meta Quest software update tool, you can update your device software to help solve issues such as slow performance and unresponsive apps.
- However, the tool is currently only supported on Chrome, Opera and Edge desktop browsers.
- We don't support mobile devices.
- Meta Quest+
- See `Meta Quest+` section below for links and more information
- Profile and Account
- Subscriptions | Meta Store - See your current subscriptions here
- Accounts Centre | meta.com - Manage your connected experiences and account settings across Meta technologies such as Facebook, Instagram and Meta Horizon.
- Account Centre (part 2) | meta.com - Manage your connected experiences and account settings across Meta technologies.
- This has different options to that of "Accounts Centre"
- Profile | meta.com - Configure your Meta profile here.
- Support
- Contact Meta Store and device support | Meta
- Has an FAQ
- Meta Community Forums
- Forum Support User
- Get Help - Meta Community Forums
- Need a hand or looking to help others? Find answers and ask questions about your headset, accessories, and apps.
- Get Help Thread (for bug reports as well)
- Getting Help from the Meta Quest Community - Meta Community Forums - 1145761
- Welcome to the Meta Community Forums! The community members here are great at helping find solutions to all sorts of trouble.
- So if you're running into anything, or want to help others, please feel free to jump in.
- And if the community can't help out, we're around to help as well.
- Meta Quest group | Facebook
- Welcome to "Meta Quest" the largest destination for all Meta Quest headset owners, VR and mixed reality enthusiasts on Facebook! Connect with passionate Quest users, dive into the latest VR news, learn insider tips and tricks, and engage in lively discussions about mind-blowing VR experiences.
- News and Keys.
- Meta Quest Help Centre | Meta Store - Meta Quest support articles
- Contact Meta Store and device support | Meta
- Developers
- Developer Support Center | Meta Horizon - Find answers to your questions and connect with other developers like you.
- General
- Other Sites
- OculusQuest | Reddit - A place to discuss the Meta/Oculus Quest, Quest 2, Quest 3, and Quest Pro
- VRDB.app - VR Store Statistics - VR Store Statistics
- Specs
- Meta Quest 3: New mixed reality VR headset – Shop now | Meta Store | Meta Store - Discover the latest VR headset from Meta – the Meta Quest 3. With a diverse category of VR games and new mixed reality, experience the metaverse like never before.
- There is no SD card slot.
- Meta Quest 3: Full Specification - VRcompare - The Meta Quest 3 is a Standalone VR headset, released 2023. Features Qualcomm Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2, 110° FoV, 2064x2208 per eye resolution, 8 GB memory.
- Meta Quest 3: Specs, 3 vs. 3S, & everything you need to know | Android Central - The mixed-reality Meta Quest 3 is getting some changes thanks to the Quest 3S. Here's what you need to know about it.
- Performance
- BEST TIPS To Increase PCVR Performance (in 2024!) - YouTube | RealityRise - A NO fluff guide to quickly increase the performance on your VR headset when playing PCVR. A video that will go from the basics to an amazing tool that will deliver those sweet frames per second!
- Equipment
- VR Treadmills
- Controller Stocks
- Maintenance / Looking after your Quest
- Things You Should NEVER Do With Your Quest 3... - YouTube | GetHip - Today I go over things you should NEVER do with your Quest 3. This is a sequel to my Quest 2 video "Things You Should NEVER Do With Your Quest 2" & covers the melted port issues, lens burning, charging problems, and more. Check out my other videos for VR Tips & Tricks, Top 10's & News.
- Clean your Meta Quest 3 headset and lenses SAFELY. Complete Quest 3 cleaning guide. - YouTube | VR Reviews - Comprehensive guide on cleaning your quest 3 lenses, headset and controllers properly and safely. Affiliate links to some of some of the cleaning products used in this video can be found below.
- Legal / Warranty
- Meta might be trying to get around EU 2 year warranty with Quest 3 or they already did | Reddit
- Consider Duration from the T&Cs: 1 year from the date of purchase or delivery of the Product, whichever is later (the “Warranty Period”). If you are a consumer, this does not affect your statutory rights which may provide for longer warranty coverage.
- You're mixing the legal guarantee (2 years in the EU, regarding the seller of the product) with the commercial warranty (1 year, in most cases regarding the manufacturer). A lot of companies only offer 1 year of commerical warranty (like Apple for example).
- this. also important to know: the one year warranty that apple and meta offer are voluntary. but as nightkrwlr said: it's different from the two-year consumer law rule.
- = 2 Years warranty
- Meta Quest EU/EEA/UK consumer right of withdrawal information | Meta Quest - Under applicable law, consumers in the European Union (EU), the European Economic Area (EEA) and the UK have a right to withdraw from or cancel certain purchases for a refund.
- Meta Horizon Store Terms | Meta Quest - No meta description
- Meta might be trying to get around EU 2 year warranty with Quest 3 or they already did | Reddit
- Sign up issues
- The sign up form will only accept UK postcodes in this format
SW1 1LFand notSW11LF
- The sign up form will only accept UK postcodes in this format
- Meta keep trying to charge £59.99 for my free subscription
- I could not get the 6 months free to work, my bank kept on wanting to charge me £59.99 even thought it said the due amount today was £0.00
By ticking this box and clicking the Confirm button, you agree that the content will immediately begin downloading onto your device, and you acknowledge that you will thereby lose any statutory right of withdrawal (EU/EEA) or cancellation (UK). Learn more You will be charged £59.99, including tax, when this free trial ends on 26 Feb 2025 and every year when this subscription is automatically renewed until you cancel. Cancel at any time in your account settings at least 24 hours before the end of this free trial or the next billing date to avoid future charges.By selecting Confirm, you agree to the Meta Quest Store Terms.
- So this is what I did to fix it:
- Created a virtual card with £10 on it to prevent my account from getting charged.
- Using the phone APP I signed up using my information and the virtual card
- When I get to the point it wants to test my card is valid, the amount being charged to my account is £59.99
- A 2FA notice appeared in a browser thing, I clicked cancel on it ignoring any messages on my phone to accept or deny the transaction through my banking App.
- This is not the link that is sent to your phone's banking app asking you to approve.
- Never approve it and don't cancel it either.
- I let the request in my banking app expire. It should only take 10 mins.
- Bingo, it works
- Research
- Meta Quest support is useless, they will just keep asking you the same question over and over again about your purchase date and because you get someone different each time you will never get this resolved. I almost returnd my Quest becasue of this.
- I can’t activate the free 6-month subscription to Quest+ (included with Quest 3) - Meta Community Forums - 1102153
- Meta quest trying to charge 12 months immediately at start 6 month free activation - Meta Community Forums - 1200063 - Just activated a new meta quest 3 and on trying to redeem the 6 months free Meta Quest + I am asked to pay for 12 months up-front! Is this correct?
- I could not get the 6 months free to work, my bank kept on wanting to charge me £59.99 even thought it said the due amount today was £0.00
- Cloud Backup
- About cloud backup | Meta Store
- When cloud backup is turned on, Meta backs up your device's app data, such as app progress or app settings, to the cloud. This allows you to easily pick up where you left off in a game if you reinstall an app, factory reset your device or set up a new device.
- To keep your cloud backup data safe, your app data is encrypted on the device and remains encrypted on our servers.
- About cloud backup | Meta Store
- User Setups
- gnarsasquatch | TikTok - This guys as a cool setup using the Quest in his helicopter simulator setup.
- Setup video - gnarsasquatch | TikTok - A quick look around his helicopter simulator setup.
Meta Quest+
- Meta Quest+ subscription | Meta Store
- Experience the ultimate gaming adventure with Meta Quest+. Enjoy instant access to over 25 games, exclusive deals and monthly drops. Cancel at any time with no hidden fees.
- Meta Quest+ is your subscription for premium games and more. Discover and play on repeat. You'll get instant access to a growing content catalogue and curated monthly drops of top titles, all for just £7.99 a month. Plus, you'll get exclusive deals and offers as a subscriber. Get ready to explore new apps and worlds.
- Meta Quest Plus (Horizon+) - Homepage | Meta Store
- Claim your free games here every month, both the permanent ones and the ones in the rotating games catalogue.
- Monthly titles and Games catalogue | Meta Store
- Claim your free games here every month, both the permanent ones and the ones in the rotating games catalogue.
- You get a selection of free games every month in 2 categories, both of which require you to redeem them to gain access but they have different retention terms.
- Monthly Games
- Every month you are given 2 games you can redeem.
- You need to redeem these games, when offered, to keep them.
- Once redeemed, these games are added to your library permanently.
- Games catalogue
- The majority of the game catalogue will remain consistent month over month, but each month, one or more titles may leave or be added in order to keep content fresh.
- If you have a redeemed a game that is removed from the `Games catalogue` you will loose access to it and will need to purchase it to continue using it. Your game saves should remain preserved.
- Monthly Games
- Examples of Meta Quest+ game listings
- Redeem

- Redeemed
- Redeemed - Soon to be removed from the `Games catalogue`

- Redeem
- How to view you application and games library
- Website:
- You cannot view your library via the website.
- Meta Horizon App:
- Menu --> Device Management --> Library
- Headset: ....
- Website:
Q&A
- What happens if I unsubscribe or resubscribe?
- Once you are no longer a paying Meta Quest+ subscriber, you will lose access to all previously redeemed Meta Quest+ titles and not be able to redeem any more titles.
- When you resubscribe, you will regain access to all previously redeemed Meta Quest+ titles and the titles that are currently available for as long as you are a subscriber.
- You will keep access to games and titles you have purchased.
- Do I need a Facebook account? = No
- Introducing Meta Accounts: A New Login for VR | Meta Quest Blog - Today we’re introducing Meta accounts: a new way for people to log into their VR headsets that doesn’t require a Facebook account. When we announced that we would start requiring people to log into Meta Quest using a Facebook account, we received a lot of feedback from the Quest community. We took that feedback into account as we designed a new Meta account structure that gives people flexibility and control.
- Should I buy 128GB or 512GB model? = buy 512GB
- Meta Quest 3 extra storage - can you expand storage? - Explore the potential of Meta Quest 3 extra storage in our guide. Learn if expanding your storage with an external storage device is actually possible.
- Meta Quest 3 Storage: Is 128GB Enough? - Quest 3 is shipping now, but is 128GB storage enough for the new VR headset? Let's take a look:
- Which Meta Quest 3 Should You Buy? Meta Quest 3 128gb or 512gb Storage - YouTube - Which Meta Quest 3 Should You Buy? 128gb or 512gb Lots of comments regarding which Meta Quest headset to buy. Either the Meta Quest 128gb or the Meta Quest 512gb and I am going to try to provide my reasoning for whihc headset is right for you and me.
- What can you do with Quest?
- You can use Quest for PCVR games
- With a 3rd party App and capture card you can play your xbox.
- SteamVR games can be played on the Oculus now
- Where can I buy games and apps from
- Official
- Meta – Shop VR headsets & Smart glasses | Meta Store - Discover Meta's revolutionary technology from virtual reality to social experiences. Shop Meta Quest, Ray-Ban Stories and VR accessories.
- Curated Lists / Coupons
- Discounted Games Megathread OculusQuest | Reddit - Here is an updated list of all current game sales in order of discount. Please let me know if anything expires or if there are any new ones available and I will do my best to keep this version updated.
- Rift
- Where to buy oculus quest 2 games | oculus | Reddit
- Some games are on both Quest and the Oculus PC ecosystem (Rift store), and a large subset of those are cross-buy, meaning if you buy one version you can "buy" the other platform's version for free. This is a list of those.
- Oculus Quest Cross-Buy Apps - US Store Overview | vrdb.app
- Where to buy oculus quest 2 games | oculus | Reddit
- Steam/SteamVR
- SteamVR games can be played on the Oculus now
- Where is the best place to buy vr games on the quest Steam VR or Oculus Store - Meta Community Forums - 809912
- The only place you can buy games to play directly within the Quest (not connected to a PC with Link) is through the Oculus store. If you buy games on Steam, you can play them on your PC, using the Oculus as the headset with the Link feature, but once you disconnect from the computer, the game will not be on your Quest to play remotely.
- There are advantages and disadvantages in buying on Steam. Many times you can get a better deal on Steam. However, some games have cross buy, meaning if you buy a Rift game on the Oculus store you also get a Quest version that you can play when mobile (here is a hidden page of cross buy titles https://www.oculus.com/experiences/quest/section/2335732183153590/#/?_k=i6lcbk) The Steam version would not give you a Quest version along with the Rift version. Sometimes games come with DLC on Steam, but not on the Oculus store, like Dirt Rally 2.0.
- Google Play?
- Cheap Key Sites
- Kinguin.net | Steam CD Keys and PC Game Keys - Compare & Buy
- Watch this space for cheap keys
- Asgard's Wrath 2 Meta Quest Gift | Buy cheap on Kinguin.net
- EOLIA Oculus Meta Quest 2 CD Key | Buy cheap on Kinguin.net
- game keys | OculusQuest | Reddit
- I have bought a few of my OQ2 games through Kinguin. Good discounts. Never had a problem using the codes. Just search VR Oculus Quest. But you must use the codes on your mobile phone app, unlike how the instructions detailed on the Kinguin site.
- CDKeys.com
- You cannot buy Quest games here yet but you can but PCVR games
- The Walking Dead: Saints & Sinners VR | PC | CDKeys
- G2PLAY.NET
- PCVR keys, no quest stuff yet.
- Kinguin.net | Steam CD Keys and PC Game Keys - Compare & Buy
- Other
- itch.io - itch.io is a simple way to find, download and distribute indie games online. Whether you're a developer looking to upload your game or just someone looking for something new to play itch.io has you covered.
- Official
- Transferring Games to Other Meta Account Profile
- Solved: Transfering Games to Other Meta Account Profile - Meta Community Forums - 1015979
- Games are locked to an account, not a headset.
- Solved: Transfering Games to Other Meta Account Profile - Meta Community Forums - 1015979
Apps
- System
- SideQuest: Oculus Meta Quest Games & Apps including AppLab Games ( Oculus App Lab )
- SideQuest is the early access layer for Virtual Reality Get access to the latest Oculus Quest Games Oculus App Lab games lots of free apps on applab and sideload.
- This is used to sideload apps onto the Quest which runs on android.
- SideQuest: Oculus Meta Quest Games & Apps including AppLab Games ( Oculus App Lab )
- YouTubeVR
- Cannot load the app, keeps on crapping out
- 5 Ways to Fix YouTube VR if It’s Not Working on Oculus Quest - To fix Oculus Quest YouTube VR not working issue, you will need to tweak some settings and follow additional steps shown in this article.
- Solution
- Setup you boundary area before you start YouTubeVR
- You must share boundary information when asked otherwise the app will just crap out with no message.
Casting and Inputting
Remote Desktop / Productivity
- Virtual Desktop
- Your PC in VR
- Watch movies, browse the web or play games on a giant virtual screen.
- Immersed - Have your desktop in VR on Mac, PC, and Linux with Immersed!
- Meta Horizon Workrooms | Meta For Work - virtual office and meetings
- Fluid on Meta Quest | Quest VR games | Meta Store - Turn your Quest into a spatial personal computer with Fluid.
- Fluid VR | OculusQuest | Reddit - Using the app I've been working on for the last year to turn any hotel room into a portable office + built-in multiscreen computer feels awesome.
Casting from Quest to (Phone|Computer)
- How to cast to a screen with Meta Quest | meta.com
- Learn how to use the casting feature to stream what you see in your headset from your Meta Quest headset.
Play PCVR Games on Quest
- General
- How to play PCVR games on Oculus Quest with Virtual Desktop — techtipsVR - With Virtual Desktop from Virtual Desktop, Inc. you can use your PC from your within your Oculus Quest VR headset. You can do all the normal stuff you would do on your desktop like web browsing, spread-sheeting, or pretty much whatever else you might do on your computer, but with an resizable screen in a VR environment!Event Better, you can also play your PCVR (SteamVR or Oculus Rift) games wirelessly on your Oculus Quest by adding a patch with SideQuest.
- How to Play PC VR Games on an Oculus Quest 2
- The Quest 2 is great as a standalone VR headset, but did you know you can use it as a PC VR headset too?
- The process is relatively easy, works with a wired connection or wirelessly, and gives you full access to SteamVR and a large universe of PC VR games..
- How to Play PCVR on Quest 3 | Steam Link, Airlink & Virtual Desktop - YouTube
- The Best Way to Play PCVR on meta quest 3 with steam link, airlink and virtual desktop in 2023.
- This is the full guide on how to play PCVR games on Quest 2 and Quest 3 with steam link, airlink or virtual desktop so that you can play Steam vr games directly on your vr headset.
- Meta Quest Link App / Link / Air Link
- Common
- Set up and connect Meta Quest Link and Air Link | Meta Store
- You can connect your Quest headset to a Windows PC with a USB-C cable to use PCVR applications and games.
- You can also connect your headset to your PC wirelessly with Air Link.
- Install the Meta Quest Link app for your PC | Meta Store
- You can connect your Meta Quest headset to a Windows PC with a USB-C cable to use certain PC apps and games. You can also connect your headset to your PC wirelessly with Air Link.
- To set up Meta Quest Link or Air Link, you'll need to download the Meta Quest Link PC app on your Windows computer.
- The Meta Quest Link PC app requires approximately 10 GB of space on your hard drive to install.
- Download the PC App from this page.
- Requirements to use Meta Quest Link | Meta - If you'd like to use Meta Quest Link to connect your Meta Quest headset to a Windows PC, please start by reviewing the compatibility requirements.
- Set up and connect Meta Quest Link and Air Link | Meta Store
- Air Link
- `Air Link` might just refer to connecting over wireless as oppose the `Link` cable.
- Air Link Setup | Meta Quest 2 - YouTube - Learn how to wirelessly connect your Meta Quest 2 to a compatible gaming PC with Air Link.
- Connect Meta Quest to your PC over Wi-Fi with Air Link | Meta
- Meta Quest Air Link allows you to wirelessly connect your Meta Quest to your PC using a secure Wi-Fi network.
- Before you set up Air Link, make sure that your computer meets the requirements for using Meta Quest Link, and review the best practices listed below for optimal performance.
- How to use Airlink wireless at 960mbps (Quest Setup Guide) - YouTube - A guide on how to use Airlink wirelssly at 960mbps and below.
- Common
- Steam Link / SteamVR (From Steam)
- Steam Link runs SteamVR and Steam apps directly on Quest -- but YOU SHOULDN'T | 360 Rumors
- But the new free Steam Link app for Quest now enables the Quest 3, Quest 2 or Quest to run SteamVR (or non-VR Steam games) without the need to launch the Oculus desktop app. Not only is this more convenient but should result in lower overhead — in theory.
- HOW TO PLAY STEAM VR GAMES ON META QUEST 2 or 3! | Link Cable Setup Guide 2023 - YouTube
- Want to play Oculus or Steam PC VR games on your Meta Quest 2or Quest 3? This complete guide shows you everything you need, and the easy to follow steps on getting it all set up, so you'll be playing your first PCVR game in no time at all!
- 3 main requirements
- VR Ready PC
- USB Cable (a suitable one)
- Install some software
- Steam Link can now wirelessly stream VR games to your Meta Quest headset - The Verge - It’s now much easier to play Steam games on your Quest.
- Steam Link runs SteamVR and Steam apps directly on Quest -- but YOU SHOULDN'T | 360 Rumors
HDMI Input (Meta Quest HDMI Link) from (Xbox One|SteamDeck|Playstation)
- Meta Quest HDMI Link: Official App for HDMI Outputs - Full Setup & Review - YouTube | Hudson DIY
- Exciting news for Meta Quest 3 users! The new Meta Quest HDMI Link app is here, providing an official way to connect a capture card to your headset and display HDMI outputs inside the headset.
- In this video, we’ll walk you through the setup and review the app’s performance.
- Quest as a BIG screen for Nintendo Switch, Steam Deck etc. How to connect it in the most simple way - YouTube | Voland's reality
- Explains which devices to get and how to set them up
- Quest as monitor via HDMI cable. It doesn't require any software on PC. Works even in BIOS! - YouTube | Voland's reality
- Explains which devices to get and how to set them up
- Can VR Replace Your Monitors in 2024? - YouTube | RealityRise - Will VR be able to replace your monitors in 2024? How is the resolution? Does everything work snappy? Let's find out!
- How to Connect STEAMDECK to QUEST 3 (via USB-C!!!) - YouTube | Philly Cinema - Here's my super easy/simple way of using my Quest 3 as a huge virtual monitor for my SteamDeck. Should work with any USB-C/HDMI device (Nintendo Switch, iPhone 15, Rog Ally, etc).
- Can the Quest 3 Replace your Monitors? | Immersed | Meta Horizon Workrooms - YouTube | Mystery VR - In this video I will answer the question that can Quest 3 replace your screen. I will be exploring two apps immersed and Meta Horizon Work Rooms in which you can mirror your computer screens and can actually work.
- Meta Quest 3 Xbox hdmi monitor - YouTube | bogietek
- Thanks bro! I got it to work. A few missing steps though like:
- create Meta developer account (free)
- download .apk file for USB camera app
- download Sidequest app on your PC
- turn on developer mode on Quest and restart
- connect Quest to PC
- open Sidequest and load .apk file
- Thanks bro! I got it to work. A few missing steps though like:
Xbox One
Play Xbox games on Quest (General)
You can pair your Xbox controller on your Quest for using with games.
- Methods
- Xbox One HDMI Output --> HDMI USB capture dongle --> quest
- Xbox Gamepass
- is natively supported on Quest 3
- A.k.a Xbox Cloud Gaming (beta) / Xbox App
- No Xbox needed
- Xbox --> PC --> Quest
- Uses Virtual Desktop App on the Quest and PC.
- As PC VR Headset (needs a decent PC)
- 4 Ways to Play Xbox Games On Oculus Quest / Quest 2 – Smart Glasses Hub
- Can you also use the Oculus Quest and Quest 2 VR headsets to enjoy some Xbox gaming?
- The short answer is that you can play Xbox games on both the Oculus Quest and Quest 2 headsets.
- It is possible to stream the Xbox console to your headset or alternatively play Xbox games without the console by using the Xbox Cloud gaming service.
Play Xbox games on Quest (via Xbox App)
- Playing Xbox on Oculus Quest 3 | OculusQuest | Reddit
- I got the Xbox app running on the Oculus Quest 3. For anyone wanting to know how it's done, follow the steps below.
- Enable developer mode on Oculus. The requires a developer account which anyone can set up. It's super easy. This give you access to the library folder for unknown sources, more on this later.
- Install Side Quest on a PC
- Download File Manager APK from https://flashlight-clock-file-manager.en.uptodown.com/android
- Follow Side Quest steps to connect your Oculus
- Upload file manager to Oculus via side quest
- Get on your Oculus and use the web browser to search for the Xbox app APK and download from uptown.
- Go to your library, click the search bar, use the drop down to go to "unknown sources"
- use the file manager to install the Xbox APK
- connect an Xbox controller to the headset via Bluetooth setting
- log into Microsoft account and enjoy!
- It seems like a lot of steps but it only took me about 20 minutes altogether.
- Other Comments
- For some reason the xbox app uses low resolution (I'm using quest pro), still playable but sometimes annoying
- Surprisingly low in my experience, but it looks like they use a low bitrate to achieve that so it doesn’t look great. There’s a custom Xbox remote play app someone made that lets you adjust the bitrate so that may help.
- I know Xbox Cloud Gaming is officially coming to the Quest in December and I've seen some people assume that means you'd be able to remote play as well, but I'm not actually sure that'll be the case since I don't think they've specifically mentioned remote play.
- For those wondering about the screen resize, open this menu on the oculus and hit "switch view". After that you should be able to resize windows.
- Also, if anyone has any issues where the Xbox controller uses head tracking, press the start and back button on the controller at the same time and it will switch the controls.
- Sidequest (advanced) can install apks directly to the oculus headset
- FYI, there is a way easier way to do this. Just download Fluid on App Lab. Works out of the box.
- I got the Xbox app running on the Oculus Quest 3. For anyone wanting to know how it's done, follow the steps below.
- How to play Xbox games on the Meta Quest 3 | Trusted Reviews - You can stream Xbox games directly to your Meta Quest 3, as well as the Quest 2 and the Quest Pro. Here's how.
Casting to a Xbox One
- Wireless Display - Microsoft Store - Microsoft's Wireless Display app lets you wirelessly project your Windows or Androidto your Xbox One.
- New Xbox Wireless Display app brings PC streaming to Xbox One | Windows Central - Microsoft's new Wireless Display app for Xbox One brings native Miracast streaming for PC games and video.
- How to Cast to Xbox One and Xbox Series From Your Smartphone - Desperate to share smartphone videos to your TV? Here's how to make it easy by casting to your Xbox One or Xbox Series using Android and iPhone.
- How To Mirror Your PC Display To Your Xbox One, Xbox Series X - Guide | Pure Xbox - Did you know Microsoft has created an official method for you to mirror (and even control) your Windows 10 PC via your Xbox? It's true, and it actually works much better than you might expect.
- How to stream PC games and movies to your Xbox console with a free app - The Verge - Using Microsoft’s Wireless Display app, you can easily output the games from your Xbox to your Windows PC screen. Conversely, it’s possible to stream what’s on your PC to the TV that you’re using with your Xbox — you can even control it from the console, and setting it up is surprisingly simple.
- Meta (Oculus) Quest 2 - How To Mirror Gameplay To The Xbox Series X/S - Learn how to mirror Meta Quest 2 gameplay using and Xbox Series X/S.
- How to Use Your Xbox One or Xbox Series X|S as a Wireless Display - Stream music, movies, and even games to your Xbox with the official Wireless Display app for Xbox.
Casting from a Xbox One
- How to Stream Xbox One to Your PC
- You can stream Xbox One to any PC as long as they're both running Windows and are connected to the same network. Here's how to do it.
- Page is faulty, click on the TOC links on the left hand side to navigate.
Play Xbox games on your PC
- Stream games from your Xbox One console to your PC - Microsoft Support - Here's how to stream games from your Xbox One console to your PC
Purchases
random thing to look at later, I have not made a descicion and do not know the quality of the brands, this is more an idea holders
- Stock Controller accessories / Gun Stocks etc...
- World's Most Adaptable VR Shooter Accessory –Wield VR OneStock - World's Best VR Gunstock for ultimate immersion and performance with improved aim and consistency in VR FPS.
- MODJUEGO Magnetic VR Stock Controller Handle - Fit for Oculus Quest 2 Gamepad Controller Lightweight Stabilizer Cool Handle Holder… : Amazon.co.uk: PC & Video Games
- HDMI input
- Batteries
- Meta Quest 3 128GB and Venom Rechargeable 3000mAh Power Bank for Meta Quest 3 : Amazon.co.uk: PC & Video Games
- 5000mah Battery Pack for Meta Oculus Quest 2 & Elite Head Strap, Lightweight Portable VR Power Charger Battery Extender Rechargeable for Meta Accessories for 3 Hours Extended Playtime : Amazon.co.uk: PC & Video Games
- Headset Straps and Mounts
Troubleshooting
- Solved: Meta Quest app - stuck on the "Pair a new device" ... - Meta Community Forums - 1153444
- Q:
- I'm stuck on the "Pair your headset with the Meta Quest app to continue." step during the Meta Quest 3 setup. The smartphone app tells me to "Allow permissions", which I have already done. I have "Use precise location" enabled as well. Pressing the blue "Continue" button does nothing. The Meta Quest 3 button is greyed out. I have a code displayed in the headset that I'm supposed to input somewhere in this app. What do I do?
- My Meta Quest app is up to date. I have already installed all system updates on my smartphone. My smartphone and Meta Quest 3 are on the same WiFi network.
- A:
- I had the same problem. Make sure your location is turned on from the swipe down panel.
- Q:
- Solved: Passthrough turns on - can't use menu button - Meta Community Forums - 1078491
- Q: My Oculus would not load the menu screen without passthrough on. With passthrough on the oculus would not load apps/games. The app on my phone says the apps are open on the device.
- A:
Hey there! Thank you for letting us know the experience you're having with your device as this is not what we want. We do have a few users having the menu button disappear and a Factory Reset has gotten them back on track. However, I am not seeing some users not having the button load overall even when factory resetting.
- Stuck on Passthrough with Menus not working - Meta Community Forums - 1173053
- Q: I'm stuck in pass through but the home music cuts in and out and I can't open any menus or nothing
- A: With the device being stuck viewing your play area, we'd like to hard reboot the headset by holding the power button down for 30 seconds.
- Hand tracking not working
- Some solutions I have figured out
- Turn the Meta Quest on without the controllers in site
- Pinch Thumb and index finger with palm facing you for a about 10 - 15 seconds and hand tracking will start
- Solved: hand tracking does not work for me - Meta Community Forums - 977838 - I have enabled hand tracking, removed the controllers out of headset sight, but it doesn't switch to hands. I just don't have any hands. Does anyone here know what I'm doing wrong and what I can do to fix this?
- How To Turn On Hand Tracking On The Meta Quest 3? - In this article you will learn how to turn on hand tracking on the Meta Quest 3.
- How To Fix Meta Quest 3 Hand Tracking Not Working - NetworkBuildz - To fix Meta Quest 3 hand tracking not working, power cycle your headset.
- Some solutions I have figured out
- Cannot login to the Meta Quest community forum
This call accesses the User ID platform feature, which requires certifying through the Oculus Data Use Checkup program. Please visit this page for more detail: https://developer.oculus.com/distribute/publish-data-use/. If you have already completed a Data Use Checkup, please ensure that all compliance issues are resolved by visiting the Compliance Dashboard: https://developer.oculus.com/resources/publish-compliance-dashboard/.
- If you get this error below when you try and login to the Meta Quest community forum then you should know:
- this is nothing you have done but is the garbage infrastructure and support team from Quest. A billion dollar corporation cannot keep their own API key updated and then when it needs swapping takes nearly 2 weeks to fix. Meta need to change their support team from wherever they have outsourced it to.
- This is a common occurrence
- Solved: Login to user forum problems | Meta Community Forum
- Developer account data use checkup. | Overclockers UK Forums - Has anyone with a dev account had this pop up when trying to log into the meta forums
- If you get this error below when you try and login to the Meta Quest community forum then you should know:
- not authorized to relay messages to the server that reported this error
- This is caused by Meta's really poor support system. This is nothing you have done and you can not fix it.
- Error message when trying to respond to Meta Quest Support emails - Meta Community Forums - 1064479
- Meta Quest app - stuck on the "Pair a new device" screen - Meta Community Forums - 1153444
- Q:
- I'm stuck on the "Pair your headset with the Meta Quest app to continue." step during the Meta Quest 3 setup.
- The smartphone app tells me to "Allow permissions", which I have already done.
- I have "Use precise location" enabled as well.
- Pressing the blue "Continue" button does nothing.
- The Meta Quest 3 button is greyed out.
- I have a code displayed in the headset that I'm supposed to input somewhere in this app.
- What do I do?
- A:
- Make sure your location is turned on from the swipe down panel.
- Q:
My Pond Notes
These are my notes on rebuilding my pond
Purchasing
- Pipe / Hose
- Buying notes
- Do not buy that garbage pipe on eBay where it is only made out of PVC. This means that to form the ridges on the outside it must form grooves on the inside of the pipe making these almost impossible to seal properly. the low quality pipes also rip very easily and I am not sure on how resistant to UV they are.
- When buying a pipe make sure it has a smooth bore, this makes sure you get a good seal.
- I went with 25mm (1 inch) pipe as this is universally supported.
- When defining a pipes size (i.e. 25mm) you are referring to the diameter of the bore (the internal measurement).
- Types
- Flexible Pond Hose Durable, Kink-Resistant Water Tubing for Garden Ponds Var Siz | eBay | Silicone Hose UK
- I used this one - Good value and a strong pipe with a smooth bore.
- Lightweight PVC hose with a rigid crush resistant white PVC helix. Tough, flexible and extremely durable under normal operating conditions. The cross section is maintained even when highly flexed.
- Minimum frictional loss is achieved by the smooth bore. The corrugation in the hose gives it strength and flexibility, allowing you to turn tight corners without it kinking.
- Quality PVC reinforced with an integral helix of rigid PVC, corrugated outer surface provides high flexibility and small bending radius. Smooth inner surface ensures it is excellent for the conveyance of liquid, air & powders. High abrasion resistant.
- MANUFACTURER: Auto Silicone Hoses
- Product Code: PDH
- Specs:
- Wall Thickness 2mm / 4mm
- Inside Diameter: 25mm
- Outside Diameter: 30mm
- Working Pressure: 6 Bar
- Bursting Pressure: 18 Bar
- Temperature Rating: -10C to +55C
- Auto Silicone Hoses
- Brother of above
- BLACK CORRUGATED FLEXIBLE POND HOSE PUMP GARDEN PIPE FLEXI TUBE FISH MARINE | eBay | Auto Performance Silicone Hoses
- Auto Silicone Hoses - Performance Hose Specialists - Silicone Rubber Hoses - AutoSiliconeHoses.com - AutoSiliconeHoses.com The UK's largest Silicone & Performance Hose Specialists | Flexible Hoses, Ducting. Coolant, Radiator, Turbo Applications. Aluminium & Steel Pipework. Manufacturer & Distributor of Hoses for all applications. Auto Silicone Hoses
- PVC Corrugated Flexible Duct Hose - AutoSiliconeHoses.com
- Has a datasheet
- Product Code: PDH-ASH / PDH025
- Has clip recommendations:
- 25mm(1") HEAVY DUTY Flexible Hose Pipe - Marine Boat Garden Fish Pond Flexi | eBay | Discount Leisure Products
- This Heavy Duty hose has a 3mm(approx) wall which is reinforced for strength. The inside bore of the pipe is smooth so does not restrict the water flow. Flexible Heavy Duty Hose.
- This pipe is easy to seal to connections using hose clips due to the smoother outer surface of the pipe compared with the deeper ribbed hose available.
- This is the high end pipe.
- Extra Long 20M Corrugated Flexible Pond Hose Pump Marine Garden Tube Pipe 1 INCH | eBay
- This is an example of garbage pipe and should not be used for you pond project
- Length: 20M. Universal Heavy Duty PVC Extra Long Flexible Pond Hose. Durable Corrugated Plastic Hose Is Designed For Use In Fish Ponds, Water Features And Water Filtration Systems.
- External: 32mm
- Internal: 25mm
- Flexible Pond Hose Durable, Kink-Resistant Water Tubing for Garden Ponds Var Siz | eBay | Silicone Hose UK
- Buying notes
- Clips (Hose|Pipe) / (Clips|Clamps)
- General
- The clip max size would = the max diameter of the pipe you are clamping, but does not harm to get your pipes max diameter in the middle of this range to allow for easy fitting.
- Jubilee Clips / Band Clips / Worm Drives
- Will only work on pipe that has smooth bore.
- Stainless steel clips might be fine in the actual pons if W4 or W5 grade.
- Easyfix Blue Zinc-Plated Hose Clips 20-32mm 10 Pack - Screwfix
- I have used these galvanised jubilee clips (20-32mm) from screw fix for my valve assembly.
- Easyfix Self-Finish Hose Clips 15-30mm 10 Pack - Screwfix
- Jubilee Clips Stainless Steel 316 - Absolute Koi use a good quality Jubilee clip or our Hose Tail Easy fasteners.
- EK Brakes
- Jubilee Clips (other brand)
- p/n: 505257
- 25mm - 35mm
- W4 Steel
- Pack of 10
- £14.86 inc VAT
- 2 - 3 Days, Not kept in stock.
- Jubilee Clips (other brand)
- Worm Drive Hose Clamps Jubilee Clips Oetiker Mikalor – HCL Clamping UK/Europe - A full range of Worm Drive Hose Clamps including, JCS Hi-Torque, Jubilee Clips, Mikalor ASFA, Oetiker Narrow Worm Drives and HCL's Budget Worm Drive Hose Clip.
- Hose Clips, Jubilee Clips & Hose Clamps - Westfield Fasteners Ltd - Choose from our wide range of Hose Clips, Jubilee Clips, Mikalor Clamps and more. Available in stainless steel A2 or A4, Brass and Nylon | Next Day Delivery.
- Pond Aquarium STAINLESS STEEL HOSE JUBILEE CLIP - single | eBay | Midland Waterlife Ltd
- 12-20mm - 1/2"
- 16-25mm - 3/4"
- 20-32mm - 1"
- 25-40mm - 1 1/4"
- 32-50mm - 1 1/2"
- 40-60mm - 2"
- Buy Clips Online from Ace Fixings (Cumbria) Ltd
- DLP 25-44mm Stainless Steel Flexible Pipe Hose Clip - Pond Supplies from Discount Leisure Products UK - 25-44mm Stainless Steel Flexible Pipe Hose Clip DLP Pond Supplies 32mm(1.25") from Discount Leisure Products.
- Stainless Steel Jubilee Hose Clip | Pond Supplies | CD Aquatics - Buy Stainless Steel Jubilee Hose Clip from CD Aquatics, West Midland's no.1 store for Hose Clips - free delivery on orders over £50
- Stainless Steel Jubilee Style Hose Clips | Water Pipe Clamp Sets | Aquatix-2u - Pisces Stainless Steel Jubilee style hose clips comes in a variety of sizes and fittings. Ideal for any size pond hose. Designed to fit snugly around any pond hose, the jubilee style hose clips are sturdy and durable clips. Each clip is made of stainless steel and is easy to adjust over your preferred size hose.
- Double wire hose clips
- Are very difficult to get working.
- Don't buy the cheap ones from China.
- Make sure you get the thick steel ones that you cannot bend with your hands.
- I found the best size of these (when you get them fresh and are fully open) is .......
- Double Wire Clips - Absolute Koi
- For those of you using the Ribbed flexible hose then you will certainly need to secure the hose to the connections we have listed in this section and will need to use a good quality Double Wire Clip
- These are the thing ones and I would be cautious using them.
- 25mm (1") corrugated flexible pond pipe repair joiner/connector+2 x double wire hose clips : Amazon.co.uk: Garden
- Says the double wire clips are 25-29mm for use with 25mm (1 inch) pipe.
- DOUBLE WIRE HOSE CLIPS POND PIPE SCREW TIGHT KOI FISH FITTING FILTER PUMP WATER | eBay | aquatics4all
- Ideal for use with corrugated pipe. Screw fitting.
- Made from Spring Steel.
- Double Wire Flexible Hose Pipe Clip | Pond Supplies | CD Aquatics - Buy Double Wire Flexible Hose Pipe Clip from CD Aquatics, West Midland's no.1 store for Hose Clips - free delivery on orders over £50
- Herbie / Nibble Clips / Double toothed hose clamp / Plastic Hose Clamp / Snap Grip Hose Clamps
- General
- For 25mm garbage corrugated pipe, buy: Size N: 29.4-32.7mm (9.1mm wide)
- These are plastic clips
- There is a special tool for closing and opening these but nis not always needed.
- Different materials
- Nylon vs Polypropylene: Comparison of Properties, Applications, and Processing - Explore the key similarities and differences between Nylon and Polypropylene. Understand the unique properties of these polymers and investigate their best uses as we explore their unique characteristic and possible limitations. Comparing Nylon vs PP provides comprehensive knowledge to help you select suitable material.
- PA6 vs PA66 Plastic: Differences Between Nylon 6 & Nylon 66 Material - We compare and discuss the differences between PA6 and PA66 engineering plastics in terms of Chemical Composition, physical properties, application, injection molding process, price, etc.
- Polyamide (Nylon): Guide to PA6, PA66, PA11, PA12 Variants - Explore key facts about Polyamide or Nylon and learn what are the benefits and popular applications of some common polyamides: PA6, PA66, PA11, PPA...
- Polypropylene vs. Nylon: What’s the Difference? - Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer used in a variety of applications, known for its chemical resistance, while nylon is a synthetic polymer, notable for its strength and elasticity.
- Herbie Clips (by HCL Fastners) (Plastic)
- General
- HCL are the original developers and are based in the UK.
- Herbie Clip Original - Grip Nylon Hose Clamp From HCL - HCL creator and supplier of the original Herbie Clip, The most popular grip nylon hose clamp. Wide range in stock, and can be made to order.
- There are 2 materials that these are made out of, "PA66 (Nylon 6.6)" (the most common) and "PP (Polypropylene)". Each has slightly different properties.
- Available in natural (white) and black colour.
- Nylon is stronger but susceptible to water ingression.
- Size N seems to be the most popular as this is what is shown in all product pages.
- Official Tools
- Official Shops
- eBay
- Herbie Clip Natural Polymer Nylon Plastic Hose Clamp Clip Double Grip Snap Fit | eBay | HCL Fasteners
- Designed and manufactured by HCL to the highest quality the Herbie Clip is the original double grip plastic hose clamp.
- It offers exceptional strength due to it’s unique double row of interlocking toothed jaws which offer over twice the clamping forces achieved by similar toothed products.
- The Herbie Clip is a high-quality hose clamp made from Nylon 6.6 and offers the largest range of Snap Fit Style Hose Clamps with 38 sizes ranging from 5.6mm to 169mm diameter.
- The clamp is highly versatile and lends itself to a wide variety of applications meaning that Herbie Clips can be found in Agricultural Machinery, Automotive Engines, White Goods and many other applications.
- HCL Herbie Clip Black Nylon Plastic Ratchet Pipe Installation Hose Clamp | eBay
- Plastic Hose Clamp - Herbie Clip Fitting Tool | eBay - Plastic Hose Clamp - Herbie Clip Fitting Tool.
- Plastic Hose Clamp Removal Tool - Herbie Clip/Snapper/Hellerman/Essentra | eBay - Plastic Hose Clamp Tool - Herbie Clip Removal Tool.
- Herbie Clip Natural Polymer Nylon Plastic Hose Clamp Clip Double Grip Snap Fit | eBay | HCL Fasteners
- Shop for Hose Clamps Smart Ties Banding and Clamping Tools for Sale – HCL Clamping UK/Europe
- Buy HCL Plastic Hose Clamp - Herbie Clip - 28.8-32.2mm - Black - PA66 – HCL Clamping UK/Europe
- PA66 (Nylon 6.6)" (Size N)
- Buy HCL Plastic Hose Clamp - Herbie Clip - 28.8-32.2mm - Black - PP – HCL Clamping UK/Europe
- PP (Polypropylene)" (Size N)
- Also these supplier all other types of clamps and clips i.e. jubilee clips.
- Buy HCL Plastic Hose Clamp - Herbie Clip - 28.8-32.2mm - Black - PA66 – HCL Clamping UK/Europe
- eBay
- Other shops
- Herbie Clip Nylon Snap Fit Plastic Ratchet Clamp Irrigation Garden Hose Pipe UK | eBay - Herbie Clip® Plastic (Nylon) Hose Clamp Double Grip. Manufactured by HCL.
- Cheaper than the official eBay shop.
- Herbie Clips in Plastic (Black Nylon Polyamide) - Westfield Fasteners Ltd - Herbie Clips in Plastic (Black Nylon Polyamide). Manufactured in the UK by HCL. Purchase in box or sachet quantity | Next day Delivery.
- Snap Grip Hose Clamps 24.1-26.2mm, 7.9mm Width, Black | Vital Parts - This Snap Grip Hose Clamp, also known as a herbie clip, has a clamping diameter range of 24.1-26.2mm and is made from Nylon 6/6. This clip has ratcheting teeth which allows for this hose clamp to be tightened easily by hand.
- Herbie Clip Nylon Snap Fit Plastic Ratchet Clamp Irrigation Garden Hose Pipe UK | eBay - Herbie Clip® Plastic (Nylon) Hose Clamp Double Grip. Manufactured by HCL.
- General
- General
- General
- Pipe Connectors
- HOSETAIL CONNECTOR FITTING BARBED BSP PLASTIC POND POOL HOSE PIPE ADAPTOR | eBay | Hortafix
- Hosepipe adapter
- Fitting Size: 3/4" to 25mm
- Fitting Type: Male Connector
- MPN: PHTM020025
- Barb goes into a pipe with a 25mm internal pipe, the 3/4 thread will allow a standard hose pipe adapter to be screwed on.
- 3/4 inch is the thread on standard outside taps.
- Hosepipe adapter
- Hose Tail Connector. Barbed to Male BSP Thread. Pond, Pool, Hose Pipe Adapter | eBay
- Has BSP thread sizes.
- Pipe fittings 25mm 1" (internal) Barbed Tee, Elbow, Coupler. Ponds Hydroponics | eBay | Hortafix
- Pipe fittings 25mm 1" (internal) Barbed Tee, Elbow, Coupler. Ponds Hydroponics. Pond Pipe Fittings. MDPE Fittings. Useful Links.
- I bought Elbow, Joiner, Tee (25mm/1 inch/1", Eve Brand)
- HOSETAIL CONNECTOR FITTING BARBED BSP PLASTIC POND POOL HOSE PIPE ADAPTOR | eBay | Hortafix
- Valves
- DLP 25mm Inline Pond Hose Flow Control Tap/Valve Plastic Flexible Pipe Fitting - Pond Supplies from Discount Leisure Products UK
- I bought 5 of these for my valve assembly
- Code: 25MM2WTAP
- Inline tap to fit 25mm(1") internal diameter flexible hose
- This range of hose taps are made from a tough copolymer polyproplyene that can handle a pressure of up to 8 bar at ambient temperature and a max of 80 degrees C temperature at a lower pressure
- Allows the control of water flow to water features, pumps, filters etc.
- DLP 25mm Inline Pond Hose Flow Control Tap/Valve Plastic Flexible Pipe Fitting - Pond Supplies from Discount Leisure Products UK
- Pipe Mounts
- Plastic Hinged MDPE Water Pipe Clip Pack Of 10-20MM.25MM.35MM Brand New
- I bought 10 of these on eBay - They work fine for the garbage pipe and the decent pipe from Auto Silicone Hoses (30mm wide)
- SKU: Select Size: 35mm (32-35mm), Select Colour: BlacK
- Brand: Talon
- Has the number 35 on the clip
- Talon MDPE BLACK Single Hinge Pipe Clip 32-35mm (Box Of 50)
- TALON BLUE WATER PLUMBING PIPE HINGED NEW MDPE CLIPS 20mm,25mm,35mm 4 PACK * | eBay
- Talon clips will fit the following diameters
- 20mm clips will accept tube from 19-21mm
- 25mm clips will accept tube from 25 - 27.4mm
- 35mm clips will accept tube from 32 - 35mm
- Talon clips will fit the following diameters
- Locking Pipe Clip - Absolute Koi
- Without doubt more and more Koi and pond enthusiasts are turning to using the Grey Pressure Pipe (PVC) pipe and fittings and this is something that we wholeheartedly welcome, mistakes made in pipe work in the initial stages are sometimes very hard to correct, or perform repairs to, so by using these types of pipe work and fittings you can be sure that the installation is going to be sound and, hopefully, trouble free.
- Very expensive version.
- Plastic Hinged MDPE Water Pipe Clip Pack Of 10-20MM.25MM.35MM Brand New
- Filter Box
- UV Bulb
- Philips TUV 4W G4 T5 - UV Bulb/Tube
- Two pins each end
- 148mm from pins to pins
- 15mm Diameter
- Philips G4 T5 UVC 4 watt lamp ultra violet uv tube fish pond bulb | eBay
- UV Bulb
- Pumps
- I have a Bermuda: Wi-Fi Filter Pump 10000 (SKU: BER4501) bought from aquatics4all on ebay
- Rated for continuos operation
- Get model number from the pump.......
- Bermuda: Wi-Fi Filter Pump 10000 - Alton Garden Centre - Bermuda Wi-Fi Filter Pump (10000)
- Features:
- Wi-Fi Filter Pump are high performance energy efficient filter & waterfall pumps.
- Can be controlled by app on your mobile device or external controller.
- For medium to large garden ponds
- Low electricity usage with high output,
- Pump is near silent when in operation,
- Pump can be used in or out of the pond.
- Specifications
- Model: 10,000
- Ouput: 10000 Iph
- Power: 70W
- HMAX: 5.0m
- OUTLET: 1 1/2"
- Dimensions: 296 x 140 x 173mm
- Features:
- I have a Bermuda: Wi-Fi Filter Pump 10000 (SKU: BER4501) bought from aquatics4all on ebay
- Other Suppliers
- Woodlands Garden Centre Cumbria | Water Garden Specialists | - Pond Pumps - Hi! Welcome to Woodlands Garden Centre near Crooklands, Kendal, Cumbria, specialists in water gardens, extensive selection of plants, flowers for all occasions, open daily
- Swell UK - The UK's biggest pond and aquarium specialist - Swell UK is the UK's largest online pond and aquarium store. Order by 4pm for same-day despatch during the week, or 1pm at the weekend.
- Aquarium Supplies Online | Aquacadabra - Welcome to Aquacadabra! Over 6,000 products with FREE UK SHIPPING for Coldwater, Tropical & Marine fish tanks and products - all at great low prices.
Tutorials
- Fitting pipe on barbed connectors
- Q: These adapters are incredibly tight and I cannot seem to get them inserted more that one barb of depth. my pipe is standard 25mm internal diameter, corrugated black pipe. Is there a knack to inserting these or are they faulty?
- A:
- Use potable silicone grease.
- Use Vaseline
- Warm the pipe by dunking it in hot water.
- Pond Pipe Videos
- Changing the Pond Tubing (hose) - YouTube - Shows the use of a Jubilee clip.
- Best GARDEN POND plumbing & flexible PVC WATER FEATURE tubing - YouTube - Different pipe types.
- How to Repair Split Pond Tubing - YouTube - Fix a split in tubing, he uses jubilee clips
- Tubing and Barbed Fitting Adjustments | How to get a tight seal - YouTube - Tubing and fittings, getting a tight seal, uses tape for a nice seal
- Selecting tubing for ponds and water features - YouTube - Different types of pipe, uses jubilee clip
- Practical Pond Product Review Ep: 8 - "What Type of Plumbing Should I Use?" - YouTube - Join Nate Brunk from Practical Garden Ponds as he gives his practical opinion on many products for your pond. In this episode, Nate talks about different types of plumbing and tubing to use on your pond or water feature.
- Steel Classifications and their applications
- Jubilee - Material Data
- https://www.jubileeclips.co.uk/assets/uploads/2019/02/Material-Data-219.pdf
- Steel Technical Data and Stainless Steel Classifications:
- 410 (W3), 430 (W3), 304 (W4), 316 (W5)
- Steel Technical Data and Stainless Steel Classifications:
- https://www.jubileeclips.co.uk/assets/uploads/2019/02/Material-Data-219.pdf
- Steel Grades and Seawater Corrosion - The relationship between steel and seawater is complex and it can be challenging to diagnose steel grades for offshore and shipbuilding applications.
- Selection of 316, 304 and 303 types of stainless steels for seawater applications – British Stainless Steel Association
- Is Stainless Steel Waterproof? - Everything You Need To Know - Stainless Steel Guide - You probably just got a new stainless steel bracelet or necklace, and you're wondering- 'Is stainless steel waterproof?'
- Why?
- That’s because chromium is responsible for the waterproof nature of stainless steel.
- The chromium in stainless steel reacts with the oxygen in water and air to form a thin, hard, and resistant oxide layer on the surface to make it ‘rust-resistant.’
- This layer is a lot slimmer than the wavelength of light, so modern instruments (a transmission electron microscope) are needed to see them.
- This makes the underlying metal shine through, hence the name stainless steel.
- And because of this layer, there are about 150 different recognized grades of stainless steel, each with different properties and rust resistance.
- According to the Nickel Institute, 304 and 316 stainless steel grades can tolerate up to 2ppm (parts per million) and 5ppm of localized corrosion of chlorinated fresh water.
- You can’t wear stainless steel in the ocean because there are a lot of microorganisms and chemicals that can speed up the metal’s corrosion rate.
- Oceans contain salt and traces of chloride ion (Cl-), which react through the electrolysis process.
- Now you know that although stainless steel has a passive, protective layer reducing the corrosion rate by water, and that the layer can still rust due to metal oxides and hydroxides.
- But because it forms readily and tightly, the passive layer coating only corrupts/rusts on the atomic level, giving the “stainless” impression.
- To answer your question, Is stainless steel waterproof? Stainless steel is completely waterproof.
- Why?
- Materials used (from HCL Fasteners)
- Zinc Plated Steel (W1)
- Zinc Plated & 430SS (W2)
- 430 Stainless Steel (W3)
- 304 Stainless Steel (W4) - from Westfield Fasteners - W4 (A4 marine grade stainless steel)
- 316 Stainless Steel (W5) - from Westfield Fasteners - W5 (A2 standard stainless steel)
- Titanium
- Stainless Steel Grades: The Ultimate Guide | MachineMFG
- From 304 to 316, our comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about stainless steel grades. Get expert insights now!
- Presently, the most widely used stainless steels are 304 and 316.
- Unraveling the Facts of Stainless Steel: Why It Resists Rust - Discover stainless steel's rust-resisting power, types, prevention tips, and how to pick the perfect grade for enduring performance.
- Jubilee - Material Data
- Pump
- Tips to Calculating Pond Pump Size > Pondliners online - Before buying a pond pump, there are a number of considerations that need to be made to ensure you choose the size most suited to your pond.
- Repairing a Pump mains wire
- How to repair pond pump cable? | DIYnot Forums
- 6A Gel Insulated Straight Through Joint - 3 Core Flex - IPx8 | Wiska (SH0325W)
- Hylec TeeTube 2-Entry 3-Pole In-Line Cable Joint - Screwfix
- Hylec 2-Entry IP68 Gel In-Line Connector Black - Screwfix
- I used paint on "Liquid Insulation rubber Coat / Liquid Electrical Tape / Liquid Insulating Tape" from AliExpress
- Pipe Width
- How to Choose the Correct Size Pond Tubing - Hydrosphere Water Gardens - What size pond tubing should I use with my pump? Choosing the correct diameter of kink free or PVC tubing is crucial in how well your pump will perform.
- Pipe Size Guidelines | AquaNooga Pond Supplies - In this article we've provided a list of pipe sizing guidelines. For pumps with flows up to 300 gph use 1/2" tubing Flows from 300:600 gph use 3/4" tubing &more.
- What size pipe should i use? - YouTube | Sacramento Koi - Proper pipe size is extremely important to consider when building a pond. Volume and head pressure must be factored in properly prior to building.
- Controlling Duckweed
- How to Remove Duckweed from A Pond: 5 Tips from the Pros - If you want to know how to remove duckweed from a pond or lake on your property, the following tips from Coastal Spray can help.
- Duckweed and Watermeal - Duckweed and watermeal are free-floating aquatic plants that are commonly encountered in Pennsylvania. They are commonly found in nutrient-rich ponds with stagnant or little flow.
- Duckweed in Ponds | Duckweed Control | The Pond Guy - What is duckweed and how can you control duckweed in ponds? In this guide, we'll cover how to get rid of duckweed via a variety of methods.
- Duckweed Control: How To Get Rid Of Duckweed | Gardening Know How - Duckweed is a rapidly spreading aquatic plant that deprives ponds of oxygen. It is important to get rid of duckweed for the health of your pond and existing aquatic life. The following article can help.
- Duckweed / RHS Gardening - Duckweed is a familiar sight to pond owners. The tiny, rounded leaves float on the water surface, resembling a mass of young cress plants. They multiply rapidly and quickly fill any open surface of water unless regularly cleared.
- Duckweed Control | Ecopond - Duckweed Control effectively and safely treats duckweed which is often found in garden ponds by reducing the nutrients critical for its growth.
- I have not used this
- What Do I use, add when I use it, it is in the garage somewhere and where did I biy
- TAP No More Duckweed Pond Water Algae Treatment Duck Weed Garden Fish Koi | eBay
- Not advised for use in a Nature pond.
- I have bought this
My Discourse Notes
Just a collection of my notes for installing and using Discourse
- General Integration / SSO
- SSO, or Single Sign On, is a kind of middle-ground for that.
- SSO for joomla and Discourse?
- Setup DiscourseConnect - Official Single-Sign-On for Discourse (sso) - admins - Discourse Meta - DiscourseConnect is a core Discourse feature that allows you to configure “Single Sign-On (SSO)” to completely outsource all user registration and login from Discourse to another site. Offered to our standard, business and enterprise hosting customers.
- WordPress Intergration
- How to Use Discourse Community Forums with WordPress - Discourse is one of the most popular community forums software platforms available today. Unlike a lot of its WordPress-based competitors, Discourse doesn’t run off of WordPress architecture. It has to be contained on its own server. That shouldn’t scare you, though. The developers understand that 1/3 of the internet can’t be ignored (WordPress’ market share), so they made it exceptionally easy to make these two powerhouse platforms play nice with each other. With the official Discourse WordPress plugin, you can make these two platforms interact like they were made with the other in mind.
- Automatically Sync ALL WordPress users to Discourse - wordpress - Discourse Meta - I need all existing Wordpress users Synchronised/Imported into Discourse so that they are active Discourse users WITHOUT the users needing to first login to Wordpress to trigger the SSO Discourse account creation process. Is this a feature that’s currently available or do we need to develop a custom feature for this?
- How To Integrate Discourse Forum With WordPress: 2024 Guide - Learn how to integrate your Discourse Forum with WordPress blog in this tutorial - Installing Discourse WordPress Plugin and configuring the settings. The main highlights include the ability to publish selected posts as Forum topics on Discourse and use Discourse for comments and discussions for WordPress posts.
- Joomla Integration
- How to Enable Single Sign-on (SSO) in Joomla - Joomlashack
- Single sign-on (SSO) is a very useful tool for managing multiple sites.
- Single sign-on is often used by large companies that have many different software platforms.
- If all those platforms are connected using Single sign-on, then users only need to remember one username and password.
- SAML SSO for Joomla, by miniOrange - Joomla Extension Directory - Joomla SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) allows you to secure your Joomla site by allowing users to login into Joomla site by different SAML Identity Providers like Azure AD, Okta, GSuite / Google Apps, Keycloak, ADFS, Salesforce, Office 365, Shibboleth2, Shibboleth3, OneLogin, PingFederate, FusionAuth or any SAML compliant Identity Provider. Joomla SAML Single-Sign-On addresses the challenge of maintaining the credentials for each application separately, streamlining the process of signing on without the need to re-enter the password.
- How to Enable Single Sign-on (SSO) in Joomla - Joomlashack
- Using Discourse
- Editing Titles in Discourse - support - Discourse Meta
- What’s the deal with people being able to edit titles? Can only Regulars do this? I ask because on another forum, we are having some issues with people editing topic titles.
- Because you’re a longtime, trusted, “Regular”, you get elevated privileges, so you can fix bad titles.
- Editing Titles in Discourse - support - Discourse Meta
Forward Proxy, Reverse Proxy, TrueNAS, Virtualmin and Discourse
Suggested alternative Titles - might replace - current one
- Run a TrueNAS Docker container through Virtualmin by using it as a Reverse Proxy
- Run Discourse on the internet from a TrueNAS Docker container, through a Virtualmin Reverse Proxy
- Run Discourse on the internet through a Virtualmin Reverse Proxy from a TrueNAS Docker container
- Run Discourse on the internet through a Virtualmin Reverse Proxy using a TrueNAS Docker container
- Run Discourse through a Virtualmin Reverse Proxy using a TrueNAS Docker container
- Run Discourse through a Virtualmin Reverse Proxy using a TrueNAS Docker container as the source
Terms block
- WebSocket
- WebSocket Proxy
- :80 --> ws://
- :443 --> wss://
- Reverse Proxy
- Forward Proxy / Gateway Proxy
- Unix Socket
- ProxyPass
- ProxyPassReverse
Setup instructions
- Setup truenas
- setup Discourse Docker
- setup virtualmin
- setup virtual server
- setup proxying
- bridge wordpress/Joomla with discourse using a SSO (single Sign On)
This article will explore Forward Proxies, Reverse Proxies with a practical example to set up Virtualmin to access a remote Discourse server. We will also use phpmyAdmin to show case a locally hosted App. I will be using Apache but nginx can act as a reverse proxy.
Technologies used in this tutorial
- Ubuntu
- Webmin/Virtualmin
- Apache
- ProxyPass / ProxyPassReverse
- Discourse
- Docker
- TrueNAS
Proxying allows you to map a URL path in a virtual server's website to one or more destination URLs. It can be used to make other services available via a URL path on your website. For example, you might map the path /nodejs to the URL http://localhost:3000, an instance serving the application running on your Virtualmin system.
A proxy maps some URL on a virtual server to another webserver. This means that requests for any page under that URL path will be forwarded to the other site, which could be a separate machine or another webserver process on the same system.
- General
- A reverse proxy is a server that sits between a client and a web server, acting as an intermediary for requests. It retrieves resources on behalf of the client from the server, and then returns the response to the client.
- Proxy Paths, 2 Ways
- sockets = good when all sites are on the same site, a lot mor esecure and quicker (unix sockets?)
- external ?? = when not on same server, a little less secure and probably slower.
- phpMyadmin App (local example)
- install phpmyadmin on its own domain sub domain on your primary domain.
- use proxypaths to redirect a clients domain here. also you can use unix sockets.
- use the server templates to install this.
- add this section when i have done proxypaths. I might be able to get www.example.com/phpmyadmin path (not whole domain) to work
- Installation Discussions
- Installing Discourse Forum on Virtualmin - #4 by Joe - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- I’ve discussed this in the past, as well. But, the most important thing is:
ProxyPass / unix:/var/discourse/shared/socket-only/nginx.http.sock|http://localhost/ ProxyPassReverse / unix:/var/discourse/shared/socket-only/nginx.http.sock|http://localhost/
- Note the socket can be wherever you put the Discourse directory, including in a domain owner home directory. This is just the path you’d use if installing Discourse exactly according to the docs, and then changed Docker to listen on a socket rather than directly on an IP and port 80/443 (which can’t happen on your Virtualmin system because Apache or nginx is already there).
- And, as always, if you want to use Let’s Encrypt in Virtualmin or via certbot using web validation, you’d also need to exclude the
.well-knownpath, and let it be served from the file system. Again, this is always true, nothing special about Discourse or Virtualmin being involved.
- I’ve discussed this in the past, as well. But, the most important thing is:
- I want to install using a reverse proxy for Apache - installation - Discourse Meta
- Installing Discourse Forum on Virtualmin - #4 by Joe - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- Different Types of Proxies
- ? Forward Proxy = forwards requests to the new domain/target. The user is semi aware of the redirection. (i.e. the browser is aware, this fact is hidden from the user).
- ? Reverse Proxy - web server requests the information for you and then supplies it to the user. the user never sees the secodn server.
- Forward proxy vs. reverse proxy: What's the difference? | TheServerSide
- Great article
- Despite similarities, the use case for forward proxy vs. reverse proxy are vastly different. Here are key differences between a forward and reverse proxy.
- A forward proxy accepts connections from computers on a private network and forwards those requests to the public internet. It is the single point of exit for subnet users who want to access resources outside of their private network.
- As the name implies, a reverse proxy is the opposite of a forward proxy. The reverse proxy acts as a single point of entry for external systems to access resources on a private subnet.
- Forward Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy: The Difference Explained - In this post we dissect the differences between proxy & reverse proxy and explain how admins can use a reverse proxy for easy access management control.
- webserver - What's the difference between a proxy server and a reverse proxy server? - Stack Overflow
- Proxy vs Reverse Proxy - What's the Difference? (Pros and Cons)
- Proxy vs Reverse Proxy – What’s the Difference? (Pros and Cons).
- A proxy server is one of the tools that help protect a network and the assets that are connected to it. They make sure users, data packets and computers are safe and can communicate effectively.
- We will have a look at Proxy vs Reverse Proxy, make a comparison to distinguish which one should be used, their use cases and pros and cons for each proxy.
- Proxy vs Reverse Proxy: Understand the Difference - Netnut - Proxy vs Reverse Proxy: An in-depth comparison detailing their unique roles, benefits, and usage in network security and performance enhancement.
- Reverse Proxy Guide - Apache HTTP Server Version 2.4
- In addition to being a "basic" web server, and providing static and dynamic content to end-users, Apache httpd (as well as most other web servers) can also act as a reverse proxy server, also-known-as a "gateway" server.
- In such scenarios, httpd itself does not generate or host the data, but rather the content is obtained by one or several backend servers, which normally have no direct connection to the external network. As httpd receives a request from a client, the request itself is proxied to one of these backend servers, which then handles the request, generates the content and then sends this content back to httpd, which then generates the actual HTTP response back to the client.
- There are numerous reasons for such an implementation, but generally the typical rationales are due to security, high-availability, load-balancing and centralized authentication/authorization. It is critical in these implementations that the layout, design and architecture of the backend infrastructure (those servers which actually handle the requests) are insulated and protected from the outside; as far as the client is concerned, the reverse proxy server is the sole source of all content.
- Virtualmin (General)
- Proxy Paths - Is this Pro - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- It is not a bug. It moved into GPL with the most recent version.
- I wanted it to be more clear that you can use app servers and Docker/Podman in Virtualmin, and easier to explain how to do that. Since the way you use app servers or Docker/Podman is to proxy to it. So, there it is. Nobody can imagine it’s complicated anymore (but, they will anyway, as a lot of folks don’t know that the way you use Docker in any hosting deployment is to proxy to it).
- Proxy Paths is what’s new in GPL. You could always do proxying in GPL, it just wasn’t obvious how for users unfamiliar with proxying in Apache. You could, at any point in the past, setup a Docker container, or whatever app server, and setup proxy rules to make the app available on a path, but we’ve had so many people yell at us about not being able to run whatever random crap they want to run, that I wanted it to be as simple as we could make it, so people would stop saying, “You can’t use Docker with Virtualmin”. (They won’t stop saying it, but at least I tried.)
- You don’t need to delve into any of the other proxy-related stuff (unless you want to), you only need to setup Proxy Paths for your apps. None of those other forms are relevant to this new feature, and it shouldn’t require too much in the way of documentation to use it, though I think the naming of the options is weird…it should also have popup help, I’m not sure why I missed that it didn’t.
- Anyway, this is just about making a local app server or docker container visible to the world through a proxied path, in a very simple form. The Pro feature was always about making it simple, not about a thing that was impossible in GPL. I’ll try to make sure the next release has help files, though, so we’ve got some popup help for these options.
- Q: should there not be a one for http and one for https?
- A: No. http is dead. Don’t treat them differently, or you’ll break your website for some browsers. The only thing you should ever do with http is redirect it to https (and some browsers are going to do that automatically anyway).
- Basic Reverse Proxy? Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- Ok, so there are actually two different proxy sections under server configuration, ‘Edit Proxy Website’ and ‘Proxy Paths’.
- ‘Proxy Paths’ seems to invoke mod_proxy_balancer, which is actually something I would like to do in the future, but still can’t get it to do SSL.
- However ‘Edit Proxy Website’ is very straightforward and is working as one would expect so that’s good enough for now.
- Squid Proxy Server | Webmin
- This article explains what an HTTP or FTP proxy server is, and then explains how Webmin can be used to configure the popular Squid proxy server.
- An HTTP proxy server is basically a program that accepts requests from clients for URLs, fetches them on behalf of the client, and returns the results to the client. Proxies are used on networks where clients do not have direct access to the Internet but still need to be able to view web pages. A proxy is also used for caching commonly requested pages so that if more than one client wants to view the same page it only has to be downloaded once.
- Proxy Paths - Is this Pro - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- Proxy setting locations in Virtualmin
- Virtualmin --> Web Configuration --> Edit Proxy Website
- This form can be used to enable and configure the URL to which all requests to this virtual server's website are forwarded.
- This will proxy the whole website/domain.
- Virtualmin --> Web configuration --> Configure Website |Configure SSL Website --> Proxying
- This will allow you to configure Proxying of the website with more control than the above option.
- Virtualmin --> Web Configuration --> Proxy Paths
- Proxying allows you to map a URL path in a virtual server's website to one or more destination URLs. This is typically used to make Ruby on Rails applications served by multiple Mongrel instances available under a URL path in the server's website. It can also be used to make other webservers such as Tomcat available via a URL path on your website.
- For example, you might map the path /radiant to the URLs http://localhost:3001 and http://localhost:3002, which are the ports for two Mongrel instances serving the same application running on your Virtualmin system.
- This is now the preferred method to setup proxying.
- This has been moved from the Pro version.
- You can proxy the whole website or just individual directories
- Virtualmin --> Web Configuration --> Edit Proxy Website
- Virtualmin errors people had
- Behind reverse proxy: Failed Loading Terminal : Websocket connection error · Issue #557 · virtualmin/virtualmin-gpl · GitHub
- Q: When proxied via cloudflare, recent login ip just says 127.0.0.1 is there any way to get the actual IP. Cloudflare sends the IP in header CF-Connecting-IP
- A: Webmin --> Webmin Configuration --> IP Access Control --> Trust remote IP address provided by proxies?
- Lets Encrypt/Proxy website | Virtualmin
- Q: Can the lets encrypt support in virtualmin either exclude the challenge directory or temporary disable proxy website when renewing the LE certificates, as otherwise you have to disable proxy website, renew the Cert then re-enable it.
- A: Open Apache website config and add:
ProxyPass /.well-known/acme-challenge/ ! ProxyPassReverse /.well-known/acme-challenge/ !
- Virtualmin Reverse Proxy Redirects to IP Address Instead of Domain Name - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community - A worked example with useful insight.
- website proxy does not support websockets · Issue #305 · virtualmin/virtualmin-gpl · GitHub
- A: This is a discussion about websockets. Would the same issue would still exist even if you're using a secure websocket connection wss rather than ws?
- Q: The relevant code is here : https://github.com/virtualmin/virtualmin-gpl/blob/master/balancer-lib.pl#L57
- Behind reverse proxy: Failed Loading Terminal : Websocket connection error · Issue #557 · virtualmin/virtualmin-gpl · GitHub
- Virtualmin Reverse Proxy Tutorials
- Can I run Webmin or Usermin behind reverse proxy? - FAQs | Webmin
- How to install Discourse alongside Virtualmin - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- Covers both Apache and nginx
- Uses Unix Sockets
- node.js - Reverse proxy to serve local reactjs application on a static url with virtualmin - Stack Overflow
- General Reverse Proxy Tutorials
- How to Set Up a Reverse Proxy With Apache - Apache is a versatile web server which offers a full complement of supporting features, some of them via extensions.
- Discourse General
- WP Discourse – WordPress plugin | WordPress.org - This plugin allows you to use DiscThe WebSocket API (WebSockets) - Web APIs | MDN - The WebSocket API is an advanced technology that makes it possible to open a two-way interactive communication session between the user's browser and a server. With this API, you can send messages to a server and receive event-driven responses without having to poll the server for a reply.ourse as a community engine for your WordPress website.
- What forum software used by Virtualmin? - #2 by Joe - Site Feedback - Virtualmin Community
- It’s self-hosted Discourse 4. I’ve talked about it a bunch, including a couple/few News posts.
- It has only minor customizations, mostly to styles. We use a couple of plugins, Solved for marking questions solved, and Akismet (with a paid account) for spam filtering.
- As the admin/maintainer of it, I love it, and I think most users are pretty happy with it. It integrates relatively well with WordPress using an off-the-shelf plugin, Ilia added a bit of code so we can see people’s license information on their posts (since only Pro customers can request private support via PM, we like to be able to refer GPL users to the public forums without having to check their account in WordPress).
- Akismet is only average at catching spam, but the basic Discourse auto-moderation tools work really well. The built-in stuff catches far more spam than Akismet does, actually, but combined they add up to a very effective system.
- It’s also reasonably fast, though could always be faster.
- Compared to the old Drupal forums we cycled through (and the forums before it on Joomla and OpenACS), Discourse is a dream. I have very few complaints. The way it deals with Tags is incompatible with my brain, and last I checked it still had a bug that meant I can’t let others create Tags. But, that’s so minor, and none of the previous forums even had tags (and I had to do a lot more customization and bugfixes to the features we were using). Discourse is so remarkably better than any forum I’ve ever used (which is a lot of them; five or six for Virtualmin alone) it feels petty to complain about anything.
- Discourse Chat Overview
- Discourse Chat is now available. - Chat is here! Enable conversations in your community to flow between faster-paced chat and slower-paced discussions.
- An overview of features in Discourse Chat - users - Discourse Meta - You may have noticed Chat recently being added to your community, or here on Meta. In this topic we’ll take a look at the various features included in Chat, and how you can make the most of them!
- Discourse Chat Integration Plugin - plugin - Discourse Meta
- As this is an official plugin maintained by the Discourse team, support, bug, ux, and feature requests can be made in the respective categories here on Meta, and tagged with the appropriate plugin tag.
- discourse-chat-integration allows sending notifications about new Discourse posts to ‘group chats’ on a number of instant messaging platforms.
- Notifications can be triggered by new topics, new replies, messages to a group, or mentions of a group.
- Official Discourse Chat Plugin - plugin - Discourse Meta
- This plugin is bundled with Discourse core.
- There is no need to install this plugin separately.
- As mentioned in our initial announcement and most recent update, this plugin adds chat functionality to your Discourse so it can natively support both, long-form and short-form communication needs of your online community.
- Discourse Install Tutorial
- How Do I Install Discourse? | Discourse Docs - GitHub
- The only officially supported installs of Discourse are Docker based.
- You must have SSH access to a 64-bit Linux server with Docker support.
- We regret that we cannot support any other methods of installation including cpanel, plesk, webmin, etc.
- How Do I Install Discourse? | Discourse Docs - GitHub
- Discourse proxying setup errors
- Discourse behind reverse proxy and https - installation - Discourse Meta
- I’m trying to setup Discourse behind my Apache reverse proxy but I can’t get it working properly with https.
- I’ve had a lot of problems getting this far. Right now I have Discourse on a server and an Apache server in front of it acting as a reverse proxy.
- Discourse behind reverse proxy and https - installation - Discourse Meta
- Docker vs Podman
- Virtualmin app server plugin · Issue #626 · virtualmin/virtualmin-gpl · GitHub
- Yeah, podman is generally considered recommended across the Linux distro landscape, because Docker hasn't been super friendly to Open Source. And, technically, podman is superior on several fronts (no daemon BS, not tied to any commercial cloud services, uses a bunch of more modern Linux security features). But, and this is a big but, nobody knows the name "podman", and everybody wants "Docker support". So, I guess we need to detect if the user has the docker tools installed (from third party sources, probably) and allow use of those instead. Because podman doesn't use a daemon, it isn't entirely compatible with Docker on the same system; so, even though they have almost identical command line options and use the same Dockerfile syntax, if you list containers with podman you won't see the ones Docker is managing and vice versa, AFAIK, and you can't stop/start/pull/push/etc. across the two. I prefer podman, and I hope most users who don't know the difference will just accept it.
- Virtualmin app server plugin · Issue #626 · virtualmin/virtualmin-gpl · GitHub
- WebSockets
- General Information
- What is web socket and how it is different from the HTTP? - GeeksforGeeks - An excellent article to explain this technology with simple diagrams.
- WebSocket - Wikipedia
- WebSocket explained - What is 'WebSocket'? Discover how to master WebSocket, with free examples and code snippets.
- Introducing WebSockets - Bringing Sockets to the Web | Articles | web.dev
- WebSockets handbook - WebSockets revolutionized the web, turning clunky, slow real-time interactions into sleek, low-latency experiences, making them the go-to for dynamic, user-friendly applications.
- What are WebSockets? | Web Security Academy - WebSockets are a bi-directional, full duplex communications protocol initiated over HTTP. They are commonly used in modern web applications for streaming ...
- API and programming
- The WebSocket API (WebSockets) - Web APIs | MDN - The WebSocket API is an advanced technology that makes it possible to open a two-way interactive communication session between the user's browser and a server. With this API, you can send messages to a server and receive event-driven responses without having to poll the server for a reply.
- WebSocket - Web APIs | MDN - The WebSocket object provides the API for creating and managing a WebSocket connection to a server, as well as for sending and receiving data on the connection.
- WebSocket | javascript.info - No meta description
- General Information
What is CGI, FastCGI and PHP-FPM
I have struggled for years to understand what the point of the cgi-bin folder was for which then lead me to research into the whole area and what was the point of this technology.
What is CGI?
- CGI stands for 'Common Gateway Interface'
- CGI is a standard for external gateway programs to interface with information servers such as HTTP servers.
- Or in other words, programs in other languages can be used and utilised via HTTP requests.
- A way to run a server side script (PHP, Perl, Python,...) when a HTTP request comes.
- This allows Binaries and scripts of other programming languages to be run such as Python and C programs.
- Currently maintained by the NCSA (National Center of Supercomputing Applications).
- CGI has been around long before PHP.
What is the purpose of CGI?
CGI allows the use of scripts and binaries from many other languages and the benefit of this are:
- You can utilise these languages and their inherent feature sets directly from a website.
- Different languages have different abilities
- Programming is not limited to the web-based languages.
`cgi-bin` folder, why do I have this on my web server?
This is the only folder allowed on your server where you can runs CGI applications and is usually created when you install the package `php-cgi`.
How Does it work?
- Place scripts or binaries in the folder /cgi-bin/ with the file extension .cgi, other might work such as .py but I have not tried this.
- Run the script accessing the relevant URL such as https://example.com/cgi-bin/mytest.cgi
- The Script:
- is started
- reads the Stdin (Standard in) and Environmental variables as required
- processes the data
- outputs the response to the Stdout (Standard Out)
- is terminated
- The webserver returns the Stdout as the http response
- The file extension .cgi can be changed if required when setting up the server.
- The .cgi files can be either scripts or binaries.
- A CGI can only external interact externally as follows (but this does not include what its internal routines do):
- Read the Stdin
- Read the Environmental Variables
- Output the Stdout
- When a CGI App is started a single process for it is created and when it has finished executing the process is terminated removing it from RAM etc.
- You can easily upgrade a CGI script by just changing the CGI file.
Running PHP via CGI, FastCGI, PHP-FPM
PHP can be run via any of the following wrappers but this is not the same for CGI Apps
- mod_php
- Old, insecure and slow.
- Never use this.
- This is the original way to run PHP and is here for reference only.
- CGI
- PHP runs as a CGI App
- Opens a single process for each request, runs it and then when finished, is immediately closed.
- FastCGI
- PHP runs as a FastCGI App
- Maintains a pool of workers for running scripts
- FastCGI can use a single persistent process which handles many requests over its lifetime.
- PHP-FPM
- FastCGI Process Manager (FPM)
- FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) is a primary PHP FastCGI implementation containing some features (mostly) useful for heavy-loaded sites.
- Only runs PHP, does not allow for traditional CGI or FastCGI apps.
- This now the recommend method for PHP and is by far the fastest.
- This is know as PHP-FPM rather than just FPM because it only runs PHP.
- The Linux package name is php-fpm
Notes
- CGI is one process for each request and has large overheads.
- FastCGI
- uses a persistent process and requires more settings for this.
- is a bit more complicated because the processes start up at the very beginning of the server.
- FastCGI keeps a pool of scripts running whereas CGI opens a single process, runs it and then when finished is immediately closed. Because the processes are always open there is no overhead of starting up the process any more.
- CGI and FastCGI Apps are not the same, but are similar. FastCGI Apps need extra code to handle persistent states.
- You can run a CGI App under FastCGI but you need a wrapper app.
- CGI and FastCGI are almost always run from the cgi-bin folder
- The file extensions of .cgi and .fcgi are use as appropriate
CGI and FastCGI are getting replaced
These technologies are getting or already have been replaced with proxying and dedicated server modules such as mod_perl and mod_python.
Most programming languages offer their own dedicated servers so it makes sense to have those do the relevant work and then return the results to your web server. Proxying allows a web server to do this invisibly just as CGI and FastCGI have done in the past and allows the resource hit to be offloaded.
Proxying is configured in your Apache Config files.
What about PHP-FPM?
This technology is dedicated to running PHP, and in a sense is probably now a dedicated engine for PHP only.
I cant see this going away anytime soon but it will only ever run PHP.
Virtualmin
I have put my Virtualmin notes here as they are more relevant to this niche feature.
- Virtualmin only supports CGI Apps out of the box. You can manually add FastCGI support.
- Virtualmin installs mod_fcgi, because it is a dependency of the php extension php-fpm which is installed by default.
- mod_fcgi requires you to set the correct handlers in the Apache conf and these are not set by Virtualmin.
- Virtualmin supports CGI Apps out of the box as and has GUI pages for this.
- Your PHP mode does not affect the running of CGI Apps, they are separate.
- Does the php-cgi module include cgi and fastcgi
- no, php-fpm includes FastCGI and PHP-FPM
- php-cgi includes only CGI
- GUI Locations
- Webmin --> Servers --> Apache Webserver --> Global Configuration --> CGI Programs
- Webmin --> Servers --> Apache Webserver --> Existing virtual hosts --> select virtual server --> CGI Programs
- Virtualmin --> Web configuration --> (Configure SSL Website | Configure Website) --> CGI Programs
- Changing the PHP mode does not change whether the server is going to run CGI or FastCGI Apps, it only alters how PHP s run.
- Should ExecCGI be removed from the public_html folder apache directive? - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
Q:- My understanding is that ExecCGI is the command that can enable or disable the running of a CGI.
- In the code below it looks like the apache directive is allowng the enabling of CGI Apps in the root of the public_html folder.
- So my question is, should ExecCGI be removed from the public_html folder or have I missed something, perhaps this is required for PHP to be run?
<Directory /home/example/public_html> Options -Indexes +IncludesNOEXEC +SymLinksIfOwnerMatch +ExecCGI Require all granted AllowOverride All Options=ExecCGI,Includes,IncludesNOEXEC,Indexes,MultiViews,SymLinksIfOwnerMatch </Directory> <Directory /home/example/cgi-bin> Require all granted AllowOverride All Options=ExecCGI,Includes,IncludesNOEXEC,Indexes,MultiViews,SymLinksIfOwnerMatch </Directory>
A:AllowOverridemeans.htaccesscan override the default configuration. The default configuration does not haveExecCGI.- You can, of course remove it, if you don’t want to allow that to be overriden by
.htaccess. Historically it was pretty common to run CGI scripts in public_html, too, but much less so these days. - Presumably you allow execution of PHP in
public_html, if you’ve got any web apps installed. So, if a remote attacker gains ability to write topublic_html, it’s already over. There would be no need to modify.htaccessto run scripts, they’d just drop a PHP shell inpublic_htmland be done.
- Does Virtualmin support FastCGI Apps - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- Q: I know Virtualmin supports standard CGI Apps, but does it support FastCGI Apps?
- A:
- Apache (and nginx) support FastCGI. Virtualmin isn’t your web server.
- It generally needs some app-specific configuration, which kinda depends on what language(s) and app server(s) you’re using and how you’re using them. The things Virtualmin knows how to configure with FastCGI it does so (Install Scripts might use FastCGI, for example, and that will get configured). There is no fcgi-bin directory, though, by default, so there’s nowhere you can just drop a FastCGI application and expect it to magically run.
- The necessary Apache module (mod_fcgid) is installed by default, though. mod_fcgid - FastCGI interface module for Apache 2 - The Apache HTTP Server Project
- Best selection of PHP extensions - #13 by Jamie - Virtualmin - Virtualmin Community
- php-fpm is independent of running PHP apps via fcgid+suexec (which uses php-cgi and predates the existence of php-fpm). FPM is an application server for PHP apps that speaks the FastCGI protocol. FastCGI is a protocol, not any specific implementation, and there are several ways to run Apache+PHP apps using the FastCGI protocol.
- You should use FPM, if you can. The implementation is much simpler (from the user perspective), it is much more actively maintained, it is more efficient, etc. And, it provides the same security benefits of suexec.
- Can I remove the system default CGI PHP
- php-cgi has nothing to do with the virtualmin miniserv which runs on Perl.
- The CLI version of PHP has nothing to do with CGI.
- Can I safely remove CGI on my alternative php versions?
- yes
Links
- CGI
- The Magic of cgi-bin - YouTube | Philip Bohun
- An introduction to cgi and why you might want to think about using for your web project.
- This would be the first Video I watched.
- W3 Security FAQ: CGI (Server) Scripts - Discusses security issues with CGI scripts.
- Definition of CGI script | PCMag
- What does CGI script actually mean? Find out inside PCMag's comprehensive tech and computer-related encyclopedia.
- Although CGI scripts are still used, PHP and other languages are more popular. Active Server Pages (ASPs), JavaServer Pages (JSPs) and Java servlets have also been used to tie a request to a database. See PHP, ASP, JSP, servlet and FastCGI.
- Apache Tutorial: Dynamic Content with CGI - Apache HTTP Server Version 2.4 - This document will be an introduction to setting up CGI on your Apache web server, and getting started writing CGI programs.
- The Magic of cgi-bin - YouTube | Philip Bohun
- FastCGI
- General
- FastCGI.com Archives
- This is the Github FastCGI Archives of FastCGI.com site.
- Since fastcgi.com is not available anymore (last backup on wayback machine are at 20/03/2016), I (mcarbonneaux) created this repository and linked website fastcgi-archives.github.io to host the FastCGI information backup.
- FastCGI A High-Performance Web Server Interface | FastCGI.com Archives - This is Technical White Paper.
- Understanding FastCGI Application Performance FastCGI | FastCGI.com Archives - Just how fast is FastCGI? How does the performance of a FastCGI application compare with the performance of the same application implemented using a Web server API?
- Guides/FastCGI - J Wiki - J can be used for FastCGI programming. Here are some considerations and examples.
- FastCGI - Wikipedia
- FastCGI — The Forgotten Treasure - This paper shows developers how high-performance web applications can be implemented quite easily using the FastCGI interface and C++. After a brief introduction to the FastCGI interface, a generic C++ framework for web-based applications using FastCGI will be discussed, including the advantages and disadvantages of this approach.
- FastCGI.com Archives
- Apache mod_fcgid
- mod_fcgid - FastCGI interface module for Apache 2 - The Apache HTTP Server Project - mod_fcgid is a high performance alternative to mod_cgi or mod_cgid, which starts a sufficient number instances of the CGI program to handle concurrent requests, and these programs remain running to handle further incoming requests. It is favored by the PHP developers, for example, as a preferred alternative to running mod_php in-process, delivering very similar performance.
- mod_fcgid - Apache HTTP Server Version 2.5 - Provides for execution of FastCGI applications
- Installing mod_fcgi
- How to Install and Configure FastCGI and PHP-FPM on CentOS 8 | Linode Docs - This guide will show you how to install and configure the mod_fcgid and PHP-FPM protocols for dynamic content generation and processing using Apache on CentOS 8.
- mod_fcgi htacces directives
- CGI | Virtualmin
- This is what my new .conf file looks like (added +ExecCGI + MultiViews and added .cgi Handler)
Options -Indexes +IncludesNOEXEC +FollowSymLinks +ExecCGI +Multiviews allow from all AllowOverride All AddHandler fcgid-script .php AddHandler fcgid-script .php5 AddHandler cgi-script .cgi FCGIWrapper /home/domain/fcgi-bin/php5.fcgi .php FCGIWrapper /home/domain/fcgi-bin/php5.fcgi .php5
- This is what my new .conf file looks like (added +ExecCGI + MultiViews and added .cgi Handler)
- .htaccess - Hiding fcgi script file name from url in django app hosted with fastcgi and apache - Stack Overflow
- CGI | Virtualmin
- General
- CGI vs FastCGI vs PHP-FPM
- How does Fast CGI work? - YouTube - A simple video but explains the difference well
- Fast CGI - YouTube | Philip Bohun
- A quick video describing fast CGI, how it differs from CGI, as well as its pros and cons.
- PHP: CGI and command line setups - Manual | php.net
- By default, PHP is built as both a CLI and CGI program, which can be used for CGI processing.
- PHP CGI and FPM, what are they? - Stack Overflow
- PHP: FastCGI Process Manager (FPM) - Manual | php.net
- php fpm - Differences and dis/advanages between: Fast-CGI, CGI, Mod-PHP, SuPHP, PHP-FPM - Server Fault
- CGI vs FastCGI vs PHP-FPM. CGI: CGI stands for Common Gateway | by Miladev95 | Medium - CGI:CGI stands for Common Gateway Interface.- It is a standard protocol that defines how web servers can interact with external
- CGI
- While CGI was revolutionary in its time and enabled dynamic web content, it has certain limitations, including performance overhead and scalability issues. As a result, modern web development has largely moved away from CGI in favour of more efficient and scalable server-side scripting technologies like PHP, Node.js, and various application frameworks.
- Today, CGI is mostly used in specific cases where compatibility with legacy systems or specialized environments is required. For general-purpose web development, more efficient alternatives are preferred.
- In summary, CGI is the simplest and oldest method for executing server-side scripts but suffers from performance overhead. FastCGI improves upon CGI by introducing a persistent process pool, resulting in better performance. PHP-FPM, on the other hand, is a specific FastCGI implementation tailored for PHP execution, providing superior performance, scalability, and security for serving PHP applications. For modern PHP applications, PHP-FPM is the recommended method for handling dynamic content.
- FastCGI
- FastCGI is widely used in web server configurations to handle dynamic content generation efficiently. Popular web servers like Nginx and Apache support FastCGI, making it a standard choice for hosting dynamic web applications written in languages like PHP, Python, Ruby, and more.
- In summary, FastCGI is an extension of CGI that significantly improves the performance and resource utilization of web applications by employing a persistent application process pool to handle incoming requests.
- PHP-FPM
- Overall, PHP-FPM is a valuable tool for PHP application deployment, providing improved performance, security, and scalability for serving PHP-driven web applications.
- In summary, CGI is the simplest and oldest method for executing server-side scripts but suffers from performance overhead. FastCGI improves upon CGI by introducing a persistent process pool, resulting in better performance. PHP-FPM, on the other hand, is a specific FastCGI implementation tailored for PHP execution, providing superior performance, scalability, and security for serving PHP applications. For modern PHP applications, PHP-FPM is the recommended method for handling dynamic content.
- CGI
- What are CGI and fast CGI - This is part of the Semicolon&Sons Code Diary - consisting of lessons learned on the job. You're in the web-development category.
- Which PHP mode? Apache vs CGI vs FastCGI - Layershift Blog - There are multiple ways to execute PHP scripts on a web server. We’re often asked about the difference between these modes, so here it is!
- Difference between PHP-CGI and PHP-FPM | BaseZap - When running PHP through the web server, there are two distinct options: running it using PHP's CGI, or running it as a PHP-FPM, for the web server.
- What is difference between PHP cli and PHP cgi? - Stack Overflow
- Basically it's a way to run a server side script (PHP, Perl, Python,...) when a HTTP request comes.
- Excellent descriptions.
- CGI, FastCGI and PHP-FPM - Some basic questions - Help! (Home for newbies) - Virtualmin Community
- Q: Is running CGI Apps now considered an old way of doing things?
- A: Generally, yes. For large applications, having them load all their dependencies on every run is wildly inefficient. For tiny little apps that don’t load a bunch of extra junk, it may be fine. e.g. if you just need to serve out one tiny API endpoint and you can write a Perl/Python/Ruby/PHP script that runs in a few milliseconds, then it may make sense to use CGI (but an app server probably isn’t notably worse than CGI in those cases, either…it’d be about balancing CPU vs. memory usage).
- Q: FastCGI - allows CGI Apps to be run in cgi-bin
- A: No. FastCGI can not run CGI scripts. It requires applications built to communicate via the FastCGI protocol, which is not the CGI protocol. A CGI script is not a FastCGI script without a wrapper. We provide a wrapper (fcgiwrap), so you can run CGI applications on systems that don’t have suexec available, but it does not mean FastCGI is running CGI scripts. fcgiwrap runs CGI scripts and communicates with the web server via the FastCGI protocol. It is the application server in this context.
- Q: But, this is a bit misleading: “Virtualmin only supports CGI Apps out of the box. You can manually add FastcGI support.”
- A:
- Virtualmin supports, with full UI support, PHP apps via many execution modes, including FastCGI, and multiple versions of PHP (when installed). Virtualmin also supports setting up proxy rules to any other kind of application server (many app servers do not use FastCGI, they just use HTTP, and that is the most common way to run most apps other than PHP at this point in history). FastCGI is on the way out, too.
- We brought proxy paths support from Pro into GPL just recently to ease that use case. And Virtualmin Pro is about to get app server and container-based app support (where it has some awareness of the app server or docker/podman and configures the proxy rules automatically).
- So, nearly any way you want to run apps in Virtualmin is very easy to do.
- Old Technology
- How to run PERL scripts - #7 by Joe - Help! (Home for newbies) - Virtualmin Community
- You should be moving your apps to a modern execution mode. Plack is probably the easiest way to migrate CGI Perl scripts to something modern. https://plackperl.org/
- Q: Do I need Plack, if I use Apache?
- A:
- CGI is the slowest way to run a web app, so the web server is completely irrelevant in your deployment, so I recommend you use the one that is most commonly used for CGI scripts, which is Apache.
- You don’t need Plack. I was offering you a solution for improving the way you’re executing your apps. Plack is a low-friction path from CGI to running apps under a long-running Perl app server (this saves significant startup time for each request). If you use Plack, you no longer need CGI script support in your web server or a wrapper (because it is the wrapper and it provides a fastcgi interface you can proxy to). If you were to use Plack, you would be able to use nginx. Performance still wouldn’t matter, but at that point I would recommend whichever web server you’re most comfortable with rather than having a relatively strong opinion that Apache is the better choice.
- I don’t know anything about the app you’re running; there’s nothing I can tell you about it. But, I know how CGI works with Apache and how it doesn’t work with nginx (unless you wrap it). So, if you’re running CGI scripts, you should go the path of least resistance, unless you have a good reason to do otherwise (performance is not a good reason, because the web server cannot save you from CGIs relative poor performance).
- How to run PERL scripts - #7 by Joe - Help! (Home for newbies) - Virtualmin Community
- Programming
- Simple CGI and Apache examples on Ubuntu Linux - Linux Tutorials - Learn Linux Configuration - Simple CGI and Apache examples on Ubuntu Linux
- Create first cgi script - YouTube | Greg Reichelt - Nice and easy to follow.
- CGI on C Programming - YouTube | beci67 - A multipart tutorial on making a simple C program and the deploying it to a CGI server. It starts of explaining the fundamental technologies.
- Python - CGI Programming - YouTube | Tutorialpoint - Very basic description.
- Python CGI Programming Tutorial | How to run CGI Programs in Python | Python Training | Edureka - YouTube - This Edureka video on 'CGI Programming In Python' will help you understand how we can write and Execute CGI scripts in Python.
- cgi — Common Gateway Interface support — Python 3.11.8 documentation
- depreceated in python
- CGI Programming with Perl
- Useful Examples
- FastCGI - Mythic Beasts
- A single script written in both CGI and FastCGI so you can see the differences.
- This is the most useful article I have found. It explains a lot.
- FastCGI — MapServer 8.0.1 documentation - An example of a FastCGI App and all of the relevant settings and procedures to get it running.
- PHP FastCGI Example | NGINX - How to configure NGINX with PHP FastCGI Process Manager.
- Remember FastCGI? - a moderately technical blog
- Alternative function for deprecated cgi - Python Help - Discussions on Python.org
- Simple CGI and Apache examples on Ubuntu Linux - Linux Tutorials - Learn Linux Configuration
- Simple CGI and Apache examples on Ubuntu Linux
- CGI works with multiple languages, but for now we start with bash shell.
- Examples for Bash, Perl, Python, C, C++
- FastCGI - Mythic Beasts
- Run CGI Apps on FastCGI
- fcgiwrap
- simple server to run CGI applications over FastCGI
- fcgiwrap is a simple server for running CGI applications over FastCGI.
- Its goal is to provide clean CGI support to the nginx webserver, although can be used with others.
- fcgiwrap is lightweight and has no configuration, making it possible to use the same pool to run different sites.
- How to execute CGI scripts using fcgiwrap | sleeplessbeastie's notes - I am an enthusiast of the uWSGI project. You are still not limited to it as you can use fcgiwrap, a very lightweight and straightforward FastCGI wrapper for CGI scripts that do not require additional configuration.
- GitHub - leejo/cgi-fast
- The new home for CGI::Fast, removing it from the original CGI.pm distribution - leejo/cgi-fast
- CGI::Fast is a subclass of the CGI object created by CGI.pm. It is specialized to work with the FCGI module, which greatly speeds up CGI scripts by turning them into persistently running server processes. Scripts that perform time-consuming initialization processes, such as loading large modules or opening persistent database connections, will see large performance improvements.
- FcgiWrap - Community Help Wiki
- fcgiwrap is a simple server for running CGI applications over FastCGI. It hopes to provide clean CGI support to Nginx (and other web servers that may need it).
- fcgiwrap can be used together with Nginx to serve CGI or Perl scripts (.cgi).
- How to execute CGI scripts using fcgiwrap | sleeplessbeastie's notes - I am an enthusiast of the uWSGI project. You are still not limited to it as you can use fcgiwrap, a very lightweight and straightforward FastCGI wrapper for CGI scripts that do not require additional configuration.
- fcgiwrap
- Alternatives
- ipc - Are there alternatives to CGI (and do I really need one)? - Stack Overflow
- Even under moderate loads, CGI is a pretty unscalable beast. FastCGI is an option, but you'll probably also find a mod_XXXX package where XXXX is the name of your language. There's a mod for ruby, perl, and python for instance and probably a fair few others.
- Is CGI still a thing? Which alternatives are there? | Reddit
- I stumbled upon CGI and tried to set it up on a server – provided by uberspace.de – but failed. Their support told me that CGI isn’t too relevant for them anymore, as basically any language has its own webserver nowadays and that I should just run the one I want as a service listening to a specified port
- CGI was a way of running a specific script through an http request.
- ipc - Are there alternatives to CGI (and do I really need one)? - Stack Overflow
