Items filtered by date: December 2014
My Diet and Health Regime Notes
TL;DR I am not a doctor. These are notes for myself that other people might find useful. Your health and body are your problem and if you have any health issues consult your doctor, not me.
I have had some general health issues which are probably due to bad diet and lifestyle. The advise I got from a Urinary Consultant was limited and in one particular case wrong, so I have decided to figure this out myself and write it up here for a reference.
My Regime
TL;DR
- For a Man
- Reduce Visceral Fat
- Reduced Cortisol Levels
Food
Timetable
| Time | Food | Fluids | Supplements | Exercise | Notes |
| 00:00 | |||||
| 01:00 | |||||
| 02:00 | |||||
| 03:00 | |||||
| 04:00 | |||||
| 05:00 | |||||
| 06:00 | |||||
| 07:00 | Breakfast Meal |
|
|
NB: Keep heart in fat burn zone |
|
| 08:00 | |||||
| 09:00 | |||||
| 10:00 | |||||
| 11:00 | |||||
| 12:00 | Meal Replacement / Protein thing |
|
|||
| 13:00 | |||||
| 14:00 | |||||
| 15:00 | |||||
| 16:00 | |||||
| 17:00 | Normal Meal |
|
|||
| 18:00 | |||||
| 19:00 | Stop Eating | Stop Drinking |
|
||
| 20:00 | |||||
| 21:00 | |||||
| 22:00 | |||||
| 23.00 |
|
|
- = Sleep
Meals I can eat
- Breakfast
- Meal 1
- Steak piece (butcher) and 2 x scrambled eggs with a little milk
- Meal 1
- Normal Meals
- Meal 1
- Pickled Onions
- Iceberg Lettuce
- 2 x Butcher's pork sausages
- Spoonful of cheese
- Meal 2
- Pickled Onions
- 2 x Fried eggs
- Steam mixed vegetables
- Meal 1
Notes
- General
- Total water per day = 2.5l - 5.0l (i am working on this)
- 1g of protein per pound of ideal weight
- Once you have diet sorted, fast 1 day a week (TBA), you must be doing the diet for a while and it be your routine.
- Do not buy processed food.
- No processed, get meat from a butcher that has not been processed
- Most processed foods tend to be high load GI and not good for you because all of the fibre and other stuff is removed.
- Steam, not Boil
- Grill rather than Fry
- Low Glysomic rate food is better?
- High Protein Foods: 16 Foods for High Protein Meals - Research shows it's really important to eat enough protein. These high protein foods can help you lose weight, gain muscle, and feel great.
- Meal target types
- Breakfast = protein
- Dinner = Protein + carbs
- Food for Exercise
- Before: Carbs
- After: Protein
Diet Suggestions (to sort)
These are just some a collection of ideas.
- My Diet suggestions ?
- 3 lites water a day
- No carb
- No sugar
- Smaller portions (trick yourself by using a smaller plate at the same time)
- Strength sensei
- No fruit ?
- Supplements
- My Diet suggestions 2 ?
- Breakfast
- 2 x eggs that are omega3 enriched (at least free range) (3 eggs a day is safe)(this guy eats 3 -6
- veggies
- some protein (possibly)
- probably better in that steam achine of mine with less destruction
- Notes
- low carb diet seems to be a good thing
- more protein in diet causes more metabolism of it burning up my calories
- eggs are not bad, maybe only with a high carb diet.
- more protein in diet tend to remove belly fat (see articles)
- eating six eggs 3 x 3 (breakfast/dinner/tea) not a bad thing
- hard boiled eggs for snacks
- eggs are a super food
- eggs with omega3 in and/pasture from fed chickens is better
- Whole eggs are among the healthiest and most nutritious foods on the planet.
- Brussels sprouts are really high in protein
- Eggs
- They are loaded with vitamins, minerals, healthy fats, eye-protecting antioxidants and brain nutrients that most people don’t get enough of.
- Whole eggs are high in protein, but egg whites are almost pure protein.
- Protein content: 35% of calories in a whole egg. 1 large egg contains 6 grams of protein, with 78 calories
- Breakfast
- Specific Foods
- Eggs
- Egg, whole, cooked, hard-boiled | USDA FoodData Central - USDA FoodData Central produces thorough resources for navigating and understanding nutritional info to support dietary choices and nutritional analysis.
- how much protein in an egg | Google Search
- Nice lookup table
- Egg, boiled: 13% protein
- Egg, fried: 14% protein
- Egg Nutrition - Official UK Information | Egg info
- Eggs are a natural source of many nutrients including high quality protein, vitamins and minerals. Including B2 (riboflavin) and B12. Find out more about the nutritional value of eggs.
- Protein in egg | How much protein in an egg | Egg info
- On average, a medium-size egg contains around 6.4 grams of protein which makes up around 12.6% of the overall edible portion. Find out more about protein in eggs.
- There are on average between 5.2 and 7.5 grams of protein in an egg, depending on its size. For information on all sizes see below.
- Eggs and a balanced diet | Egg Recipes | Egg info
- Our bodies require a broad range of different nutrients to stay healthy - these nutrients ensure we are able to carry out our basic functions to keep alive and well.
- A healthy diet can be achieved by consuming foods in their correct proportions and quantities which provide us with all the vital nutrients we need.
- The Eatwell plate illustrates how to get your proportions right for a healthy diet.
- How Many Eggs Can You Eat in a Day? The Surprising Truth - YouTube
- For many decades, people have been advised to limit their consumption of eggs, because the yolk is high in cholesterol.
- It was thought that if you ate cholesterol, it would raise cholesterol in the blood and contribute to heart disease... That was wrong.
- Eggs
Gym
Timetable
| Day | Time | Exercise | Notes |
| Monday | |||
| Tuesday | |||
| Wednesday | |||
| Thursday | |||
| Friday | |||
| Saturday | |||
| Sunday |
Exercises
- Treadmill
- 10 Mins
- Pec Fly / Rear Deltoid
- 3 x 10
- This is the joysticks one
- do both far back where i pull in, and close together where I push out
- The leg one / Leg Curl
- 3 x 10
- push and pull
- Seated Row
- 3 x 10
- Pad in chest
- Start with arms straight with a little tensions
- keep arms in tight on my chest and back
- Biceps / Triceps
- 3 x 10
- Dog Rope
- arms at 90 and pull down keeping shoulders straight
- keep arms in tight on my chest and back
- Abdominal / Low Back
- 3 x 10
- Hug the roller
- Keep back straight
- Lat Pull Down
- 3 x 10
- ones with the thumb issue
- keep back straight
- this one gets me
- Multipress
- 3 x 10
- Chest press / incline press / shoulder press
- This is too nar at the minute
- This is the lifting and pushing one
- Assisted Pull Ups
- 3 x 10
- I just sank on this one
- not for me yet
Notes
- Getting down on toes and forearms exercises most muscles in the body
Recommended Daily Nutrient Intake
Recommend intakes of various stuff.
Vitamins and Minerals
| Vitamin / Mineral | Nutrient Reference Intake (NRV) | Notes |
| Beta-Carotene |
|
|
| Calcium |
|
|
| Chromium |
|
|
| Copper |
|
|
| Iodine |
|
|
| Iron |
|
|
| Magnesium |
|
|
| Manganese |
|
|
| Molybdenum |
|
|
| Omega 3 |
|
|
| Pantothenic Acid |
|
|
| Phosphorus |
|
|
| Potassium |
|
|
| Selenium |
|
|
| Sodium Chloride (salt) |
|
|
| Vitamin A |
|
|
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) |
|
|
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) |
|
|
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) |
|
|
| Vitamin B6 |
|
|
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) |
|
|
| Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid / Folate) |
|
|
| Vitamin B12 |
|
|
| Vitamin C |
|
|
| Vitamin D |
|
|
| Vitamin E |
|
|
| Vitamin K1 |
|
|
| Zinc |
|
|
Vitamin Bottle values might be different to the NHS ones because:
- They are rounded.
- They are European values.
- The NHS values on the article are out of date.
Life Style Nutrients
These are not needed for a normal life but aid in improving it.
| Nutrient | Recommended Intake (RI) | Potential Benefits for | Notes |
| Ashwagandha |
|
|
|
| Creatine |
|
|
|
| L-Theanine |
|
|
|
| Melatonin |
|
|
|
| Modafinil |
|
|
|
Typical Values / Food Groups
The different types of food you should eat as part of a healthy diet
| Reference Intake of an average adult. | |
| Typical Values | Reference Intake (RI) |
| Energy | 8,400kJ / 2000kcal |
| Fat | 70g |
| of which saturates | 20g |
| Carbohydrates | 260g |
| of which sugars | 90g |
| Fibre | - |
| Protein | 50g |
| Salt | 6g |
Units and Measures
- General
- SI multiples - Kilogram - Wikipedia - Gives the various names and symbols of the different measurements.
- Microgram - Wikipedia
- The abbreviation
mcgis preferred for medical information in the United States (US), but prescription writing guidance in the United Kingdom advises that "microgram" should not be abbreviated.
- The abbreviation
- RNI vs DRV vs RDA vs NRV: Nutrient Intakes Explained - DRV, RDA, NRV or RNI? Nutritionist Sarah Dumont-Gale explains the confusing terminology surrounding dietary recommendations and nutrient intakes.
- Traditional Measurements
g(Gram)- 1g = 1000mg = 1000000μg
mg(Milligram)- 0.001g = 1mg = 1000μg
μg / mcg(Microgram)- 0.000001g = 0.001mg = 1μg
- Types
RI= Reference IntakeNRV= Nutrition Reference Value
- International Unit (IU)
- To convert international units (IU) to grams (g), you need to know the specific conversion factor for the substance you are measuring.
- International unit - Wikipedia
- In pharmacology, the international unit (IU) is a unit of measurement for the effect or biological activity of a substance, for the purpose of easier comparison across similar forms of substances. International units are used to quantify vitamins and biologics (hormones, some medications, vaccines, blood products and similar biologically active substances).
- International units as used in pharmacology are not part of the International System of Units (SI)
- What Is an International Unit (IU) Measurement? - Biology Insights - Learn what the International Unit (IU) is and how this standard ensures consistent biological activity and potency for essential substances globally.
- International units converter (between IU and g/mg/mcg) — MY PHARMA TOOLS - Easily convert between IU and g/mg/mcg
- RE, α-TE, and N
- When you see RE, α-TE, and NE on nutrition labels or in dietary tables, they are standardised units used to express vitamin activity, not just raw weight. Here’s what each means:
- RE – Retinol Equivalents
- Used for Vitamin A.
- Vitamin A comes in different forms:
- Preformed vitamin A (retinol) from animal foods
- Provitamin A carotenoids (like beta-carotene) from plant foods
- Because these forms have different biological activity, they’re converted into a common unit: Retinol Equivalents (RE).
- Classic conversion (older system):
- 1 µg retinol = 1 µg RE
- 6 µg beta-carotene ≈ 1 µg RE
- 12 µg other provitamin A carotenoids ≈ 1 µg RE
- Note: Many countries now use RAE (Retinol Activity Equivalents) instead of RE, which has slightly different conversion factors.
- α-TE – Alpha-Tocopherol Equivalents
- Used for Vitamin E.
- Vitamin E exists in multiple forms (tocopherols and tocotrienols), but alpha-tocopherol is the most biologically active form in humans.
- So vitamin E content is expressed as α-TE, meaning the amount adjusted to reflect the activity of alpha-tocopherol.
- 1 mg alpha-tocopherol = 1 mg α-TE
- Other forms of vitamin E are converted into alpha-tocopherol equivalents based on their biological potency.
- NE – Niacin Equivalents
- Used for Vitamin B3 (Niacin).
- Niacin can come from:
- Niacin (nicotinic acid)
- Nicotinamide
- Tryptophan (an amino acid the body can convert into niacin)
- to account for this, it’s expressed as Niacin Equivalents (NE).
- Conversion:
- 1 mg niacin = 1 mg NE
- 60 mg tryptophan ≈ 1 mg NE
Health Issues and Causes
Bad diet and lifestyle can lead to these issues.
- Cause of Fatigue
- Too much exercise
- Electrolyte depletion
- Not enough energy (usually in the form of carbohydrates)
- Dehydration
- Causes of frequent Urination
- Drinking to much on one go - The kidneys will try and get rid of most of the liquid to regain balance.
- Cortisol presence during sleep cycle
- Too much Caffeine
- Diabetes
- Hypercalcemia (lack of calcium)
- Constant Pee-ing at night can be caused by
- drinking to much before bed (i.e. after 18.00)
- The body is trying to get rid of excess sugar
- What compulsive peeing REALLY means - YouTube | Foot Doc Dana
- Can be linked to OCD or anxiety.
- Causes of getting up through the night (not always urination)
- Cortisol presence during sleep cycle
- Drinking after 18.00
- not leaving 3-4 hours after last meal before going to bed.
- Night Eating Syndrome (NES)
- Investigate
- Why when I drink water does it go straight through me
- Why Does Water Go Straight Through Me? - Biology Insights - Ever wonder why water seems to go straight through you? Discover how your body efficiently processes hydration and when to be concerned.
- Caffeine is diuretic
- Rapid consumption of a large volume of water can also trigger a quicker excretory response. The body’s systems respond promptly to large fluid inputs to prevent imbalances. While the small intestine rapidly absorbs water, the kidneys work to process this influx, especially if the body perceives it as an excess.
- Why Does Water Go Right Through Me? Understanding the Science Behind Frequent Urination - Water Filter Spruce - Have you ever wondered why water seems to go right through you? Perhaps you’ve noticed that you need to go to the bathroom frequently after drinking water, or maybe you’ve experienced a feeling of bloating or discomfort in your abdomen. Whatever the case may be, there are a number of reasons why water might seem to pass through your body quickly, and in this article, we’ll explore some of the most common explanations.
- Caffeine is diuretic
- Tips for Optimizing Hydration
- Consume electrolytes
- Drink enough water
- Limit diuretics
- Monitor urine color : Monitoring the color of your urine can help determine whether you are properly hydrated. Aim for a light yellow color, indicating adequate hydration.
- Tips for Staying Hydrated
- Carry a water bottle with you wherever you go
- Flavor your water
- Set reminders
- Eat water-rich foods: Many fruits and vegetables, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and strawberries, are high in water content and can help you stay hydrated.
- Avoid sugary drinks: Sugary drinks like soda and sports drinks can actually dehydrate you, so it’s best to stick with water or other low-sugar options.
- Most people urinate between six and eight times per day.
- Tips for Optimizing Hydration
- Avoid These Big Mistakes When Drinking Water - YouTube - Tired of hearing conflicting information about how much water you should drink? Watch this video to learn about some common myths surrounding drinking water and what the truth really is.
- Your urine should not be clear.
- You ned electrolytes and Sea Salt (t=150)
- 2.5 litres of water a day
- Don't drink lots before you eat
- Low carb ketogentic diet + lots of water --> Keto flu of Keto Fatigure = need more salt to fix
- Vegetables: 80% - 90% is water
- Meat: 60% and 65% is water
- When you oxidise fat (exercise), you generate water and CO2
- diabetes or to much calcium in the blood (Hypercalcemia) makes you thirsty, can cause excessive urination, which is probably why you are thirsty.
- Caffeine is diuretic
- Jons Thoughts on drinking
- Dont drink 1Litre in one go, your kidneys will go into overdrive to get balance.
- You must work out the max amount of water you can drink per hour eg: 1 x 300ml drink per hour
- Which does not cause you to piss it out 1 hour later. This is no hydrating you if it happens.
- NB: When you drink water you effectively dilkute your electrolytes, so drinking water with electrolytes should be a consideration in formualting a drinking pattern.
- --do i have notes lesewhere---
- nurse said
- he drinks between 4-5litres a day and that 2 litres a day is not enough for me.
- if you get dry lips you are not drinking enough
- when you drink a lot of water your dilute you electrolytes and also cause them to get flushed out of your system quciker than you want. They will need replacing.
- Definately do not drink the water all in one go
- Amount of water
- dont drink lots of water in one go, it will cause the kidneys to go into overrdirve. 500ml max an hour and this is the most you should do in one go.
- 750ml is classed as a full bladder, you can go up to 950/1000ml if you hold very strongly.
- nurse said 4-5 litres
- work up to it from 2l by 500ml every couple of days to find my balance.
- if my lips are dry at any pint of the night or day my water intake is not enough
- I must make sure I take on electrolytes because the more water you use the more dilute they become and could obviously be excreted out at a greater rate.
- Why Does Water Go Straight Through Me? - Biology Insights - Ever wonder why water seems to go straight through you? Discover how your body efficiently processes hydration and when to be concerned.
Notes (Useful Sites)
- Nutrition
- Nutrition Assessment, Vitamins and Safety | Dr Alan Stewart - A referenced resource for professionals and public interested in nutrition, nutritional assessment and safety of nutritional supplements.
- Guide to Nutritional Supplements | Dr Alan Stewart - Guide to Nutritional Supplements
- Foods Nutritional Values
- USDA FoodData Central - USDA FoodData Central produces thorough resources for navigating and understanding nutritional info to support dietary choices and nutritional analysis.
- Nutritional Values For Common Foods And Products - Nutritional facts database with detailed analysis, advanced search and tools.
- Composition of foods integrated dataset (CoFID) - GOV.UK
- McCance and Widdowson’s 'composition of foods integrated dataset' on the nutrient content of the UK food supply.
- Download McCance and Widdowson’s The Composition of Foods Integrated Dataset 2021: user guide
- McCance and Widdowson’s The Composition of Foods integrated dataset is the official UK national food composition database, providing comprehensive macronutrient and micronutrient profiles of more than 3000 most commonly consumed food and recipes in the UK.
- EuroFIR » European Food Information Resource
- EuroFIR AISBL is an international, member-based, non-profit Association under Belgian law was set up in 2009 to ensure sustained advocacy for food information in Europe.
- Our mission is to be an independent provider of validated food composition and supporting information across Europe and beyond in cooperation with FAO Infoods. We are committed to advancing FAIRification of food-related data and fostering its application through research and commercial endeavours to support improved nutrition and health amongst citizens
- Food composition data is at the heart of what we, at EuroFIR, do. It feeds into the numerous Food Composition Databases (FCDBs) we have in FoodEXplorer.
- Glycemic Index – Glycemic Index Research and GI News | The University of Syndney - Search our comprehensive database of GI tested foods. Complete with data for Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load, serving size, direct references to the studies used to CALCULATE the VALUES, and more!
- Nutrient Information / Recommended Intake (RI)
- Vitamins and minerals - NHS - Find out about common vitamins and minerals, including what they do, how much you need, and how to ensure you get enough.
- Government Dietary Recommendations PDF (2016) | Public Health England - This document provides a concise summary of the government's recommendations for energy and nutrients for males and females aged 1 – 18 years and 19+ years.
- What we SHOULD be eating every day (according to the Government) | Daily Mail Online - The new dietary advice, published by Public Health England (PHE), the Government’s public health quango, is intended to help the meet official nutrient requirements.
- UK government's healthy eating guidelines (PDF)
- The UK government's healthy eating guidelines are represented in the Eatwell Guide, which illustrates the proportions of different food types needed for a balanced diet.
- The guide emphasizes the importance of including a variety of foods from all food groups, such as fruits, vegetables, carbohydrates, proteins, and dairy, to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- You can find more detailed information in the official guide.
- Foods and their Benefits / Help sites
- The Eatwell Guide - GOV.UK
- The Eatwell Guide is a policy tool used to define government recommendations on eating healthily and achieving a balanced diet.
- Tis is a plate of food that illustrates how to get your proportions right for a healthy diet.
- The Eatwell Guide - NHS - Read about the Eatwell Guide, which shows how much of what we eat overall should come from each food group to achieve a healthy, balanced diet.
- The Eatwell Guide and Resources | Food Standards Agency - The Eatwell Guide makes healthy eating easier to understand by giving a visual representation of the types of foods and drinks we should consume and in what proportions to have a healthy, balanced diet.
- Food facts - Healthier Families - NHS - We're here to help your family be healthier and happier. Find out more about what's really in the food we eat and how to make healthier food swaps to cut back on the sugar, salt and fat in your family's diet.
- Weight Loss & Diet Plans - Find healthy diet plans and helpful weight loss tools - From healthy diet plans to helpful weight loss tools, here you'll find WebMD's latest diet news and information.
- Action on Sugar - Action on Sugar - Action on Sugar is a group of specialists concerned with sugar and its effects on health. Learn more here about sugar and it's effect on health.
- SELF Magazine - Women's Workouts, Health Advice & Beauty Tips
- The Eatwell Guide - GOV.UK
Glossary
- OMAD
- One Meal a Day
- Electrolytes
- Water vs Electrolytes: What You Need to Know About Hydration - YouTube - What's the difference between plain water and electrolytes? Who needs to add electrolytes to their water?
- Drinking to much water without adding electrolytes can make dehydration works
- Sodium, potassium and magnesium
- when you exercise, sweat or are on a low carb diaet you are loosing electolytes
- if you are only drinking plain water you are diluting your electrolyte conecntration even more, this can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, muscle cramps, brain fog adn dizzinessor headaches
- so if you are someone who does not eat a lot of processed food, if you eat a lower carbohydrate diet, if you are an athelete or use saunas regulary you need to be replenishing your eletrolyrtes.
- but before you grab any electrolyte drink, make sure to check the label, most have added sugar and dont actually have a lot of eletroytes = use SODIE (15% off with code HCK15)
- Do electrolytes make a difference? Experimenting with SaltStick! - YouTube - Electrolytes are minerals including sodium, potassium, calcium, and more that everyone's body requires. But they seep out in sweat, so as we demonstrate in this experiment, it's important to replace them any time you sweat a lot. Water alone is not enough.
- Electotlyes are minerals, including salt that our body needs to function.
- runing drinking loads of water but mouth is still dry
- Low electrolyte symptoms include:
- cramping
- fatigue
- headaches
- confusion
- Heat exhaustion
- They demo'ed: SaltStick Tablets
- Adding This To My Water Changed Everything - YouTube
- Use Celtic Salt
- Most people think hydration is just about drinking more water. But if water is going straight through you... or you feel bloated, tired, or still dehydrated... it’s not a water problem, it’s a cellular hydration problem.
- Hydration happens inside the cell, not just in your bottle.
- That’s why minerals matter.
- That’s why electrolytes matter.
- And that’s why how you hydrate is just as important as how much.
- Once I understood this, my energy stabilized, headaches became less frequent, and I stopped feeling like I needed to constantly chug water all day.
- Do electrolytes make a difference? Experimenting with SaltStick! - YouTube
- Electrolytes are minerals including sodium, potassium, calcium, and more that everyone's body requires. But they seep out in sweat, so as we demonstrate in this experiment, it's important to replace them any time you sweat a lot. Water alone is not enough.
- We've tried tons of electrolytes, and SaltStick is our favorite because it's EASY. You just eat it like candy in addition to drinking water (it tastes as good as candy too)! The alternatives are bottles of sports drink or electrolyte powders that you mix into water, both of which add complexity to a hike or workout. With FastChews, you don’t need to mix or wait… just chew ‘em!
- Water Isn’t Enough: The Importance of Electrolytes for Hiking and Running – Thruhikers: Renee and Tim
- So, what are electrolytes? They’re the minerals in our bodies that carry an electrical charge. They include sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and more.
- This is a deep dive.
- Water vs Electrolytes: What You Need to Know About Hydration - YouTube - What's the difference between plain water and electrolytes? Who needs to add electrolytes to their water?
- Viseral Fat
- Visceral fat is a type of body fat located deep inside the abdomen, wrapping around organs such as the liver, pancreas, intestines, heart, and kidneys. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which lies just under the skin and can be pinched, visceral fat is not visible from the outside and cannot be felt easily. It is sometimes called “active fat” because it actively influences how your body functions, including hormone regulation and metabolism.
- Visceral Fat: Why It's Dangerous and How to Lose It - Visceral fat is hidden fat that wraps around your abdominal organs. Find out why this belly fat is dangerous and how to get rid of it.
- What Is Visceral (Belly) Fat? Weight Loss & Getting Rid of Body Fat - Visceral fat is belly fat that wraps around the abdominal organs inside your body. Unlike subcutaneous fat, you cannot feel or see visceral fat, making it harder for weight loss.
- What Is Visceral Fat & How To Get Rid of It
- Visceral fat is a type of body fat everyone has. Learn about how it can impact your health.
- some excellent ways of getting rid of it including fasting.
- Cortisol
- These sources include Cortisol Notes which helped for my new diet.
- I Might Get Banned for Saying This About Cortisol & Insulin (not what you think) - YouTube
- Why Your Belly Fat Won't Budge (The Cortisol-Insulin Connection)
- Discover the hidden hormonal pattern that keeps belly fat stuck—even when you eat clean and exercise daily. This video explains the science behind visceral fat, cortisol receptors, insulin resistance, and provides 6 evidence-based solutions you can implement today.
- 10 to 20 minute walk after meal, and must be within 30 mins
- Salt and honey before bed
- Once you have diet sorted, fast 1 day a week You must be doing the diet for a while and it be your routine.
- Meal target types
- Breakfast = protein
- Dinner = carbs
- 12 Signs of HIGH CORTISOL You Can See - Doctor Explains - YouTube
- Cortisol is your body’s main stress hormone, and while it’s essential for survival, too much of it over time can cause real harm. In this video, Dr. Barron goes over 12 physical signs that may point to elevated cortisol levels, like facial puffiness, stretch marks, and easy bruising, and explains what sets normal stress responses apart from more serious conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or the effects of long-term steroid use. She also covers what causes cortisol to rise, when to consider testing, and how to bring levels down naturally through sleep, nutrition, and recovery. If you’ve noticed changes in your body and you’re wondering whether cortisol could be involved, this video will help you make sense of what’s going on and what to do next.
- Cushings Syndrome = a severe condition that can cause the symptoms below
- 12 Signs:
- Moon Facies (only for severe) (a.k.a Cortisol Face)
- Buffalo Hump - Hump at the top of the neck (only for severe)
- Purple Striae - Stretch marks on the upper legs and gut.
- Easy Bruising caused by thin skin
- Central Obesity (i.e. viseral fat). This is hard to fix with addressing the cause of the high cortosol
- Muscle Weakness
- High cortosol can cause your muscles to break down over time
- You may notice weakness in your arms and legs.
- Find it hard to get out of a chair or climb stairs
- Insomnia or restless sleep
- Hair thinning
- Acne and Oily skin (leading to adult achne)
- Elevated Blood pressure
- Cortosol causes you blood to retain sodium increasing tension in your blood vessels
- Recurrent infections or slow healing
- cuts, scrapes or injuries take longer to heal than they use to
- get sick more often
- Anxiety, Irritability, or Emontional Numbness
- Causes of High Cortisol
- Medical, chronic stress or lifestyle
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Causes the body to uncontrollably produce cortisol
- Rare
- Can be caused by a tumor
- Corticosteroid Medications.
- Long term use of steroids is the highest cause ofr medically induced high cortisol
- Long term use can give symptoms to cushing's syndrome
- Physiologic Elevation
- Chronic Stress
- Pain
- Illness
- Sleep Distruption
- NB:In the short term it's a healty survival response. But over tiome is the stress is not addresses, those elevated levels can begin to wear down the body.
- Pseudo-Cushings
- Can be caused by:
- Alcoholism
- Major Depression
- Sever Obesity
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- NB: The key difference is that once the underlying problem is treated, cortisol level usually goes back to normal
- Can be caused by:
- How to lower cortisol
- Go to bed at the same time every night and try to sleep 7 to 9 hours.
- Avoid screens like phones or TV before bed. They keep your brain alert and can raise cortisol.
- Along with sleep mental rest is just as important.
- Deep Breathing
- Stretching
- Yoga
- Quiet time (without ditractions)
- NB: These can calm your nerveous system. These activities tell your body that it's safe, whihc helps lower stress hormones like cortisol.
- Your diet plays a major role too.
- Don't dkip meals
- Choose food with protein, fibre and healthy fats instead of sugary snacks.
- When you blood sugar goes up and down too quickly, your body may release too much cortisol.
- Natural Suppliments can help
- Ashwagandha: is a herbal suppliment that has been shown in some studies to gently lower cortisol levels.
- Balance your physical activity
- Exercise is good, but too much intense exercise without enough rest can raise your cortisol level instead of lowering it.
- Make sure your body has tome to recover between workouts and mix in lighter activity like walking or stretching.
- Always Waking Up at Night? - 1 TBSP Kills Cortisol FAST To Fall Back Asleep - YouTube
- If you’re waking up at 3 a.m. with your heart racing and your mind wired — it’s not a sleep problem, it’s a cortisol problem. In this episode, Ben explains why your body wakes up during “liver time,” the real reason behind nighttime cortisol spikes, and the 1-tablespoon sleep hack that shuts it down fast.
- You’ll learn exactly how raw honey and sea salt work to stabilize blood sugar, balance hormones, and calm the nervous system — plus five long-term steps to reset your metabolism, improve sleep, and burn fat more effectively.
- Take these (Honey, Salt, Magnesium)
- 1 table spoon of raw organic unfiltered honey with sea salt right before bed or even when you wake up at 3am
- Also take a high quality magnesium suppliment beofre bed. There are 7 different types and you can get a suppliment with them all in.
- Has links in description.
- 5 steps to fix this issue long term
- Stop eating 3-4 hours before bed.
- Cut out seed oils and refined sugar.
- Support the live daily.
- Get morning sunlight exposure
- Get Vitamin G
- first thing in the morning and last thing at night.
- This is a social thing, not chemical.
- Vitamin Gratitude, it is the feeling of gratitude.
- Nighttime routine to prevent 3 AM Wakeups
- Dim lights 1 hour before sleep.
- Do 5 minutes of slow breathing or gratitude journaling.
- Avoid screens or blue light after 9p.m. (or at least an hour before bed)
- Take magnesium glycinate or L-theanine if you're under stress.
- End the night with your 1 tablespoon of honey and sea salt mix. (right before bed)
- FAQ
- honey and salt trick should be only for 7 - 14days as you fix the other things. it is not for long term but can be re-inroduced if required in the future.
- It has to be unrefined sea salt. normal salt will not work.
- You can test Cortisol levels at home using saliva, and it is called the `Dutch Test`, or via uring. can only be got from practitioner.
- Do You Have a Cortisol Face? - YouTube | Drberg
- Are you struggling with a round, puffy face—even though your diet hasn’t changed? It might not be what you're eating… it could be your stress hormones.
- When your body produces too much cortisol, it starts to break down muscle from your legs and butt, turning it into fat around your belly and face. This leads to the classic “Cortisol Face” – a bloated, swollen face caused by chronic stress, not overeating.
- It's coming from stress not your diet.
- When your body has too much cortisol it robs protein from your legs and your butt and turns it into fat around your midsection, it also puts it around the face, giving you this roundish face.
- On of the best antidotes to lowering cortisol is something called L-Theanine. It increases Alpha brain waves to help calm you down so you can get into a really nice deep sleep and sleep through he entire night.
- L-Theanine also increases GABA and Serotonin as well as melatonin which is the sleep hormone.
- the best time to take L-Theanine is about an hour before you go to sleep at night.
- Tests
- Cortisol Test: Understanding High vs. Low Cortisol Levels - Cortisol is an important hormone that regulates blood pressure, sugar, and metabolism. Learn about blood, saliva, and urine tests conducted for cortisol.
- Cortisol Exeter Clinical Laboratory International - Test information and an explanation behind the bio-mechanics.
- Cortisol Test | South of Tyne and Wear Pathology Centre - Test information and ranges.
- expected cortisol levels during the day | Google Search
- Cortisol levels follow a strict circadian rhythm, peaking early in the morning (6 a.m. to 8 a.m.) at 10–20 mcg/dL and declining throughout the day to their lowest levels around midnight. Levels typically drop to 3–10 mcg/dL by 4 p.m., ensuring the highest concentration upon waking.
- Typical Daily Cortisol Rhythm (Blood Serum)
- Morning (6 a.m. – 8 a.m.): Highest levels, typically 10 to 20 mcg/dL (roughly 275–555 nmol/L).
- Late Afternoon (Approx. 4 p.m.): Significant decline, usually 3 to 10 mcg/dL (roughly 85–275 nmol/L).
- Midnight: Lowest levels (nadir).
- Key Details on Cortisol Variation
- Cortisol Awakening Response (CAR): Levels often surge by 50–60% in the 30–40 minutes immediately after waking.
- Measurement Units: Results are generally measured in micrograms per deciliter (mcg/dL) or nanomoles per liter (nmol/L).
- Factors Affecting Levels: Stress, infections, illness, and medication (such as steroid use) can significantly influence these levels.
- Exceptions: People working night shifts may have a reversed rhythm.
- If testing for deficiency, doctors usually order a morning test; for excess (like Cushing's syndrome), a late-day test is more likely.
- Sources
- Cortisol Test: What It Is, Purpose, Types & Results - A cortisol test can help diagnose certain conditions, like Addison’s disease or Cushing syndrome. Learn more here.
- Interpreting serum cortisol | Buku Medicine
- Cortisol in Blood Test | Healthwise
- A cortisol test is done to measure the level of the hormone cortisol in the blood.
- The cortisol level may show problems with the adrenal glands or pituitary gland.
- Cortisol is made by the adrenal glands.
- Cortisol levels go up when the pituitary gland releases another hormone called adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
- Simpke vs Complex Carbohydrates
- Simple vs. Complex Carbohydrates: Function and Examples - You may have heard that eating complex carbohydrates is better than eating simple carbs. But why? And if itâs so important to know, why donât nutrition labels tell you if the carbohydrate content is simple or complex? We explain the importance of carbohydrates and how to identify simple carbs vs. complex carbs.
- Simple vs. Complex Carbohydrates / Nutrition / Carbs - As a dietitian, I'm often asked to explain the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates. While most people have heard that complex carbohydrates are better for you than simple carbohydrates, what's often unclear is how the two differ, and why the differences between the two affect your health.
- Good Carbs and Bad Carbs: The Truth about Carbohydrates - Carbs have a bad reputation in the dieting world but should not be completely eliminated from our diets. There are good carbs and bad carbs we explain which ones are good for you.
- The Carbohydrate Advantage - Choose Complex Carbohydrates for Lasting Energy and Good Health
- Good vs. Bad Carbohydrates: How Do You Tell the Difference? - Not all carbs are healthy. Here’s how refined and complex carbs differ, and which sources to choose.
- Are Potatoes Good Carbs? Week& - Most nutrient-rich complex carbohydrates like potatoes have a welcome role in a healthy diet. Unfortunately, the impact of the starch in potatoes can place them in the "bad carb" category for some people.
Lifestyle Recommendations
- General
- After a meal need to do 20mins of walking (while burning virseral fat off)
- It's Embarrassingly Simple - YouTube | Papa Tates - Fitness and nutrition is really that simple
- Carbs before lift
- Protein after lift.
- Fruits before and after.
- Water and electrolytes all day
- Caffeine when you're lazy.
- It's really that simple.
- Stop overcomplicating.
- 4 Ways to Lose Weight Without Counting Calories - YouTube
- This video outlines 4 evidence-based ways to lose weight without counting calories or consciously controlling portions. We all know that the standard advice to "eat less, move more" doesn't work that well.
- hi carb foods: reducing these helps loose weight: sugars, sodas, bread, pasta
- How Long Does It Take to Put on Muscle? | The Art of Manliness - Don't be fooled by unrealistic expectations. Learn the truth about building muscle and how long it takes to see noticeable results.
- Do You Chew Your Food Enough? Doctor Explains - YouTube | Dr Sermed Mezher
- Chewing your food thoroughly is more than just a mechanical step in digestion; it is a critical signal to your endocrine system.
- The process of mastication, or chewing, triggers a complex hormonal cascade that communicates with the brain to signal satiety.
- Alternative Diets
- 30-30-30
- 80-20 diet ?
- Collagen diet
- Anatoly uses this
- Wisey 28 day plan
- Paleo Diet
- Paleo Diet Recipes & Tips | The Paleohacks Website - No meta description
- 30-10-30
- I Tried the 30-10-30 Workout Method – It’s Low Volume, Maximum Effort and Highly Effective - This high-intensity protocol packs 90 seconds of tension into every set. I put it to the test to see if seven working sets were really enough.
- Keto diet with intermittent fasting
- 4 months hard keto intermittent fasting | Google Search
- A four-month commitment to a "hard" keto and intermittent fasting (IF) regimen is a highly restrictive approach that combines high-fat, ultra-low-carb intake (under 30-50g per day) with 16:8 or 18:6 eating windows, or even One Meal A Day (OMAD). Many individuals in this scenario report significant weight loss—often ranging from 30 to over 50 pounds depending on starting weight—due to accelerated fat-burning and reduced calorie consumption.
- Here is a breakdown of what to expect based on 4 months of hard keto and IF:
- 4-Month Results and Experience
- Rapid Initial Weight Loss: Many report losing 10-15 pounds in the first month alone, with, in some extreme cases, up to 100 pounds lost over 4 months.
- Fat Loss vs. Weight Loss: The focus often shifts from scale weight to body composition changes, as the combination of keto and IF helps preserve lean muscle while burning stubborn body fat.
- Adaptation Phase: The first 2-4 weeks often involve the "keto flu" (fatigue, headaches, irritability), which typically subsides as the body becomes fat-adapted.
- Physical Changes: Clothes become noticeably looser, and people often experience a significant reduction in bloating and inflammation.
- Sustainability Challenges: After 3-4 months, many find strict keto difficult to maintain due to limited food variety, leading to potential "cheating" or burnout.
- Benefits of the Combination
- Enhanced Ketosis: IF accelerates the depletion of glycogen, forcing the body into ketosis faster.
- Reduced Appetite: High-fat meals paired with reduced eating windows often lead to a natural, effortless decrease in calorie consumption.
- Increased Mental Clarity: Participants frequently report sharper focus and increased energy levels.
- Challenges and "Hard" Side Effects
- Physical Side Effects: Constipation, bad breath (ketosis breath), insomnia, and reduced energy during workouts can occur.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Long-term strict keto (3-6 months) can lead to deficiencies in vitamins A, C, K, and folate.
- Potential for Overeating: Due to small eating windows, some may feel pressured to overeat, causing stomach discomfort.
- Heart Health Concerns: Sustained high saturated fat intake can lead to increased LDL cholesterol in some individuals.
- Tips for Success over 4 Months
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to avoid side effects like low blood pressure.
- Electrolytes are Crucial: Replenish sodium, potassium, and magnesium to prevent keto flu symptoms.
- Listen to Your Body: If extreme fatigue sets in, consider easing the fasting window (e.g., move from 18:6 to 16:8).
- Focus on Whole Foods: Avoid relying solely on processed, high-fat "keto snacks" to ensure adequate nutrition.
- Disclaimer:
- It is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting such a restrictive diet, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medication.
- 4-Month Results and Experience
- Sources
- 15 Burning Questions About the Keto Diet, Answered - The ketogenic diet involves eating few carbs and a whole lot of fat. But since the diet is restrictive and causes some weird side effects, it’s more complex than other diets. Here are answers to 15 frequently asked questions about keto!
- Intermittent fasting for weight loss - Mayo Clinic Health System - One of the latest diet trends is intermittent fasting. Learn about the approaches and if itâs a safe weight-loss option for you.
- Ketogenic and Intermittent Fasting Diets - YouTube | Health e-University - Popular diet trends include Intermittent Fasting and the Ketogenic Diet. During this session Fatim and Veronica will answer 3 main questions: 1) Are these diets safe? 2) Can these diets be maintained? 3) Are these diets based on facts?
- Can you lose weight on the keto diet and keep it off? | ZOE - Some people lose weight on the keto diet short term but often put it back on. Diets like keto can slow your metabolism and come with other health concerns.
- Keto vs. Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss | Everlywell - What's the difference between the keto diet and intermittent fasting when it comes to weight loss? Find out more here.
- Should You Add Intermittent Fasting to Your Keto Therapy? - YouTube | Metabolic Mind
- Can intermittent fasting support ketosis and help treat serious mental illnesses like bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, depression, and anxiety?
- In this video, Dr. Bret Scher breaks down how intermittent fasting may fit into metabolic psychiatry and the potential role of intermittent fasting in ketogenic therapy for mental health.
- In this video, you’ll learn:
- What intermittent fasting is
- How fasting can impact ketone levels and metabolic health
- Why it might support (but isn’t required for) ketogenic therapy
- How to approach fasting safely, especially when mental health is a concern
- Why fasting is highly individual and may not be right for everyone
- Whether you’re exploring ketogenic therapy for yourself or supporting someone else on the path to recovery, this video will help you better understand whether or intermittent fasting could be a helpful complementary strategy to ketogenic therapy.
- Intermittent Fasting on Keto: What to Know Before You Combine the Diets for Weight Loss - Learn about combining intermittent fasting with the ketogenic diet. This guide explains how IF keto works for ketosis and weight loss, exploring expert-backed benefits and associated risks, as well as a sample menu.
- Can I Do Intermittent Fasting on the Keto Diet? | Green Chef - Is intermittent fasting during the keto diet a good idea? What about a juice cleanse or a 60 hour fast? Find all the answers in our keto fasting guide.
- How Long Does It Take to Lose Weight on Keto? - Are you on the keto diet and interested in how fast you can see results? Learn here how long it takes to lose weight on keto the safe way!
- Ways to lose belly fat: 15 practical, science-backed tips for lasting results | Zing Coach - Ways to lose belly fat: Learn science-backed workouts, nutrition, and stress strategies for lasting, sustainable results.
- 4 months hard keto intermittent fasting | Google Search
- Gut health expert DR MEGAN ROSSI shows you how to add many more years to your life | Daily Mail Online - DR MEGAN ROSSI: Cutting out red and processed meat was seen to have a positive impact on lifespan, too, though not quite as impressive as adding more legumes, wholegrains and nuts.
- Recipes
- Recipe bank | NHS England - We provide nutritious recipes that promote low carbon and seasonal ingredients that help reduce emissions, that can be locally sourced and produced and can support local farmers and economies.
- Healthy Diet Advices sort??
- 8 tips for healthy eating - NHS - Start eating well with these 8 tips for healthy eating, which cover the basics of a healthy diet and good nutrition.
- 6 High-Protein Foods That Are Super Healthy - YouTube
- People argue about carbs, fats and everything in between. However, almost everyone agrees that protein is important and has numerous benefits including increased strength and muscle mass, and helping you to lose weight.
- In this video we're looking at 6 delicious high protein foods that are super healthy. The last one is part of a super controversial meme that has been shared hundreds of thousands of times that I just wanted to clarify.
- Eat well - NHS - Information and guidance about eating a healthy, balanced diet.
- Flat Stomach Diet: Stomach Toning Foods for & Bloating Weight Loss | Glamour UK - A comprehensive guide.
- The Food Pyramid | Safefood - A healthy diet means eating a variety of foods from the major food groups and eating less salt, sugar and fat. The Food Pyramid shows how much of each food group to eat.
- Arnold Schwarzenegger Shared His Go-To Salad and Protein Shake - Including a very special ingredient.
- I'm a Dietitian, and I'll Never Give Up Pasta. Here's Why | EatingWell - Pasta gets a bad rap from some, but there are many benefits to eating pasta. Here are a few of them.
- Fish and shellfish - NHS
- Find out why most of us should eat more fish, including oily fish for omega-3. Learn how to eat fish and shellfish safely, including information on fish and shellfish allergies.
- A healthy, balanced diet should include at least 2 portions of fish a week, including 1 of oily fish.
- 8 Foods That Help Lower Your Cholesterol - If you want to lower your cholesterol, you may want to think about changing your diet. Learn more about these foods that can help lower cholesterol.
- The 7 Best Sources of Resistant Starch and How to Work These Nutritious Carbs Into Your Diet | Lose It! - Resistant starches have a deservedly good rep for keeping your gut happy and helping you lose weight, say dietitians. Here’s more about this healthy carbohydrate choice and the best foods to increase your resistant starch.
- High Protein Foods: 16 Foods for High Protein Meals - Research shows it's really important to eat enough protein. These high protein foods can help you lose weight, gain muscle, and feel great.
- 7 Potato Recipes That Are Actually Good for You - Potatoes have an unhealthy reputation, but it's more about how they're prepared that matters. These recipes for healthy baked fries, potato skins, potato salad, and more are a better way to eat and enjoy potatoes.
- 11 Healthy Foods That Help You Burn Fat - Several natural foods and beverages have been shown to increase metabolism and promote fat loss. These 11 healthy foods can help you burn fat.
- Blood pressure
- General
- Blood pressure test - NHS
- Find out why a blood pressure test is important, how it's done and what your blood pressure reading might mean.
- Your blood pressure is usually considered high if it's either:
- 140/90 or higher when checked by a healthcare professional
- 135/85 or higher when checked at home
- Blood pressure test - NHS
- High Pressure
- High blood pressure - NHS
- Find out about high blood pressure, including how to find out if you have it, what causes it and what you can do to lower it.
- can cause serious problems like strokes or heart disease, but it does not usually have any symptoms. The only way to find out if you have high blood pressure is to get it checked.
- What are high blood pressure numbers? | Penn Medicine
- Cardiologist Ross Biggs, DO, explains hypertension guidelines and how to reduce your blood pressure without medication.
- But what is normal and what is high blood pressure? Here are the current guidelines:
- Normal: less than 120/80
- Elevated: systolic between 120-129 and diastolic less than 80
- High blood pressure (hypertension) stage 1: systolic between 130-139 or diastolic between 80-89
- High blood pressure stage 2: systolic 140 or higher or diastolic 90 or higher
- Hypertensive crisis (consult your doctor immediately): systolic higher than 180 and/or diastolic higher than 120
- Michael's Mosley's favourite vegetable for weight loss that 'helps high blood pressure' - Daily Record - The diet guru issued some helpful advice on the latest instalment of his podcast.
- Does High Blood Pressure Make you Tired, Sleepy? - Feeling tired can be a symptom of heart or kidney damage as a result of high blood pressure. It may also be due to hypertension medications or coexisting conditions.
- What to avoid eating or drinking with high blood pressure - Diet can have a big impact on your blood pressure. We look at key foods that increase your blood pressure, as well as foods to eat and to avoid to lower it.
- Does Drinking Water Lower Blood Pressure? - While drinking water won't treat high blood pressure, it may help you better control hypertension. Learn how dehydration influences blood pressure.
- How to Lower Systolic Blood Pressure - A high systolic blood pressure can lead to heart attack, stroke, and even death. Here are some changes you can make right now to lower yours.
- High blood pressure - NHS
- Low Pressure
- Low blood pressure (hypotension) - NHS
- Find out about low blood pressure (hypotension), including what the symptoms are, when to get your blood pressure checked and treatments for low blood pressure.
- can cause symptoms such as dizziness or fainting.
- Low blood pressure headache: Causes and treatment - While many people with low blood pressure (hypotension) may not have symptoms, some people do experience headaches as well as other symptoms.
- Low blood pressure (hypotension) - NHS
- General
- Reduce Cholesterol
- 8 Foods That Help Lower Your Cholesterol - If you want to lower your cholesterol, you may want to think about changing your diet. Learn more about these foods that can help lower cholesterol.
- Health recommendations by WHO
- Water Intake: Drink 8-10 glasses of water daily
- Exercise: 150 minutes moderate activity per week
- Sleep: 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly
- Steps: Aim for 10,000 steps daily
- Sleeping
- No more than 8 hours should be needed normally.
- Unless you fall asleep with 20 minutes of going to bed, you are not ready for sleep
- Try THIS if you can't fall asleep! - YouTube | Doctor Myro
- If you cant fall asleep in 20 minutes your brain is stuck in an active thinking loop.
- Your brain has evolved to stay alert when something feels uncertain or unresolved.
- Staying in bed when your mind is racing is just training your brain to associate your bed with anxiety.
- To quiet your brain you need to switch from thinking to sensing, get up go to a quite room, dark environment, absolutely no screens and then read, listen to music, try a wind down exercise, but only go to bed when you are ready to sleep. If it is still not happening half an hour later, take 0.5mg of Melatonin, not more, it is a common misconception, but more just gives you more side effects. 200mg - 400mg of Magnesium Glycinate can also work wonders.
- How long should naps REALLY last? - YouTube | Dr Myro - How long do you nap?
- Your naps should never be 30 minutes because that is how long it takes for your body to enter deep sleep, even REM sleep. cutting that off and you're going to wake up groggy. Might as well be a walking zombie.
- 10 - 20 mins is where it's at. Even if you don't fall asleep, you enter non-sleep deep rest and that's great for midday brain fog, alertness, memory retention. There's even a 60% dopamine increase with a non-sleep deep rest. It's like loving life again and you're more productive.
- Now you want the same benefits as 8 hours of restorative sleep, 90 minute nap. That's all it takes.
- why do i get hungry before bed | Google Search
- You get hungry before bed due to insufficient daytime calories, unbalanced meals (low protein/fibre), poor sleep disrupting hunger hormones (ghrelin/leptin), stress, boredom, dehydration, or your body's natural circadian rhythm signaling a need for fuel after activity, with hormonal shifts like your period also playing a role. It signals your body needs energy, but it could also be emotional, so assess if you're truly hungry or just craving. (Google AI)
- Nighttime hunger often happens because of inadequate daytime eating, high activity levels, or habits that trigger the brain to crave a late-night snack. Other common factors include stress-induced high cortisol, poor sleep quality, or needing more fiber and protein to stay full. A light, balanced snack can help, but regular, intense hunger might require reviewing your daily diet.
- Key Reasons for Pre-Bed Hunger:
- Insufficient Daytime Nutrition: Not eating enough or skipping meals during the day, particularly neglecting protein or fiber, causes hunger to catch up with you at night.
- Habit and Conditioning: If you regularly eat before bed, your body becomes conditioned to expect food at that time, triggering hunger signals on autopilot.
- High Activity Levels: If you had an intense workout, your body may be demanding more energy to recover.
- Stress and Emotional Eating: Stress and anxiety can trigger increased hunger and make you crave comfort, leading to late-night snacking.
- Poor Sleep/Hormones: Poor sleep quality messes with hunger-regulating hormones (ghrelin and leptin), often causing late-night hunger.
- Dehydration: Sometimes, the body mistakes thirst for hunger
- How to manage it:
- Eat Balanced Meals: Ensure your dinner includes a mix of carbohydrates, fiber, and protein to keep you satiated.
- Smart Snacking: If you must eat, choose nutrient-dense, light options like nuts, yogurt, or fruit.
- Hydrate: Drink herbal tea or water to help calm cravings
- If you are constantly waking up famished, it could be due to blood sugar issues, and you should consider consulting a healthcare professional.
- Sources:
- Why You’re Waking Up Hungry in the Middle of the Night—and How to Fix It - Healthcare professionals explain why you're waking up hungry at 2 a.m.—and the best way to fix it.
- Why You Feel Hungry Before BedâAnd What to Do About It, According to a Registered Dietitian | SELF - An R.D. helps break down what's going on.
- Why Am I Hungry At Night? | Nourish - You should be in bed, but instead, you’re back in the kitchen with a grumbling stomach. An occasional snack is fine, but being hungry every night is too frequent. This article will teach you how you can stop getting hungry when you should be sleeping.
- Hungry at Night? Causes & How to Curb Cravings | Juniper UK - Constantly hungry at night? Here's everything you should know about nighttime eating: why it happens, how to manage it and the best late-night snacks.
- What To Eat If You're Hungry Right Before Bedtime, According To Nutritionists | HuffPost UK Food & Drink - Snacking before sleep isn't often recommended, but sometimes it's necessary. Here's what to grab.
- 6 Reasons Why You're Waking Up Hungry | EatingWell - Here’s what your appetite might be trying to tell you.
- Insanely Hungry Before Bed Every Night - Any Tips? | Reddit
- I normally sleep from 10pm to 6am on a normal night, around 8pm I start getting these intense cravings for food and sweets, even if I had a huge dinner earlier that evening. I tried pushing my dinners later into the evening but it didn't make a difference, even if I was overly-full I still got the cravings.
- Anyone here get these cravings and have tips for something I could get away with eating before bed? I read that if you eat before bed it will just sit in your stomach all night and get converted to a fat source.
- Ok, let me clarify, I have hunger cravings that keep me from being able to sleep. This helps.
- Sleeping on the Floor: Is It Good or Bad for You? | Casper Blog - Updated 9/25/2025 Sleeping on the floor may improve posture, circulation, and help you stay cool, but it can also cause discomfort, worsen allergies, or lead to restless nights. If you try it, ease in gradually, use proper support, and choose a position that keeps your spine aligned - or consider a firmer mattress for similar benefits without the downsides.
- Sleep After a Workout: Is It Good or Bad? | healthline - After doing intense exercise, some people feel the urge to take a nap. We'll discuss the pros and cons of sleeping after exercise.
- REM, Light, Deep: How Much of Each Stage of Sleep Are You Getting? - Fitbit Blog - Discover how to read and interpret your sleep-stage data with these tips from the scientists who helped develop it.
- Quitting Sugar
- I Quit Sugar for 30 Days. I Didn't Expect This... - YouTube | Mike Dee
- I Quit Sugar for 90 Days (it's changing my life) - YouTube | Mike Dee
- What happens to your brain when you give up sugar - Having high levels of sugar in your diet is known to be bad for your health, but cutting it out can be difficult, particularly as it can trigger a range of unpleasant symptoms.
- When and how should I take my Supplements
- The Truth About Supplements: Timing, Pairing & Usage Mistakes You Didn’t Know | Health and Me
- Supplements can support your health, but using them the wrong way may limit their benefits. From the best times to take them to which foods enhance absorption, and the subtle mistakes many of us make without realizing, this guide explores everything you need to know to get the most from your routine.
- Supplements should complement, not replace, a balanced diet and professional guidance.
- This has a nice table and tells you when and with or witout food.
- When to Take Vitamins and Supplements - YouTube - Are you taking supplements or vitamins that arenât as effective as you thought theyâd be? It could be that youâre just taking them at the wrong time of day. ...
- Is timing everything? Why it matters when you take your supplements
- Taking all your supplements in one go? There's a better way. Your routine can make or break how your body benefits from those nutrients, according to our expert
- Can’t I just take a multivitamin in the morning and call it a day?
- Some vitamins are better absorbed on an empty stomach, while others require food. And if certain ingredients interact negatively, they won’t be absorbed properly.
- When is the best time of day to take protein? | H&B
- Our nutritionist has done the heavy lifting and found the facts about when to take protein. Here's what you need to know about choosing the right type and fitting it into your routine
- If we look at someone who trains in the morning, then having a protein-rich breakfast such as protein-fortified cereal, eggs on toast or a protein shake will aid their recovery and help the muscles to repair after their workout.
- When we exercise to a high intensity, we need to compensate for the muscle protein breakdown, so we need an additional intake of protein.
- “A lot of people think that they need to have a source of protein immediately after exercise – or within about 30 minutes – but research suggests that it might actually extend to several hours,”
- The Truth About Supplements: Timing, Pairing & Usage Mistakes You Didn’t Know | Health and Me
- Heart Rate
- Your heart rate - BHF - Your heart rate (also known as your pulse rate) is the number of times your heart beats per minute (bpm). Everyone’s heart rate is different and can change over time.
- Sort
- How Hot Chocolate Helps Regenerate Stem Cells - YouTube - New research reveals a fascinating benefit of dark hot chocolate—drinking two cups daily can double the number of circulating stem cells in your bloodstream! Here’s why that matters:
Misc SORT
- Pooping / Stool
- General
- 11 Icky but Interesting Facts About Poop | Everyday Health - Taking a peek at what's in the toilet can benefit your health! Read on to find out everything from what it means when your poop floats to how often you should go number 2.
- When
- Why Do I Poop In The Morning — And Sometimes Twice? - Many people poop in the mornings — and sometimes they poop twice or multiple times — but is that normal? Poop experts answer all your bowel movement questions.
- When Is the Best Time to Poop? - At least according to one bowel expert.
- Black Poo, What does it mean?
- Why Is My Poop Black? What's Normal and When to Worry | verywellhealth - Black poop can be harmless or a sign of a serious condition. Learn the causes of black stool and when to consult a healthcare provider
- What Do Different Poop Colors Mean? | WebMD - What does it mean if your poop is green? What about red, yellow, white, or black? Find out possible causes and when to call a doctor.
- Why Is My Poop Black? 7 Causes of Black or Tarry Stool | WebMD - If you notice your poop is black or tarry, it might be due to something as simple as a change in your diet. Sometimes it's a sign of a medical problem. Learn why your stool may have a different color and when you should call your doctor.
- Changes in stool colour or texture (black stool) in adults | WebMD | Boots.com | WayBackMachine - Poo, also known as stool, can change colour in adults. When is this normal and when is it a cause for concern?
- General
- Lead Poisoning
- Health effects from exposure to lead - HSE - Provides information about when you are most at risk from lead.
- Lead Blood Test: What to Expect | WebMD - If you or your child has been exposed to lead, you both should be tested. A lead blood test is simple, and it provides information that could save your life. WebMD explains what you should know.
- Blood Lead Levels - Test For Lead - UK CLAW regulations and EU directives on medical surveillance of workers' blood lead levels.
- Lead Test | LabTestsOnlineUK - Describes how the lead test is used, when a lead test is requested, and what the results of a lead test might mean.
- Painful/Sore Foot
- Foot hurts when walking: Causes, treatment, and diagnosis | MedicalNewsToday - There are a variety of reasons why a person's foot may hurt when they walk. Learn more about the possible causes and how doctors diagnose and treat them.
- Plantar Fasciitis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment | WebMD - Plantar fasciitis is inflammation in the plantar fascia — the ligament that connects your heel to your toes. Learn more about its causes, symptoms and treatment at WebMD.
- Hair
- Dandruff - NHS - Find out what causes dandruff, what you can do to get rid of it and when to get medical advice.
- Balding man stops washing his hair – and 6 years later has a full head of locks - Daily Star
- A balding man says he rescued his thinning head of hair by stopping to wash it and joining the #nopoomovement.
- Nick Coetzee now has thick and healthy hair and only rinses it with water.
- Posture
- Get rid of Thigh FAT
- 10 Tips to Lose Thigh Fat - Check out these 10 tips to lose weight and target pesky thigh fat for leaner, more toned legs.
- 9 Super Quick Ways To Get Rid Of Thigh Fat - Get rid of unsightly thigh fat as quickly as possible with these 9 super-effective methods
- How to Get Rid of Inner Thigh Fat: What You Should Know
- The best and healthiest ways to burn off extra fat and tone your thighs.
- Many people struggle with having fat on their inner thighs. While you cannot get rid of fat from only a specific part of your body, you can do exercises to build the muscles in your thighs to make them look toned.
- 5 Simple Exercises to Build Your Lower-Body Strength | Lose It! - Try this quick, beginner-friendly workout to tap into the many benefits of a strong lower body.
- Salt
- When You Stop Eating Salt, This Is What Really Happens To Your Body - When you stop eating salt, a few things happen, as we often eat plenty of it in our day-to-day lives. Here's what sorts of physical changes you can expect.
- Sugar
- What Eating Too Much Sugar Does To Your Body - While sugar in moderation is totally fine if you're in good health, it becomes the devil when you eat too much. Here's what happens when you eat too much sugar.
- Oxygen Saturation
- What Is Your Normal Oxygen Level - Nonin
- The “normal”range of SpO2 is 95% to 100%
- Oxygen saturation: normal values & measurement - cosinuss°
- What Is Your Normal Oxygen Level - Nonin
- Cooking
- How to cook the perfect steak - Nicky's Kitchen Sanctuary - I’m going to teach you how to cook steak like a pro - answering all of your questions so you can cook the perfect, juicy, delicious steak.
- Tools
- BMI Calculator - Free Body Mass Index calculator gives out the BMI value and categorizes BMI based on provided information from WHO and CDC for both adults and children.
- Ashwagandha
- Ashwagandha KSM66 Capsules | Myprotein UK - Check out Ashwagandha KSM66 Capsules from Myprotein, the World's No.1 Online Sports Nutrition Brand. Free Delivery Available.
- Ashwagandha KSM-66 600mg - 30 Capsules | Holland & Barrett - KSM -66 is a superior clinically studied form of Ashwagandha. Supports emotional balance, relaxation, and general wellbeing. Suitable For Vegans.
Working out symtpons
- General
- Why am I feeling very weak during my workout routine?
- Feeling weak during workouts is common and usually results from one or more physiological, nutritional, recovery, or environmental factors. Below is a concise, structured checklist to identify likely causes and practical fixes you can apply immediately and over the short term.
- Immediate causes to consider (and quick fixes)
- Why am I feeling very weak during my workout routine?
- Twitching Muscles
- Why do my muscles twitch? | Ohio State Health & Discovery - Most people experience muscle twitching several times throughout their lives. An @OSUWexMed expert explains why they happen and when to be concerned.
- Muscle Fatigue
- Muscle Fatigue: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment - Muscle fatigue is a symptom that decreases your muscles' ability to perform over time. As you exercise, over time your muscles may begin to feel weaker and tired. This is muscle fatigue. But exercise isn't the only thing that can cause muscle fatigue. Learn the symptoms of muscle fatigue and its many causes.
- Weak after a workout
- What to Do to Stop Feeling Tired After Cardio | Livestrong.com | Archive.org - It's not abnormal to feel a little worn out after finishing a cardio workout. What you shouldn't feel is exhausted and completely drained.
- What Causes Weakness After Exercise? | livestrong | Archive.org - Feeling weak after a workout is a sign that something's wrong. Common trouble areas are breathing, hydration, nutrition, lack of cool down and overtraining.
- Shaking after a workout
- I'm Shaking After a Workout | livestrong | Archive.org - Shaking after a workout can be alarming, but it might just be a side effect of your hard work. Shaking can also be caused by muscle fatigue or low blood sugar.
- Mission.org - Life Changing Programs for Cancer Survivors | Survivorship - Why Do Muscles Shake After a Workout? - While it may feel alarming to experience muscle shakes after a workout, most of the time it is completely normal. Involuntary muscle shaking is typically caused by muscle fatigue or low blood glucose.
Hydration
- General
- 8 Signs That You Are Dehydrated - Dehydration can have dire consequences if left untreated that extend to unconsciousness, coma, organ failure, and even death.
- How To Stay Hydrated With These 12 Easy Habits | British Vogue - “Everything in your body depends on optimal hydration, from organ function to hormone balance.”
- Water, drinks and hydration - NHS - Find out how water and other drinks fit into a healthy diet and lifestyle.
- Salt & Water - Barbara O'Neill - YouTube
- How much water do you drink? Water is the 2nd most vital element needed for life, which is why you can only survive a couple of weeks without water.
- Celtic Sea Salt
- Himalayan Pink Salt
- Does Drinking Water Lower Blood Pressure? - While drinking water won't treat high blood pressure, it may help you better control hypertension. Learn how dehydration influences blood pressure.
- 6 Exercise Hydration Mistakes - Here’s what you need to know about choosing the right post-workout beverage, finding the right carbs to rehydrate, and avoiding other common hydration mistakes.
- Can Dehydration Cause Numbness and Tingling? Causes, Effects, and Solutions - Discover how dehydration can cause numbness and tingling, chest pain, or elevated heart rate. Learn the science behind it and how Warrior Salt can help.
- Tea Vs Coffee
- english breakfast tea caffeine vs coffee - Bing Search - Intelligent search from Bing makes it easier to quickly find what you’re looking for and rewards you.
- English Breakfast tea typically contains about 40 to 70 mg of caffeine per 8-ounce cup, while coffee contains approximately 95 to 200 mg of caffeine per cup, making coffee the stronger option for a caffeine boost.
- Tea or coffee: which is better for you? - BBC Food - Brits love tea and coffee. They are the two beverages we drink most of in the UK but which one is best for us?
- This Is How Your Brain Becomes Addicted to Caffeine | Smithsonian magazine - Regular ingestion of the drug alters your brain’s chemical makeup, leading to fatigue, headaches and nausea if you try to quit
- english breakfast tea caffeine vs coffee - Bing Search - Intelligent search from Bing makes it easier to quickly find what you’re looking for and rewards you.
- Does drinking water make you hungry?
- Drinking water does not directly cause hunger and often acts as an appetite suppressant by filling the stomach and reducing the sensation of hunger. While it can temporarily increase metabolism, it is generally used to reduce caloric intake rather than increase it. Many people mistake thirst for hunger, so drinking water may alleviate feelings of hunger.
- Yes, drinking more water may help you lose weight | Hub - Water does more for the body than just quench your thirst—it might even help you drop some pounds
- Increasing water intake influences hunger and food preference, but does not reliably suppress energy intake in adults | ScienceDirect
- Increasing water intake is often purported to reduce energy intake, and is recommended as a weight loss strategy.
- The few experimental studies that have been conducted to verify these claims have examined the impact of a single pre-load of water before a meal.
- Can Drinking Water Help You Lose Weight? | Henry Ford Health - Detroit, MI - Weight loss advice often includes a tip to drink more water. But why? Learn how water affects hunger, metabolism and weight loss.
- The role of water in weight loss: does it help? | Jane Plan
- Many people believe that drinking more water can also help them shed unwanted pounds, but is this just another one of those weight loss myths?
- In this article, we explore the science behind water consumption for weight loss and share the optimal amount of water to drink for weight loss benefits.
Exercising
- Physical Activity Basics and Your Health | Physical Activity Basics | CDC - Benefits, recommendations, and tips for physical activity across the lifespan.
Exercises
- General
- 15 things Dua Lipa swears by to keep fit - How the singer exercises, eats and clears her mind
- Athlean-x Shares Dynamic Tension Method for Bodyweight Exercises - Athlean-X's Jeff Cavaliere shares seven of his top exercises to use dynamic tension for more gains.
- He's unimpressed with his physique, but wins bodybuilding competitions ... at 90 | Guinness World Records | The Guardian - Jim Arrington, who was recognized as the planet's oldest bodybuilder in 2015, explains how a'low opinion' motivated him
- Misc
- Rowing Machine : TECHNIQUE and BENEFITS - YouTube - Learn how to row so you can have an amazing low impact cardio workout. If your new to rowing or new to fitness rowing machine is a great low impact alternative to running for cardio exercise.
- Squats
- The stronger your thighs the longer you live - YouTube | WayWeMove - The stronger your thighs the longer you live
- Squatting is not an exercise. It is a resting position and pose showing the overall health of a body - YouTube | WayWeMove
- 10 squats instead of 10K steps. Join my workshop - 5 steps to your youth - YouTube | WayWeMove - Let's develop 5 main qualities of your body: strength, flexibility, mobility, plasticity and elasticity during my worship starting from 32 March.
- Push-Ups
- Abs
- Weight loss: Three at-home ab exercises to tone your stomach, improve posture and enhance performance
- Belly fat is more common as we age but a number of factors can be the cause of extra weight around the midriff.
- Speaking to GB News, an expert shared the best exercises to help you tone up.
- These will also help improve posture and enhance performance in other activities.
- Intense Abs Workout - 3-Move Advanced Abs Workout - It only takes five minutes.
- 15-Minute Abs Workout - YouTube | elfersp - A 15-minute abs workout with our own Coach Nicole!
- Weight loss: Three at-home ab exercises to tone your stomach, improve posture and enhance performance
- Kegels (Pelvic Floor muscle exercises)
- kegels for men | Google Search - No meta description
- Kegel exercises for men strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, aiding in bladder control, preventing urine leakage (incontinence), and improving sexual function (erectile dysfunction). Perform them by squeezing and holding the muscles that stop urine flow for 5–10 seconds, relaxing for the same time, repeating 10–20 times daily.
- How to Perform Kegel Exercises for Men
- Locate the Muscles: Identify your pelvic floor muscles by trying to stop your urine flow mid-stream or by tightening the muscles that keep you from passing gas.
- Perform the Squeeze: Tighten these muscles, hold for 5 seconds, and relax for 5 seconds.
- Repetitions: Aim for 10–20 repetitions per session.
- Frequency: Do 3–4 sessions per day, which can be done while sitting, standing, or lying down.
- Routine: Incorporate them into daily habits, such as during your morning commute, brushing teeth, or after urinating.
- Key Tips and Benefits
- Avoid Common Mistakes: Do not hold your breath or tighten your stomach, thighs, or buttocks during the exercise.
- Do Not Use While Urinating: Avoid performing Kegels while actively urinating, as this can weaken the muscles over time and lead to bladder issues.
- Results: Improvements in bladder control or erectile function can be seen within one to several months.
- Additional Benefits: They help treat dribbling after urination and improve sexual satisfaction.
- If you have trouble locating the muscles, a healthcare professional can assist with techniques like biofeedback or electrical stimulation.
- Kegel exercises for men: Understand the benefits - Mayo Clinic - Men can benefit from these exercises. Follow these tips to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles.
- Kegel exercises tips for men - Mayo Clinic Health System - Kegel exercises for men can help improve bladder control and improve sexual function. Here are tips for doing Kegel exercises correctly.
- How To Do Kegel Exercises For Men | Kegel8 - Did you know that Kegel Exercises For Men can help with a whole range of health issues too? Pelvic floor exercises are just as important for men as for women. Read our guide now.
- How to Do Kegel Exercises for Men - Prostate Cancer | UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center - Kegel exercises for men can help with the incontinence that is sometimes a result of prostate cancer treatment. Learn how to do Kegel exercises for men.
- Kegel Exercises for Men: Benefits & How To Do Them | Cleveland Clinic - Kegel exercises can benefit everyone by helping strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Learn more about Kegels and how they can benefit you.
- Kegel Exercises for Men: Do They Work? | healthline - Kegel exercises are used to treat a variety of conditions in women, but research suggests they may also help men. Learn how Kegel exercises might benefit you.
- The Benefits Of Kegel Exercises For Men | Superdrug Online Doctor - Kegel exercises strengthen the muscles around the pelvis, which can improve erections and orgasms for men. Learn more about the benefits of kegels for men
- How to Do Kegel Exercises for Men | Advanced Urology - Why do Kegel exercises and what are its benefits for men? To find out all the answers, it is essential to learn everything about Kegel exercises.
- Kegels Exercises For Men | LloydsPharmacy Online Doctor UK - Discover the benefits of Kegel exercises for men with our expert guide. Combat erectile dysfunction today with our effective pelvic floor movements.
- kegels for men | Google Search - No meta description
- Arnold Schwarzenegger
- How To Train For Mass | Arnold Schwarzenegger's Blueprint Training Program - YouTube - Learn some of Arnold Schwarzenegger's favorite classic bodybuilding exercises and preferred training techniques for building muscle. Get the knowledge you need to train for mass!
- Three game-changing muscle-building techniques from Arnold Schwarzenegger, 74 | Fit&Well - Three essential muscle-building tips from Arnold Schwarzenegger's long career
- Arnold Schwarzenegger's Fastest Way to Lose Belly Fat: Exclusive Interview & Fitness Tips - YouTube - Welcome to our special interview with the famous Arnold Schwarzenegger! In this fun and interesting chat, Arnold talks about the best and quickest ways to lose belly fat and shares helpful fitness tips for a healthy lifestyle. If you're looking for effective weight loss strategies, this video is for you.
- 21s Bicep Curls Workout - Arnold Schwarzenegger's Arm Finisher - This count-up series can build your guns and help to mix up your training for other muscle groups, too.
- The Evolution of Arnie's Training – and the Workouts Keeping Him Strong and Lean at 78 - After 60 years of lifting, Schwarzenegger's focus has shifted to 'staying lean and avoiding injury'
- Anatoly
- Anatoly Fit - Strength training, smart programming and results - Evidence-based strength training, smart programming, and long-term physical development. Articles, systems, and principles that actually work.
- Anatoly's secrets to powerlifting success: training, nutrition, and more! - YouTube - Want to know Anatoly's secrets? Discover the training and nutrition secrets behind Anatoly's incredible powerlifting success! You won't believe his simple yet effective approach!
- Anatoly Workout Routine & Diet | FitDominium
- Vladimir Shmondenko more commonly known as “Anatoly” on Youtube and other social media platforms is a Ukrainian lifter that is freakishly strong. While he may appear like your regular, fit guy, his strength exploits and pranks have propelled him to stardom.
- In this guide we will go over the full Anatoly workout routine and diet.
- How is Anatoly So Strong? A Deep Dive into His Strength - Curious about Anatoly's strength? Explore his training, diet, and mental strategies. Learn how Anatoly achieves his incredible power.
- Anatoly’s Workout Routine – Achieve Anatoly’s Strength! | PumpX - Welcome to Anatoly’s inspired Workout routine for maximum strength, where we detail the workout and methods!
- FINALLY Arnold Schwarzenegger Meets Anatoly - YouTube | Anatoly army
- Wolverine Diet and Training
- Wolverine Workout Part 1 - YouTube - Enjoy the videos and music that you love, upload original content and share it all with friends, family and the world on YouTube.
- "The Wolverine" 4 Week Diet & Training Transformation Challenge- Final Reveal - YouTube | Cosplay Chris - After 28 days of bland food and torturous training, the Wolverine 4 week diet and training transformation challenge is complete. Probably one of the most mentally and physically challenging things I've ever embarked upon. I'd like to do a follow up video on the exact diet and training process so let me know your thoughts. A
- "The Wolverine" Diet & Training Walkthrough - YouTube | Cosplay Chris - So as promised here is my step by step diet and training routine that I followed for four weeks that led to "The Wolverine" cosplay photo shoot.
Shopping / Where and What to Buy?
- When buying food
- Don't just go to the shop, you will buy junk.
- Plan your meals, then only buy what is needed, better still, order online and don't go to the shop.
- You should by at least 1 week's worth of stuff, after this fresh food might go off.
- MyProtein Product I have looked at:
- THE Electro | Electrolyte Tablets Myprotein UK
- £6.49 for 20 Tablets
- THE Electro | Electrolyte Sachets Myprotein UK
- £14.99 for 20 Sachets
- THE Electro - HYROX | Electrolyte Powder Myprotein UK
- £14.99 for 30 servings
- Extended periods of high-intensity exercise result in significant fluid loss through sweating, which depletes your stores of sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
- Research by B. Murray (2014) concluded that sodium is crucial for fluid retention and preventing dehydration, particularly during long durations of intense physical activity.(3)
- Replenishing these electrolytes with THE Electro after exercise, along with proper hydration, helps supports normal muscle function.(1,2 )
- Potassium contributes to normal muscle function
- Magnesium contributes to electrolyte balance
- Murray, B. (2014). Hydration and physical performance. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 26(5 Suppl), 542S-548S. doi:10.1080/07315724.2007.10719661
- THE Electropower | Creatine & Electrolytes Myprotein UK
- £21.99 for 30 servings
- THE Electro | Electrolyte Tablets Myprotein UK
- Amazon Products I have looked at:
- Vitamin B12 Tablets - 450 Tablets (1+ Year Supply) - 1 Per Day - 1000mcg - 6mm in Size - Easy to Swallow - Methylcobalamin Form - Vegan Vitamin B12 Supplement for Men & Women - Made in The UK : Amazon.co.uk: Health & Personal Care - Enjoy a long-lasting supply of high-potency 1000mcg methylcobalamin B12 tablets. Supports energy, metabolism, and overall health. Vegan-friendly, 450 tablets (1+ year).
- MyProtein Alternatives
- Dolphin Fitness - Shop from our extensive range of sports supplements, health and wellbeing products, novelty and specialist foods and drinks, and fitness accessories.
My QWcrm Notes
This is a temporary holding page for my QWcrm notes.
General Finance notes from J
- A paid invoice or expense is paid/closed/zero balanced, it stays closed. Once this transaction is done, it is done.
Vouchers
- MPV (Multi Purpose Voucher) = Gift Card
- SPV (Single Purpose Voucher) = Phone Card
Payment System
- Payment.php
- PaymentTypeCreditnote.php
- Payment Types controls the specific logic for the target of the payment eg: Creditnote, Expense, Invoice, Otherincome
- PaymentMethodCreditnote.php
- Payment Methods control the specific logic for the source of the payment eg: Cash, Cheques, Credit Notes, Other Incomes.....
- These will appear as available payment menthos on the payment page, filtered when required i.e. a creditnote cannot be used to pay for a credit note, same for Vouchers (giftcards/SPV/MPV)
Credit Notes
- What are they for
- General
- Add a credit note to reduce the amount you owe your supplier, or record a refund received from a supplier.
- There are a few types of credit note and are based on payment direction.
- These can be used like cash payments but are not included in financial calculations for the purpose of turnover, profit or tax.
- Once an invoice or expense has been closed, and this also applies when closed with a credit note, it stays closed, this transaction is complete. Future refunds and credits can reference an invoice or expense but not change those transactions.
- A credit note is issued or received referenced to an expense or invoice it doe snot alter it. The credit will sit on a client or supplier to be used on a later
- When a sales credit note is issued
- A credit note can be used to clear a balance on a partial or zero paid invoice or expense without using real money.
- A credit note in QWcrm allows you to split it between real payments (refunds) and credit that can be used on other things you sell.
- Types (What are they for specifically)
- Sales Credit Note (Client)
- Store credit for a client, no attached invoice, a gesture of goodwill etc..
- Sales Credit Note (Invoice)
- Can use these to zero out a client invoice that is unpaid or zero paid without using a real payment.
- Purchase Credit Note (Supplier)
- A supplier sends you this to give you store credit and will NOT be attached/referenced to an invoice.
- These will be an uncommon thing but still exist.
- This can be applied to a future expense from this supplier.
- Purchase Credit Note (Expense)
- A supplier sends you this to give you store credit and will be attached/referenced to an invoice.
- This can be applied to a future expense from this supplier.
- Sales Credit Note (Client)
- General
- Button Locations
- client:details
- Sales Credit Note (Client)
- No restrictions
- Controlled by
creditnote::checkRecordCanBeCreated() - Used to refund real money to a client without an invoice, or they can use the credit to purchase other items
- Sales Credit Note (Client)
- invoice:details
- Sales Credit Note (Invoice)
- Must have an invoice_id and have == 0 balance
- Controlled by
creditnote::checkRecordCanBeCreated() - Used to close invoices with outstanding balances without accepting or sending real money
- Sales Credit Note (Invoice)
- supplier:details
- Purchase Credit Note (Supplier)
- No restrictions
- Controlled by
creditnote::checkRecordCanBeCreated() - Used to reduce the amount you owe your supplier, or record a refund received from a supplier.
- The refund can be in the form of credit with the supplier (via their credit note system) or a real payment such as cash or bank transfer.
- Purchase Credit Note (Supplier)
- expense:details
- Purchase Credit Note (Expense)
- Must have an expense_id and have == 0 balance
- Controlled by
creditnote::checkRecordCanBeCreated() - Used to reduce the amount you owe on an expense, or record a refund received from a supplier against an expense.
- The refund can be in the form of credit with the supplier (via their credit note system) or a real payment such as cash or bank transfer.
- Purchase Credit Note (Expense)
- creditnote:details
- Record Refund / Refund to Client
- assign a real payment to the client ? or supplier
{if ($creditnote_details.status == 'unused' || $creditnote_details.status == 'partially_used') && $creditnote_details.client_id}- This allows you to record sending real money to a client or supplier.
- Apply Credit Note to Invoice
- Use the credit note as payment on an invoice
{if $creditnote_details.status == 'unused' && $creditnote_details.invoice_id}- This allows you to easily use the credit note as a payment against the invoice specified on the credit note.
- This is the same as: the Invoice --> Apply Payment --> Select Credit Note and fill in the CR details.
- Apply Credit Note to Expense
- Use the credit note as payment on an expense
{if $creditnote_details.status == 'unused' && $creditnote_details.expense_id}- This allows you to easily use the credit note as a payment against the expense specified on the credit note.
- This is the same as: the Expense --> Apply Payment --> Select Credit Note and fill in the CR details.
- Record Refund / Refund to Client
- client:details
Creditnote::checkRecordCanBeCreated()- This functions checks if this type of credit note is allowed, it is not currently checking if the credit note will be applied successfully.
- Different Credit notes process types (do I need a standalone version)
- Sales Credit Note (Standalone) - (client:details)
- Used to refund real money to a client without an invoice, or they can use the credit to purchase other items
- Sales Credit Note - (invoice:details)
- Used to close invoices with outstanding balances without accepting or sending real money
- Purchase Credit Note (Standalone) - (supplier:details)
- Used to refund real money to a supplier without an expense, or they can use the credit to purchase other items
- Used to record a refund from a supplier without a related expense.
- The refund can be in the form of credit with the supplier (via their credit note system) or a real payment such as cash or bank transfer.
- Purchase Credit Note - (expense:details)
- Used to record a refund from a supplier with a related expense (eg: parts and services).
- The refund can be in the form of credit with the supplier (via their credit note system) or a real payment such as cash or bank transfer.
- Sales Credit Note (Standalone) - (client:details)
Payment::getCreditnoteActionTypes()- Gets the different CR types from the DB
- sales_apply => Sales Apply
- sales_refund => Sales Refund
- purchase_apply => Purchase Apply
- purchase_refund => Purchase Refund
- Gets the different CR types from the DB
- Links (might need sorting)
- Add a supplier credit note | Xero Central
- Add a credit note to reduce the amount you owe your supplier, or record a refund received from a supplier.
- How do you allocate a payment to a credit note? | Xero Central
- Create a Sales credit note in Xero for the refund amount, and then allocate the credit against one of the invoices. Then the total they paid will match your total invoices.
- Add a supplier credit note | Xero Central
How To (in QWcrm)
- Invoice partially paid (dead guy scenario)
- Invoice fully paid - refund
- Invoice partially paid - refund
- Expense fully paid - refund
- Expense partially paid - refund
- Store Credit - Using credit notes not giftcard.
Credit note Q and A from J
- Close with a sales invoice, then raise a standalone creditnote for a refund? or are they tied in some how?
- Do i need a credit note system for expenses?
- = Yes, otherwise how would i record refunds
- When you get a refund from a supplier you can add it as a cash payment, you do not have to use the credit note system but this will lack full tracking and is only for small transactions such as `Petty Cash` transactions.
- Do i need a credit note system for otherincomes? if I dont get the money, there is no other income?
- = No, you would only enter this when you get the money, not before.
- How to handle an expense with part payment?
- Post as cash received, i.e. cash ??
- How to refund a part paid expense
- zero the balance with a CR (using non-standalone via expense:details)
- refund the real payments by the client via another credit note
- Dead guy scenario - has only paid half of his bill but is now dead, how do i write off his balance
- = `Sales Credit Note` to zero the balance on the invoice. No real money will be used but I can close the invoice and it no longer annoy me.
- Credit note = Credit towards a cost
- Credit note must be attached to a purchase invoice or sales invoice
- A debit note can be used to add a payments.
- I am not sure what these are, or if needed.
My Ventoy Notes
My Ventoy notes.
Misc
- Upgrade Ventoy on USB: Easy step-by-step guide - YouTube | Bootable USBs
- Learn how to safely update Ventoy to the latest version on your USB drive. This step-by-step tutorial will show you how to maintain configurations, update iso files, and ensure compatibility with Windows 11.
- Discover the seamless way to keep your Ventoy USB drive up-to-date without losing any of your stored ISO files or configurations! This easy-to-follow tutorial walks you through the process of updating Ventoy to the latest version, ensuring a smooth transition while keeping all your data intact.
- Whether you're a first-timer or an experienced user, this guide is designed to help you upgrade your bootable USB with ease and confidence. Stay ahead with the newest features and improvements of Ventoy - watch now and update like a pro!
- Ventoy Disk Layout / Technicals
- Ventoy Disk Layout In MBR | Ventoy
- This shows how a Venoty USB drive is layed out.
- Why MBR?: MBR is the only selection in order to support Legacy BIOS system.
- Legacy BIOS Access Range Limitation | Ventoy
- When booting from legacy, there is a limit of 137GB. So if that's the case with the BIOS in your machine and you install Ventoy into a USB drive with large capacity(e.g. 256GB), you will run into problem when booting.
- There is an access limitation in some Legacy BIOS of some vendors. For example, some Legacy BIOS can't read the disk beyond 137GB. If you search "Legacy BIOS 137GB" in the internet, you will get many informations about that.
- Ventoy Disk Layout In MBR | Ventoy
- Plugins
- Windows VHD Boot Plugin | Ventoy
- Ventoy use this plugin to boot VHD(x) files with Windows 7+ in it.
- Both Legacy BIOS and UEFI are supported. Both fixed and dynamic VHD(x) are supported.
- For Windows 10 v1809+, in addition to NTFS, VHD(X) files can also be stored in the exFAT partition.
- [Shared] Windows 10 v1903 (19H1) supports exFAT+VHD(X) mode | wuyou.net
- How to boot Windows 10 VHD with ventoy at exFat partition (Windows VHD Boot Plugin) - YouTube
- In this video, I Am about to show you how to boot Windows 10 VHD from ventoy, relying on the exFAT file system.
- Since the FAT/exFAT file system, commonly used in flash storage media such as large-capacity U Disks and USB Drives. and Windows 10 1903, has been able to mount native support for VDH / VHDX virtual disk files from FAT/exFAT partitions. We can use this feature and format the windows partition to the exFAT file system to be able to boot the VHD using ventoy.
- Note:
- Use Win10 v1903 or higher (20H2 in this project used).
- It will be slower than the exFAT startup speed in the traditional model, even NTFS.
- VHD boot only supports dual NTFS or exFAT, doesn't support NTFS in exFAT, or versa.
- the virtual disk can be fixed or dynamic size but recommended to use fixed if there is no space problem
- Windows VHD Boot Plugin | Ventoy
Settings
- Set Tree View as default
- You can configure Ventoy to always show folders by adding/modifying the
ventoy.jsonfile with the following code:{ "menu_style": "tree" } - Place this file in the ventoy folder on your USB drive.
- F3 will toggle the view irrespective of this file
- You can configure Ventoy to always show folders by adding/modifying the
Upgrading the VHV/VHDX plugin
Current Issues
- either Windows 11 or my Lenovo laptop (and its drivers) are used and not compatible with my other machines, or DiskGenius does not like building a WinPE based on Windows 11.
- Win10 WinPE Rufus images will not load, winload.exe error.
- the VHD plugin needs updating to use the latest DLL etc..
- Ventoy VHDX plugin might not like my Windows11 WinPE as it moans about Partition1 being on exFAT and not NTFS.
Instructions
- Get the current Windows 10 plugin and upgrade the various files with those from my Windows 11 Pro PC. Ypu could use those from a Windows 11 Pro DVD if you do not have a live up to data system
Links
- ventoy_wimboot.img Plugin | Ventoy Forum
- change
wimboot.imgtowimboot.iso, use UltraISO to overwrite yourboot.sdiand save thewimboot.isofile, then changewimboot.isotowimboot.img - You can replace
bootmgrinventoy_wimboot.imgwithbootmgrin standardwindows11.isoand it's ok. - You can download
ventoy.wimboot.imgupdated by me as I shared here https://drive.google.com/file/d/1izQc322ZsE5InRSJaZ5CXatUlDUizcWH/view?usp=sharing - you have to get
bootmgrin standardwindows11.isofrom Microsoft - Your finding is correct, the name
bootmgrmust be capitalized asBOOTMGR - The plugin IMG are ISO images.
- change
- GitHub - ventoy/vhdiso - VHD boot template.
- [SOLVED] What is the purpose of efiboot.img on the live DVD? / Kernel & Hardware / Arch Linux Forums
- I have noticed that there is a filesystem image EFI/archiso/efiboot.img on the Arch ISO, which contains an EFI booting mechanism, and a kernel (which is the exact same kernel as in arch/boot/x86_64/).
- My question is why this image and the extra kernel are needed, as the root of the ISO already contains an EFI booting mechanism?
- bootvhd.dll file | dllsearch.net - According to our database, the bootvhd.dll file is part of the Microsoft Windows Operating System product, so the bootvhd.dll file may get onto your computer through the installation of Microsoft Windows Operating System.
- GitHub - lyshie/vhd-boot-dispatch - Windows Native VHD Boot and Dispatch.
Pictures of failed loads (old VHD plugin)
Ventoy Warning - Partition1 (exfat) is Not ntfs, the VHD(X) file may not boot normally
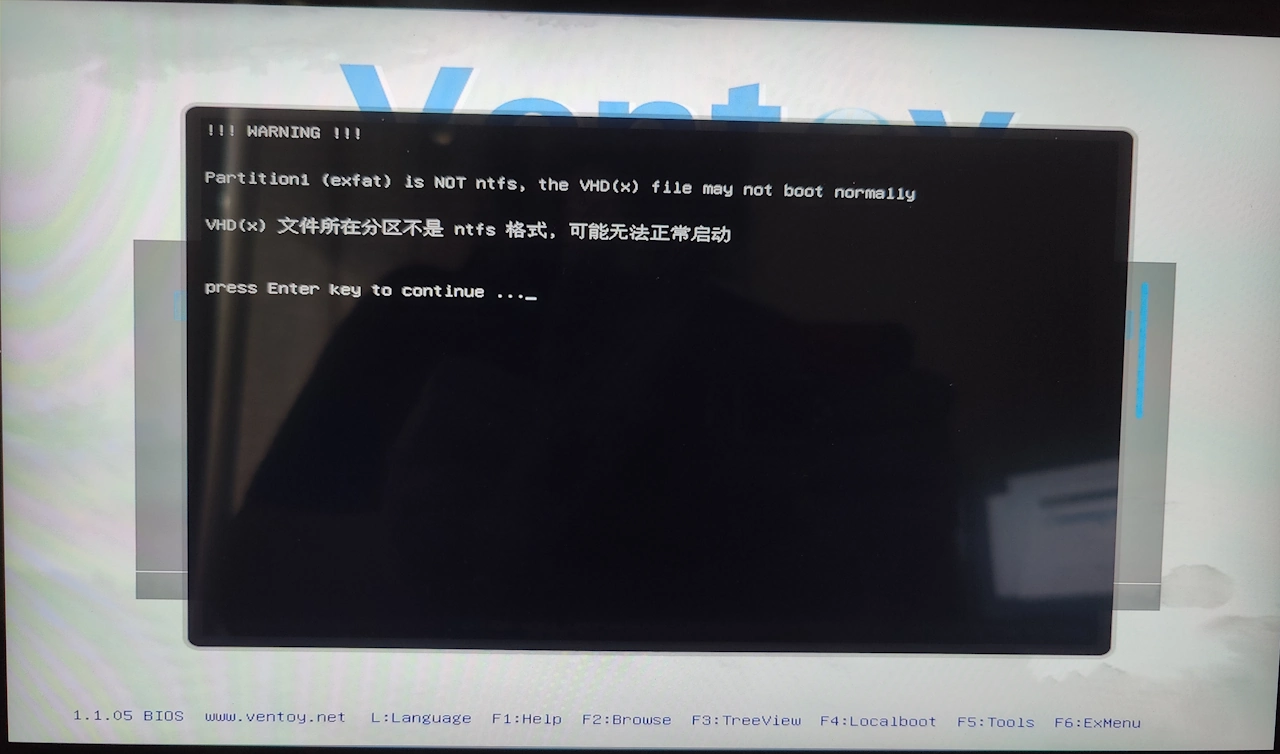
Windows Boot Manager - Boot from VHD
Windows Boot Manager - winload.exe missing
Rebuild the Windows Search Index
Rebuilding the Windows Search Index, which includes the Outlook Search, can resolve various issues:
- Windows Explorer does not responding but crashes or restarts.
- Whenever Windows Explorer is opened, it freezes and shows the "App Not Responding" dialogue. Then it crashes or shows the contents of the folder I clicked and freezes afterwards.
- Slow searching.
- Missing items in the index.
- Having trouble finding emails in Outlook?
- Is your search returning incomplete or incorrect results?
- If you search for items in Outlook and don't receive the results that you expect.
View the Index and it's Status
There are several ways and places to view the search index properties and its progress in rebuilding. After you have wiped your index it is useful to see how things are going.
- Indexing Options (Classic)
- This will only show how many items are indexed and if there is indexing in progress. There are a few ways to view this window:
- Windows Key + I --> Privacy & security --> Search --> Find my files --> Classic --> Customise search locations
- Open Start menu and type: Indexing Options
- Outlook 2021 --> File --> Options --> Search --> Sources --> Indexing Options
- This will only show how many items are indexed and if there is indexing in progress. There are a few ways to view this window:
- Windows Search (New)
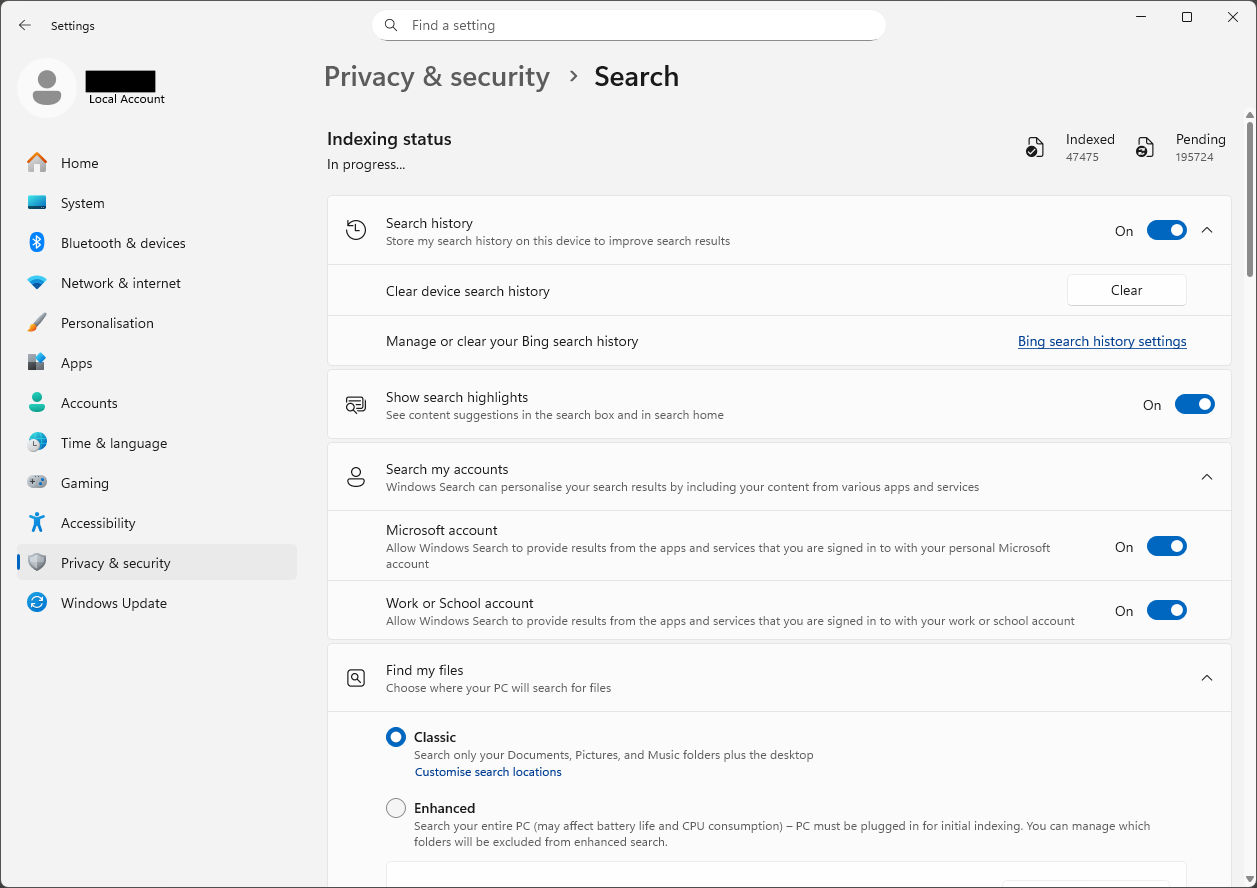
- Windows Key + I --> Privacy & security --> Search
- Now look at the top of the page and you will see the number of Indexed items and Pending counter.
- Outlook Search Index
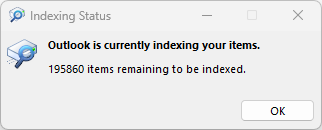
- This will shows you how many items left to be indexed
- Click in the search box
- Toolbar --> Search Tab --> Search Tools --> Indexing status
Make Indexing faster
- Instructions from here: How to Enable or Disable Indexer Backoff in Windows | Windows 10 Forums
Disabling the indexer backoff will allow indexing to finish faster while you're active on the computer instead, but it will use more system resources.
- Run
gpedit.msc - Navigate to: Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Search: Disable indexer backoff:
- Set it to
On(Default isOff) - Restart the Windows Search service
- Once your index is rebuilt, set Disable indexer backoff to
Offand restart the Windows Search service.
Make Sure Outlook Emails are Indexed
- This only applies if you have Microsoft Outlook the client installed on your PC
- Instructions from here: Outlook 2021 indexing not working - Microsoft Q&A
We need to ensure that Outlook is on the Windows Search Index
- Open Outlook
- Navigate to File --> Options --> Outlook Options --> Search --> Indexing Options
- Make sure Outlook is selected.
- Completely restart Outlook to fix minor glitches that may be affecting the search function.
Outlook items are only indexed when Outlook is open
- Once I opened Outlook and viewed the indexing progress, the number of items pending to be indexed went up, and kept going up for a while. Indexed items started increasing aswell.
- Once the items are indexed, you do not need Outlook open.
Reset Excluded Folders and Rebuild the Search Index
- I did not write this script
- Source: how to delete all exclude folders in search indexer and revert it to default? - Microsoft Q&A
- You can remove the bits from the script that you don't want to perform (Delete database | Reset Folder exclusions).
The following Powershell script fixes a lot of issue with the Windows search and is what I used.
- You can reset everything (exclusions, index database, config) back to default using this PowerShell script. It bypasses the broken GUI and directly clears both the index data and registry entries:
- This will fully wipe the Search Indexer state and restore clean defaults.
- After a reboot, Windows will begin re-indexing only the standard folders.
- A reboot is not needed, but I did it anyway.
- You should open Outlook now so all of it's emails can get indexed.
# Stop Windows Search Service Stop-Service -Name WSearch # Delete the current search index database and configuration Remove-Item -Path "$env:ProgramData\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows" -Recurse -Force Remove-Item -Path "$env:ProgramData\Microsoft\Search\Data\Temp" -Recurse -Force # Optional: Reset registry exclusions (set back to defaults) Remove-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search\Gather\Windows\SystemIndex\Sites\LocalHost" -Name "DefaultGatherPolicy" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue Remove-Item -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search\Gather\Windows\SystemIndex\Sites\LocalHost\Paths" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue # Start Search Service Start-Service -Name WSearch
Notes
- If any exclusions still reappear, it means they’re being pushed by a policy or a background process.
- It adds all of the users folders in rather than specifying document and picture folders which is the default configuration of a new Windows PC/Profile.
- This old arrangement that I had (separate Document, Picture, Video folders etc..) listed in the index might of been because my system was upgraded from previous Windows versions (XP --> Win7 --> Win10 --> Win11)
Links
- General
- Enable or Disable Enhanced Mode for Windows Search in Windows 10 & 11 - MajorGeeks
- Windows 10 has added many settings to manage Windows Search. By default, Classic mode is on by default, which only searches your libraries and Desktop. The Enhanced mode can search your entire PC.
- In this tutorial, we help you choose between the two and customize Windows 10 & 11 Search.
- Weird looking paths get added to Windows 10 search index and break search - Super User
- A few times in last weeks I have noticed that search from start menu wont find any files. Simply rebuilding the index did not fix this. Looking deeper into indexing settings I found that there was strange looking path being included in the index, one that I had not put there.
- CSC stands for "Client Side Cache" which is used to hold Offline Files. These are local copies of files that exist on SMB shares like mapped network drives. By default, Windows indexes the CSC so that you can quickly find any network files that you've opened recently. The CSC index can become corrupt and put a full bork on indexing.
- Enable or Disable Enhanced Mode for Windows Search in Windows 10 & 11 - MajorGeeks
- Explorer Crashing
- Windows Explorer Not Responding But Crashes or Restarts (Windows 11) - Super User
- Whenever Windows Explorer is opened, it freezes and shows the "App Not Responding" dialogue. Then it crashes or shows the contents of the folder I clicked and freezes afterwards.
- Solution is to rebuild the Windows Search index
- This thread also goes through how this solution was reached.
- Windows Explorer Not Responding But Crashes or Restarts (Windows 11) - Super User
- Rebuild the Windows Search Index
- how to delete all exclude folders in search indexer and revert it to default? - Microsoft Q&A
- This has a Powershell and a Batch script method.
- This is the additional batch file, just in-case it goes offline. I have not used it.
sc config wsearch start= disabled net stop wsearch REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search" /v SetupCompletedSuccessfully /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f del "%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.edb" /a del "%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.db" /a sc config wsearch start= delayed-auto net start wsearch :: reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search\Gathering Manager" :: reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search" reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search\Gathering Manager" /v *path reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search" /v *dir* reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WSearch" icacls %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\ icacls %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Temp\ icacls %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications icacls %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows PAUSE PAUSE
- How to Reset Windows Search in Windows 11 | NinjaOne - Reset Windows Search to fix slow search and missing results. Use PowerShell, Registry Editor, Control Panel, and other methods to restore search speed.
- Reset and Rebuild Search Index in Windows 11 | Windows 11 Forum
- This tutorial will show you how to manually reset and rebuild the search index for accurate search results in Windows 11.
- How to Delete and Rebuild the Windows 10 & 11 Search Index - MajorGeeks
- Windows 10 keeps an index of all your searches so that you can get the fastest search results.
- If you find that you're getting slow, missing, or incorrect results than it might be time to delete and rebuild your search index.
- How to rebuild Search Index in Windows 11 | TheWindowsClub - You can reset, repair, rebuild Search Index in Windows 11/10 via Indexing Option Control Panel applet or by using this BAT file. Learn how.
- how to delete all exclude folders in search indexer and revert it to default? - Microsoft Q&A
- Rebuild the Outlook Search Index
- How to Rebuild Your Search Index on Microsoft Outlook [TUTORIAL] - YouTube
- Having trouble finding emails in Outlook? Is your search returning incomplete or incorrect results?
- It might be time to rebuild your Outlook search index!
- In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the exact steps to fix Outlook search issues by resetting and rebuilding the indexing system — a fast and effective way to bring back accurate and lightning-fast results.
- How to Rebuild the Outlook Search Index (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Fix Outlook search issues! Rebuild your search index on Windows, Mac, or Exchange to restore accurate and fast search results.
- This guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions for rebuilding the index on Windows and Mac systems, as well as for Exchange environments.
- How to Rebuild Your Search Index on Microsoft Outlook [TUTORIAL] - YouTube
- Troubleshooting Indexing Issues
- Fix Windows 11 Indexing Issues: Troubleshooting Guide | Windows Forum
- Indexing issues on Windows 11 can be as frustrating as a stubborn jam at your favorite coffee machine—especially when you're trying to search for that elusive file during a crunch time.
- Windows indexing is the unsung hero that catalogs file properties and metadata to ensure speedy searches, but sometimes it just refuses to play ball.
- If you're encountering the notorious message “Indexing is not running” or noticing that your searches start only to stall mid-air, you're not alone.
- Here’s a deep dive into why this happens and how you can get your indexing service back on track.
- Run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter:
msdt.exe -ep WindowsHelp id SearchDiagnostic
- Fix Windows 11 Indexing Issues: Troubleshooting Guide | Windows Forum
- Outlook Search Not Working
- Outlook Search Isn't Working? Here's How to Fix It | How-To Geek
- Those emails didn't just disappear.
- Ensure Outlook is on the Windows search index. Open Outlook, then navigate to FIle > Options > Outlook Options > Search > Indexing Options, and make sure Outlook is selected.
- Completely restart Outlook to fix minor glitches that may be affecting the search function.
- Try using the Search and Indexing troubleshooter or update Outlook to resolve search-related issues.
- Outlook 2021 indexing not working - Microsoft Q&A
- After installation of outlook 2021 all the mails have been downloaded but I am not able to search any mail through search bar. indexing not working after rebuild database.
- Run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter:
msdt.exe -ep WindowsHelp id SearchDiagnostic
- Outlook Search Isn't Working? Here's How to Fix It | How-To Geek
- Disable Indexing
- Does disabling Windows search indexing speed up your computer? - Quora
- Disabling Windows Search indexing can potentially speed up your computer, particularly if you have a slower hard drive (HDD) or limited system resources. Here are some factors to consider:
- How to Disable Indexing in Windows 10 & 11 - MajorGeeks - After upgrading to Windows 11, I noticed that my drive was indexed even though I had disabled it previously. Here's how to disable indexing on your hard drive.
- Does disabling Windows search indexing speed up your computer? - Quora
- Make Indexing Faster
- Force Windows indexing to run faster - Office Watch - You can make Windows Search index your documents and Outlook data faster and 'catch up' indexing your documents, pictures and emails.
- How to Enable or Disable Indexer Backoff in Windows | Windows 10 Forums
- By default, the search indexer backoff feature will reduce indexing speed while rebuilding the index when there is user activity, and will automatically continue at full speed when no user activity is detected.
- If indexer backoff is disabled, indexing will continue at full speed even when system activity is high.
- Excluded or Included Folders
- This Excluded or Included depends on whether you are using the Classic or the Enhanced version of Windows Search.
- Add or Remove Search Index Locations in Windows 11 | Windows 11 Forum
- This tutorial will show you how to add or remove locations to be excluded or included in the search index in Windows 11.
- Microsoft is beginning to roll out a change that brings those two settings pages together so you can easily access to all the Windows Search settings under a single settings page via Settings > Privacy & security > Search.
- How to stop Windows Search from auto-excluding repository folders? - Super User
- Windows search indexer is adding most paths to repository folders (both .git and .svn) to the exclusion list.
- I can remove them manually of course, but each time I rebuild the index - they are re-added.
- I can add them as indexed locations, but I'd have to do that each and every time I add a new repository and I add them in varying locations depending on relation.
- Why is Windows excluding these and how can I alter that behavior?
- search indexing - How to reset and clear all previous Windows Index config? - Super User
- This is where Windows Indexing rules (exclusions) are located in the registry, which are not only easier to manage/export/import, but are reflected in Windows Settings awful UX for this:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search\CrawlScopeManager\Windows\SystemIndex\WorkingSetRules\ and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search\Gather\Windows\SystemIndex\Sites\LocalHost\Paths\
- This is where Windows Indexing rules (exclusions) are located in the registry, which are not only easier to manage/export/import, but are reflected in Windows Settings awful UX for this:
- Hide Files and Folders from Search Results in Windows 11 | TheWindowsClub - In this article, we will demonstrate how you can hide files and folders from your Search Results in Windows 11 or Windows 10.
My FFmpeg Notes
A collection of my FFmpeg notes
Downloading the Windows Binaries
Getting the right version can be tricky unless you know what file to download and why, but that is easy to explain.
TL;DR
- Download the latest "Full" release build from: Release Builds - CODEX FFMPEG @ gyan.dev
- The binaries have everything they need compiled into them.
- The binaries are self contained.
Static vs. Shared Builds
In general, when you compile a binary, you may prefer to include its dependencies (Static) so that users don't need to search for external dlls aftermath, or try to use the executable with an incompatible version of the dll, but it means that the same dll will have to be present in all executables that need them, so that the whole software will use more room on the HD. Shared versions are likely to save some space, but I presume they are not significantly faster than others. It is useful just to explain the difference between the two compiling types.
- Static build (essentials, full):
- The
.exe(on Windows) or binary contains all libraries compiled inside it. - Easier to use — you just download, extract, and run
ffmpeg.exe. - Bigger file size, less flexible if you want to swap/update libraries individually.
- Each binary has the required libraries and DLLs compiled in, each binary is therefore self contained and needs nothing else to run.
- All components and libraries reside in the EXE file. So, it is self-contained.
- The
- Shared build (full shared):
- The binary depends on separate
.dll(on Windows) or.so(on Linux) library files. - The main
ffmpeg.exeis smaller, but it requires those external files to run. - More modular: you can update or replace individual codec libraries without rebuilding FFmpeg.
- Useful for developers embedding FFmpeg into other applications.
- Less portable: you can’t just copy
ffmpeg.exealone to another PC — you also need all the matching DLLs. - Each ffmpeg library resides in a separate DLL, and the ffmpeg binaries (ffmpeg.exe ..etc) link to these libraries i.e. locate and access their capabilities only during execution. However, 3rd party libs are statically linked with the corresponding ffmpeg lib.e.g. libx264 resides inside avcodec.dll
- The DLLs should be in your path or same folder as the EXE. Saves space but if you have multiple av*.dll in your path, due to older versions or other builds, that is liable to create problems.
- Shared "shares" the DLLs and libraries between ffmpeg, ffprobe and ffplay.
- You’ll usually see several folders:
bin\→ containsffmpeg.exe,ffplay.exe,ffprobe.exe, and.dllfiles.lib\→ contains development libraries (.a,.lib) for compiling against FFmpeg.include\→ header files for developers.
- The binary depends on separate
What Version of FFmpeg should I download?
- Essentials
- Use case: Support features in a program like Krita or Blender
- A minimal build of FFmpeg that includes the most widely used codecs and features.
- Includes:
- Common encoders/decoders like H.264 (via libx264), AAC, MP3, VP9, etc.
- Basic formats and filters needed for everyday media conversion.
- Full
- Use case: Just converting media for personal use?
- All formats, filters, encoders and decoders are included.
- Full Shared
- Use case: Developing software or need modular updates.
- Same functionality as "Full"
- Do not use this version if you are not a software developer, otherwise you may encounter missing xxx.dll errors.
How to get the latest build for Windows
- Check the latest release version number from here.
- Go to this website for a Windows compiled release: Release Builds - CODEX FFMPEG @ gyan.dev
- Download the latest release build of the "
Full" version.
Links
- Official Sites
- FFmpeg - A complete, cross-platform solution to record, convert and stream audio and video.
- FFmpeg/Changelog at master · FFmpeg/FFmpeg · GitHub
- Which Version
- Which FFmpeg Version Should I Download on Windows? | pyVideoTrans-Open Source Video Translation Tool - Detailed Explanation of Each Version and when you should use each one.
- Where to download windows Binaries
- Builds - CODEX FFMPEG @ gyan.dev - FFmpeg binaries of Windows
- How to Install on Windows
- How to Install FFmpeg on Windows - GeeksforGeeks
- In this guide, we're going to explain how you can download and install FFmpeg on Windows 10 and 11.
- How to Install FFmpeg on Windows - GeeksforGeeks
- GUI
- 12 Best FFmpeg GUI for Windows 10/11 (Free Download 2025)
- Find the best FFmpeg GUI for Windows 10/11.
- Our 2025 guide covers 12 free tools.
- No command line needed!
- clever FFmpeg-GUI 3.4.5 Download Free - VideoHelp
- Clever FFmpeg GUI is a small, but smart GUI for FFmpeg.
- It processes Audio and Video streams separately. These can be muxed after processing.
- It's for Windows Systems, portable, x86 and x64.
- GitHub - MattMcManis/Axiom
- An FFmpeg GUI for Windows.
- Old
- GitHub - mifi/lossless-cut
- The swiss army knife of lossless video/audio editing
- LosslessCut aims to be the ultimate cross platform FFmpeg GUI for extremely fast and lossless operations on video, audio, subtitle and other related media files.
- The main feature is lossless trimming and cutting of video and audio files, which is great for saving space by rough-cutting your large video files taken from a video camera, GoPro, drone, etc.
- It lets you quickly extract the good parts from your videos and discard many gigabytes of data without doing a slow re-encode and thereby losing quality.
- 12 Best FFmpeg GUI for Windows 10/11 (Free Download 2025)
- Conversion Tutorials
- FFmpeg: Convert audio streams to AC3 – The Tech Blog
- A walk through on how to do the conversion using FFmpeg.
- How do i use FFmpeg to convert my
MKAtoFLACfiles, but keep the MKA containermkvtoolnixdoes not transcode.- If (and only if) original contents inside the
.mkafile is FLAC audio, you can useffmpegto copy the FLAC audio from the.mkafile into a FLAC container.ffmpeg -i SOURCE.mka -codec:a copy DESTINATION.flac
- If original contents is not FLAC, you can use
ffmpegtoo but there'll be a conversion:ffmpeg -i SOURCE.mka -codec:a flac DESTINATION.flac
- A quick guide to using FFmpeg to convert media files | Opensource.com
- There are many open source tools out there for editing, tweaking, and converting multimedia into exactly what you need.
- Simple and well explained instructions.
- FFmpeg: Convert audio streams to AC3 – The Tech Blog
Repairing Media Files
You’ve got an AEA audio file (Sony ATRAC encapsulation, usually .aea), and while VLC can play it, MKVToolNix won’t accept it — which strongly suggests that the container header is damaged or malformed, even if the raw audio stream is intact. Here are some free/open-source tools and workflows you can try to “repair” or rewrap it into something MKVToolNix will accept:
1. FFmpeg (best first try)
- FFmpeg is usually the most effective way to “rewrap” or re-encode damaged media.
- Since VLC can play it, FFmpeg should also be able to read it.
Try first a straight rewrap (no re-encoding):
ffmpeg -i input.aea -c copy output.wav
or
ffmpeg -i input.aea -c copy output.mka
If the header is corrupt, FFmpeg might still balk. In that case, force stream copy with re-indexing:
ffmpeg -err_detect ignore_err -i input.aea -c copy fixed.mka
If that still doesn’t work, do a lossless re-encode to WAV (PCM):
ffmpeg -i input.aea -c:a pcm_s16le output.wav
Once you have a WAV/FLAC/MKA, MKVToolNix should accept it.
2. SoX (Sound eXchange)
- Another open-source audio utility, great at handling raw audio.
- If FFmpeg struggles, you can try:
sox input.aea output.wav
3. Audacity (GUI method)
- Free, open-source audio editor.
- Import the
.aeainto Audacity (it uses FFmpeg under the hood), then export as WAV/FLAC. - This bypasses container issues and ensures you get a clean audio file.
4. Re-mux with mkvmerge directly
- Sometimes MKVToolNix GUI rejects files that
mkvmerge(the CLI tool) can still handle.
Try:
mkvmerge -o output.mkv --no-video input.aea
My recommendation: Start with FFmpeg (method 1). If -c copy fails, re-encode to WAV/FLAC and then mux that into MKV. Do you want me to give you a one-liner FFmpeg command that will automatically fix/dump to WAV even if the header is bad, so you can drag it straight into MKVToolNix? you want to keep the original audio stream untouched (no re-encoding). That means we need to focus on remuxing/repairing the container only.
1. FFmpeg (copy mode, no re-encode)
This is the safest first step:
ffmpeg -i input.aea -c copy output.mka
-c copy= stream copy (no re-encoding).mka(Matroska Audio) is usually well-accepted by MKVToolNix.
If the header is damaged, you can try forcing FFmpeg to ignore errors:
ffmpeg -err_detect ignore_err -i input.aea -c copy fixed.mka
2. Try mkvmerge directly
Even if MKVToolNix GUI rejects it, the CLI might succeed:
mkvmerge -o output.mka input.aea
or
mkvmerge -o output.mkv --no-video input.aea
3. Container rewrap (raw stream copy)
If FFmpeg can demux the stream but not mux it properly, you could dump the raw stream first:
ffmpeg -i input.aea -c copy output.oma
(.oma is another ATRAC container Sony used; Matroska often accepts it better.)
Then try adding output.oma into MKVToolNix. If all copy-only methods fail, the problem may be that the damaged AEA header prevents FFmpeg from identifying the stream type. In that case, we’d need to manually specify the codec during remuxing (still without re-encoding). Do you want me to write you an FFmpeg command that forces the codec identification (e.g., ATRAC3/ATRAC9) so it can copy the stream even if the header is broken? Perfect ? If the AEA header is damaged, FFmpeg may fail to guess the codec, but you can force it to treat the stream as ATRAC and just remux without re-encoding.
1. Identify the codec
Run:
ffmpeg -i input.aea
- Even if it errors out, FFmpeg usually prints something like:
Stream #0:0: Audio: atrac3 (or atrac3plus / atrac9), 44100 Hz, stereo
Note the codec name (likely atrac3 or atrac3plus).
2. Force remux with codec copy
Once you know the codec, run:
ffmpeg -f aea -i input.aea -c:a copy -map 0 output.mka
-f aea→ forces FFmpeg to read as AEA format.-c:a copy→ copies the stream without re-encoding.-map 0→ ensures all streams are included.output.mka→ Matroska Audio container, friendly for MKVToolNix.
3. If FFmpeg still fails to guess properly
You can force the codec by specifying it:
ffmpeg -f aea -i input.aea -c:a copy -acodec atrac3 fixed.mka
(or -acodec atrac3plus depending on what you saw in step 1). This way, you keep the original audio untouched, just rewrapped into .mka so MKVToolNix can accept it.
Do you want me to also show you how to probe the file with ffprobe to be 100% sure which ATRAC variant you’ve got before running the copy?
what is ffprobe ffprobe is a companion tool to FFmpeg.
- Where
ffmpegconverts or remuxes media, ffprobeanalyzes media and prints detailed info about streams, codecs, metadata, bitrates, etc.
It’s included automatically when you install FFmpeg (same download).
Example usage
ffprobe input.aea
You’ll see output something like:
Input #0, aea, from 'input.aea': Duration: 00:04:21.00, bitrate: 132 kb/s Stream #0:0: Audio: atrac3, 44100 Hz, stereo, fltp
That tells you:
- Container format (
aea) - Codec (
atrac3/atrac3plus/atrac9) - Sample rate, channels, etc.
Why it’s useful here
Since your AEA header may be broken, ffmpeg -i input.aea or ffprobe input.aea will tell us:
- If FFmpeg can still detect the codec
- Which exact ATRAC variant you have
- What flags we need to use for a clean stream copy into
.mka
Do you want me to give you a ready-to-run command that uses ffprobe to print just the codec name (so you don’t have to scan through a big text output)? what is the difference between ffprobe and ffpmeg -i Great question ? — they look similar, but there are some important differences between ffmpeg -i and ffprobe:
? ffmpeg -i input.ext
ffmpegis mainly a converter/remuxer.- When you run it with just
-i, it:- Prints some stream info to the console (container, codec, bitrate, channels, etc.).
- Then usually errors out because you didn’t tell it what to output.
- The printed info is meant for humans (not machine-readable).
Example:
ffmpeg -i input.aea
Output:
Input #0, aea, from 'input.aea': Duration: 00:04:21.00, bitrate: 132 kb/s Stream #0:0: Audio: atrac3, 44100 Hz, stereo, fltp
? ffprobe input.ext
ffprobeis dedicated to analysis only.- It never tries to convert or output media — it just inspects it.
- It can print:
- The same human-readable info as
ffmpeg -i - Or structured machine-readable output (JSON, XML, etc.)
- The same human-readable info as
Example (human-readable):
ffprobe input.aea
Example (just codec name in JSON):
ffprobe -v error -select_streams a:0 -show_entries stream=codec_name -of default=noprint_wrappers=1:nokey=1 input.aea
Output:
atrac3
In short:
ffmpeg -i→ Quick check, human-readable, but “side effect” is that it looks like an error run.ffprobe→ Purpose-built for inspecting files, can give clean codec info and more detailed technical metadata.
Convert AEA to FLAC from the wiki that the rest are based on
for f in *.aea; do ffmpeg -i "$f" -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "${f%.aea}.flac"; done
Your Linux command loops through all *.aea files in the current folder and converts them to FLAC using ffmpeg. On Windows (cmd.exe) you can write it like this:
for %%f in (*.aea) do ffmpeg -i "%%f" -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "%%~nf.flac"
Notes:
- If you run this directly in a batch file (
.bat), keep the double%%f. - If you run it directly in the command prompt, use a single
%f:
for %f in (*.aea) do ffmpeg -i "%f" -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "%~nf.flac"
Do you want me to also give you the PowerShell version (nicer syntax, supports Unicode filenames better), or will you run this in cmd.exe? Here’s the PowerShell version of your loop:
Get-ChildItem *.aea | ForEach-Object {
ffmpeg -i $_.FullName -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "$($_.BaseName).flac"
}
Explanation:
Get-ChildItem *.aea→ gets all.aeafiles in the folder.$_→ represents each file object.$.FullName→ full path to the file.$.BaseName→ filename without extension (so output becomesfilename.flac).
⚡ Advantage: PowerShell handles spaces and special characters in filenames much more gracefully than cmd.exe.
Do you want me to also make a ready-to-run .ps1 script that you can drop into your folder and double-click/run, or will you paste it directly into the PowerShell terminal?
Here’s a ready-to-run PowerShell script (batch file) you can save as Convert-AEA.ps1 in the same folder as your .aea files:
# Convert-AEA.ps1
# Converts all .aea files in the current folder to FLAC (16-bit, 44.1kHz)
# Get all .aea files in this folder
Get-ChildItem -Filter *.aea | ForEach-Object {
$inputFile = $_.FullName
$outputFile = "$($_.BaseName).flac"
Write-Host "Converting $($_.Name) -> $outputFile"
ffmpeg -i "$inputFile" -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "$outputFile"
}
How to use it
- Open Notepad, paste the script above, and save it as
Convert-AEA.ps1in your folder with the.aeafiles.
(Make sure the file extension is.ps1, not.txt.) - Open PowerShell in that folder.
- If scripts aren’t allowed yet, run this once to enable them:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
- Run the script:
.\Convert-AEA.ps1
Same loop as the first script, just expanded with variables and messages so it’s easier to read and debug.
Got it ✅ Here’s the PowerShell script version (Batch file) that will scan the current folder and all subfolders for .aea files, then convert them to .flac while keeping the same folder structure:
# Convert-AEA.ps1
# Recursively converts all .aea files in this folder (and subfolders) to FLAC (16-bit, 44.1kHz)
# Get all .aea files in this folder and subfolders
Get-ChildItem -Filter *.aea -Recurse | ForEach-Object {
$inputFile = $_.FullName
$outputFile = Join-Path $_.DirectoryName "$($_.BaseName).flac"
Write-Host "Converting $($_.FullName) -> $outputFile"
ffmpeg -i "$inputFile" -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "$outputFile"
}
How it works
-Recursemakes PowerShell go into all subfolders.Join-Path $_.DirectoryName ...ensures each.flaclands in the same folder as the original.aeafile.- Outputs look like:
music\track1.aea → music\track1.flac music\subfolder\track2.aea → music\subfolder\track2.flac
recursive one-liner (for pasting, and from above)
Get-ChildItem -Filter *.aea -Recurse | ForEach-Object {
ffmpeg -i $_.FullName -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 "$($_.DirectoryName)\$($_.BaseName).flac"
}
Difference from your original:
-Recurse→ searches subfolders too."$($_.DirectoryName)\$($_.BaseName).flac"→ makes sure the.flacis written into the same folder as the source file (not all dumped into the top folder).
recursive PowerShell one-liner that also skips files already converted:
Get-ChildItem -Filter *.aea -Recurse | ForEach-Object {
$outFile = Join-Path $_.DirectoryName "$($_.BaseName).flac"
if (-Not (Test-Path $outFile)) {
ffmpeg -i $_.FullName -vn -hide_banner -c:a flac -sample_fmt s16 -ar 44100 $outFile
} else {
Write-Host "Skipping $($_.FullName) → already exists."
}
}
How it works:
Test-Path $outFile→ checks if the.flacalready exists.- If yes → it prints Skipping…
- If no → it runs
ffmpegnormally.
Windows changes the WiFi Network when it has no Internet Connection
The Issue
- By default, if your current WiFi network does not have a valid internet connection, Windows will disconnect and try another WiFi network.
- This is not roaming where your WiFi NIC tries to connect to the strongest AP of the same SSID.
- Change WiFi Roaming Sensitivity or Aggressiveness to improve Wi-Fi reception & performance | TheWindowsClub - We show you how to change Wi-Fi Roaming Aggressiveness or Sensitivity in Windows 11/10 to improve Wi-Fi reception & performance.
- Windows by design marks a Wi-Fi as “Limited” if it can’t reach the internet (via the Network Connectivity Status Indicator, NCSI check). When this happens, Windows may try to roam to another SSID that looks “better”, even if you want to stay put.
Cause
- This is a common situation. Most operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS) will automatically disconnect or deprioritise a Wi-Fi network if it doesn’t provide internet access.
- Windows in particular uses a NCSI probe by sending a packet to Microsoft and this requires a valid gateway to connect to the internet.
- Network Connectivity Status Indicator overview for Windows | Microsoft Learn - The Network Connectivity Status Indicator (NCSI) helps to detect network connectivity and troubleshoot via network probing and passive polling.
- No Internet Error on Windows - NCSI Troubleshooting - Cato Learning Centre
- Windows reports that there is no internet connectivity on the Ethernet or WiFi link even though the user can successfully access the Internet.
- If NCSI receives a valid response from a DNS server, NCSI sends a plain HTTP GET request to:
http://www.msftconnecttest.com/connecttest.txt
- The whole NCSI process is described here which can aid in troubleshooting.
- wireless networking - How does Windows know whether it has internet access or if a Wi-Fi connection requires in-browser authentication? - Super User
- Network Connectivity Status Indicator troubleshooting guide for Windows | Microsoft Learn - This guide demonstrates how to perform diagnostics using the Network Connectivity Status Indicator (NCSI) to troubleshoot and determine Internet connectivity.
Solutions
TL;DR
- Best solution if you want zero hassle: Disable NCSI probing (Method 5)
- The most reliable cross-platform trick is to assign a static IP configuration (with no gateway/DNS), so the OS doesn’t expect Internet routing from that Wi-Fi. That way it just treats it as a LAN.
- There isn’t a simple toggle in Windows to say “stay connected no matter what”, but in Windows 10/11, you can force the system to stay connected to one SSID even if it has no internet.
- You can stop that behaviour by using one of the methods below. Some methods prevent the switching of SSID while there are some scripts to constantently check the SSID and if it has changed will revert tot he correct SSID.
Method 1: Make the SSID your top priority & stop auto-switching
- Press Win + I → open Settings.
- Go to Network & Internet → Wi-Fi → Manage known networks.
- Click your target SSID → Properties.
- Turn On → “Connect automatically when in range.”
- Back in Wi-Fi settings, disable:
- Hotspot 2.0 networks (if you don’t use them).
- Connect to suggested open hotspots.
- Connect to networks shared by my contacts (on older Windows builds).
- Run this command in PowerShell (admin) to prevent Windows from switching away:
netsh wlan set profileparameter name="YourSSID" connectionmode=auto netsh wlan set profileparameter name="YourSSID" nonBroadcast=connect
(ReplaceYourSSIDwith the exact Wi-Fi name.)
Method 2: Force Windows to always use that Wi-Fi (interface metric trick)
By default, Windows disconnects when a network has no valid gateway/internet. You can override that:
- Press Win + R, type
ncpa.cpl, hit Enter. - Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter → Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) → Properties → Advanced.
- At the bottom, uncheck Automatic metric, and set Interface metric = 1 (highest priority).
- This tells Windows: “always prefer this adapter, regardless of internet state.”
Optional: If you don’t need internet routing via this SSID (just local LAN), you can remove the Default Gateway entry in the IPv4 settings. That way, Windows won’t even expect internet, so it won’t try to drop it.
Method 3: Disable "Smart Disconnect"
Some Wi-Fi drivers (Intel, Realtek, Killer, etc.) have a feature that disconnects from networks without internet:
- Open Device Manager → expand Network adapters.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter → Properties → Advanced tab.
- Look for options like Roaming Aggressiveness, Smart Disconnect, or Prefer Band.
- Set Roaming Aggressiveness = Lowest, and disable any “Smart Disconnect”/“Disconnect if no Internet” feature.
There isn’t a simple toggle in Windows to say “stay connected no matter what”, but there are a few reliable workarounds:
Method 4: Use a “No Internet” Profile
- In Network & Sharing Center, set a static IP on your Wi-Fi and leave the gateway blank.
- Without a gateway, Windows won’t expect internet and won’t mark it as “Limited.”
- It will stay connected as a pure LAN.
- The downside of this method is that you do not have internet when it is available and when you manually swap networks you might have to change you IP address.
Method 5: Disable the NCSI Internet connectivity check / Probe
This disables the Windows’ NCSI Internet connectivity check forcing Windows to always report “Connected” to your Wi-Fi, even if there’s no Internet so it will never get tagged as "Limited" and then be dropped. Windows will stop testing for internet access and this alone fixes the auto-disconnect in most cases.
- Press Win+R, type
regedit, press Enter. - Navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet
- Change these values (create them if missing):
EnableActiveProbing→ set to0(DWORD)
- Restart your computer.
Disable_NCSI.reg
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet] "EnableActiveProbing"=dword:00000000
This makes Windows always report “Connected” regardless of Internet access.
Re-Enable_NCSI.reg
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet] "EnableActiveProbing"=dword:00000001
Note: With NCSI disabled, Windows will always show “Connected” even if the network is offline. Apps that rely on NCSI (like the captive portal pop-up for hotel Wi-Fi) won’t launch automatically — you’ll need to open a browser manually in those cases.
Method 6: Use Third-Party Tools
If you want more control, a few small utilities exist that can “lock” Windows to a specific SSID:
- WLAN Manager (lightweight tool that lets you pin priority SSIDs and prevent roaming).
- NetSetMan (free for personal use; can lock profiles and prevent auto-switch).
- Wi-Fi Profile Manager 8 (open source, lets you enforce one SSID as top priority).
These basically override Windows’ automatic “choose a better network” logic.
Method 7: Disable "autoSwitch" for Wi-Fi networks (Windows 11)
This method requires manual intervention but can be useful in some setups.
- Turn On or Off AutoSwitch for Wi-Fi Network in Windows 11 | Windows 11 Forum
- This tutorial will show you how to turn on or off autoSwitch for Wi-Fi networks set to connect automatically when in range on your Windows 11 or Windows 10 PC.
- When you connect to a Wi-Fi network for the first time, Windows will automatically add a profile for the Wi-Fi network. The saved profile contains the SSID (network name), security key (password), and connection and security properties used to connect to this specific Wi-Fi network.
- If you turn on connect automatically to a Wi-Fi network, Windows will automatically connect to this Wi-Fi network when in range based on priority order.
- The autoSwitch parameter controls the roaming behavior of an auto-connected Wi-Fi network when a more preferred connect automatically Wi-Fi network is in range. If autoSwitch is turned on, it allows Windows to continue looking for other connect automatically Wi-Fi networks while connected to the current Wi-Fi network. If a higher priority connect automatically Wi-Fi network than the currently connected Wi-Fi network comes in range, Windows will automatically switch and connect to it instead.
Method 8: Scripted Auto-Reconnect
If you’re comfortable with PowerShell, you can make Windows automatically reconnect to your SSID even if it drops:
Option 1 - Background Scheduled Task
- This will run silently.
- This is to be run as a background scheduled task
- Every 10 seconds this script will check to make sure the Wifi is connected to the configured SSID, and if not, it will swap it back.
- This script does not prevent switching.
# Force Wi-Fi to stay connected to one SSID, even if disconnected
$SSID = "YourSSID"
while ($true) {
$connected = (netsh wlan show interfaces) -match $SSID
if (-not $connected) {
netsh wlan connect name=$SSID
}
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
- Replace
YourSSIDwith your exact Wi-Fi name (SSID). - Save this as
ForceWiFi.ps1 - Run this as a background scheduled task
- Run Automatically at Startup
- Open Task Scheduler (Win+R →
taskschd.msc). - Click Create Task.
- On the General tab:
- Name:
Force Wi-Fi Stay Connected - Check Run with highest privileges.
- Name:
- On the Triggers tab:
- New → Begin the task: At log on.
- On the Actions tab:
- New → Action: Start a program
- Program/script:
powershell.exe - Arguments:
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:\Path\To\ForceWiFi.ps1"
- Save → Restart → it will auto-run in background.
- Open Task Scheduler (Win+R →
Option 2 - Manually run PowerShell Script (displays connection status)
- This will output the connection status to the screen on every cycle.
- You can easily stop this by closing the command window.
- Every 10 seconds this script will check to make sure the Wifi is connected to the configured SSID, and if not, it will swap it back.
- This script does not prevent switching.
# Force Wi-Fi to stay connected to one SSID, even if disconnected
$SSID = "YourSSID" # <-- Replace with your Wi-Fi name
while ($true) {
$connected = (netsh wlan show interfaces) -match $SSID
if (-not $connected) {
Write-Output "[$(Get-Date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')] Not connected. Reconnecting to $SSID..."
netsh wlan connect name="$SSID"
} else {
Write-Output "[$(Get-Date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')] Still connected to $SSID."
}
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
- Replace
YourSSIDwith your exact Wi-Fi name (SSID).
Method 9: Combined NCSI Probing and SSID Switcher
I have added this here just in-case I need to come up with a more streamlined solution.
This script will
- Applies the registry tweak (disables NCSI probing).
- Creates the PowerShell script in
C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1. - Registers a Task Scheduler job that runs it at login with highest privileges.
How to Use
- Copy the code into Notepad.
- Save as
ForceWiFiSetup.bat(Save as type: All Files, not.txt). - Right-click → Run as Administrator.
- Edit
C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1and changeYourSSIDto your actual Wi-Fi name. - Reboot.
After reboot:
- Windows will no longer drop your Wi-Fi just because it has no Internet.
- The scheduled task will always force reconnection to your chosen SSID in the background.
ForceWiFiSetup.bat (Installer)
Save this as ForceWiFiSetup.bat (Right-click → Run as Administrator):
@echo off
:: =====================================
:: Force Windows to stay connected to one SSID
:: =====================================
:: --- Create folder for script
mkdir "C:\ForceWiFi" >nul 2>&1
:: --- Create the PowerShell script
echo # Force Wi-Fi to stay connected to one SSID, even if disconnected > C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo $SSID = "YourSSID" # <-- Replace with your Wi-Fi name >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo while ($true) { >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo $connected = (netsh wlan show interfaces) -match $SSID >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo if (-not $connected) { >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo Write-Output "[$(Get-Date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')] Not connected. Reconnecting to $SSID..." >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo netsh wlan connect name="$SSID" >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo } else { >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo Write-Output "[$(Get-Date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')] Still connected to $SSID." >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo } >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo Start-Sleep -Seconds 10 >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
echo } >> C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1
:: --- Disable NCSI Active Probing in registry
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet" /v EnableActiveProbing /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
:: --- Register scheduled task
schtasks /create /tn "ForceWiFiStayConnected" /tr "powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1" /sc onlogon /rl highest /f
echo.
echo =====================================
echo Setup complete!
echo - Replace YourSSID in C:\ForceWiFi\ForceWiFi.ps1 with your Wi-Fi name
echo - Restart your computer for registry change to take effect
echo =====================================
pause
ForceWiFiRemove.bat (Uninstaller)
Save this as ForceWiFiRemove.bat (Right-click → Run as Administrator):
@echo off
:: =====================================
:: Remove ForceWiFi setup (script + registry + scheduled task)
:: =====================================
:: --- Delete the PowerShell script folder
if exist "C:\ForceWiFi" (
rmdir /s /q "C:\ForceWiFi"
echo Removed C:\ForceWiFi folder.
) else (
echo No C:\ForceWiFi folder found.
)
:: --- Re-enable NCSI Active Probing
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet" /v EnableActiveProbing /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
echo Re-enabled Windows Internet connectivity check (NCSI).
:: --- Delete scheduled task
schtasks /delete /tn "ForceWiFiStayConnected" /f
echo Removed scheduled task ForceWiFiStayConnected.
echo.
echo =====================================
echo Cleanup complete!
echo - NCSI probing restored
echo - Scheduled task removed
echo - Script folder deleted
echo =====================================
pause
PCIe Lane Diagnostics
How many PCIe lanes is your NVMe drive using in Windows
To check how many PCIe lanes your NVMe drive is using in Windows use the following apps to get the information.
CrystalDiskInfo
- Free
- Lightweight
- Simple interface
- Shows PCIe link width (e.g., "PCIe 3.0 x4")
- Download: https://crystalmark.info/en/software/crystaldiskinfo/
How to use:
- Install and run CrystalDiskInfo.
- Select your NVMe drive from the list at the top.
- Look for a line like:
Transfer Mode: PCIe 3.0 x4 | PCIe 3.0 x4
- The first value is active lanes.
- The second is maximum supported lanes by the drive.
HWiNFO
- More detailed than CrystalDiskInfo.
- Shows lane width, link speed, slot info, etc.
- Download: https://www.hwinfo.com/download/
How to use:
- Launch HWiNFO, only Sensors are needed, but you can use full mode.
- Expand "Bus"
- Expand "PCI Bus"
- Select "PCI Express Root Port", and under the "PCI Express section" on the right:
- Version is the PCIe Generation
- Read the "Maximum Link Width" and "Current Link Width" to get the NVMe port's lane information.
- Under the "PCI Express Root Port" you will probably see the following
- "PCI Express x4 Bus"
- "Samsung Electronics Pascal S4LV008 PCIe 4.0 x4 NVMe 2.0 SSD Controller" (or your drive)
- Read the "Maximum Link Width" and "Current Link Width" to get the NVMe drives lane information.
- "Samsung Electronics Pascal S4LV008 PCIe 4.0 x4 NVMe 2.0 SSD Controller" (or your drive)
- "PCI Express x4 Bus"
The drive information in this tool is just information read from the tool, it does not have current lane, just information read from the firmware.
Samsung Magician
- Clean UI
- Shows PCIe link speed and lane info (for supported drives)
- Some features are only for Samsung drives.
- Download: https://semiconductor.samsung.com/consumer-storage/magician/
How to use:
- Open Samsung Magician.
- Select your NVMe drive.
- Under the "Drive Details" or "Interface" section, it will show something like:
Interface: PCIe Gen 4.0 x4
- This means it's using 4 lanes on Gen 4.
How can I check the number of PCIe lanes in Windows?
- Use: HWiNFO
- Count Your PCIe Lanes! Easy Guide for Any PC
- Confused about PCIe lanes on your PC? Don't worry! This guide shows you simple methods to check how many lanes your system has (No software needed).
- System Information Tool
- On Windows, you can use the built-in System Information tool to find information about your motherboard and its PCIe lanes.
- Press Win+R to open the Run dialog, type “msinfo32,” and hit Enter.
- In the System Information window, navigate to “Components” > “PCI.” There, you will see a list of all PCIe devices in your system and their current link widths (corresponding to the number of lanes).
- Third-Party Software
- Some third-party software tools can provide detailed information about your computer’s hardware, including PCIe lanes.
- CPU-Z and GPU-Z are popular tools that can provide comprehensive information about the motherboard and connected PCIe devices.
- How can I check the number of PCIe lanes in Windows?
- You can check the number of PCIe lanes in Windows using the device manager by following these steps:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager.”
- In the Device Manager window, expand the “System Devices” category.
- Look for an entry named “PCI Express Root Port” or “PCI Express x16 Port” (the exact name may vary depending on your system).
- Double-click on the “PCI Express Root Port” entry to open its properties.
- Go to the “Advanced” tab, and you should see information about the number of “Current Link Width” or “Max Link Width.” This value represents the number of PCIe lanes currently used by the port.
- You can check the number of PCIe lanes in Windows using the device manager by following these steps:
General Notes
- How Many Lanes Does NVMe Use? Explained - Media Duplication Systems - Discover how many PCIe lanes NVMe SSDs use and why lane configurations matter.
USB to ISO, ISO to USB, Bootable ISO
This will cover a lot of topics to do with ISO and burning.
Software
Burners / Authoring
- ImgBurn
- ImgBurn is a lightweight CD / DVD / HD DVD / Blu-ray burning application that everyone should have in their toolkit... and it's free!
- AnyBurn
- A light weight but professional disc burning, imaging, and bootable USB drive creation software
- ShapeISO
- A free and excellent ISO editor software that helps you burn, extract and create ISO image files on Windows computers.
- PowerISO
- Create, Burn, Mount, Edit, Compress, Encrypt, Split, Extract ISO file, ISO/BIN converter, Virtual Drive.
- PowerISO is a disk image utility that can open, burn, create, edit, compress, encrypt, mount and extract ISO files.
- PowerISO comes with some unwanted programs (PUP) but you can simply turn off the internet in your PC (switch off WiFi or Ethernet) before installing PowerISO and it will skip the installation of the PUP.
- Menu: Tools --> Create ISO from USB
USB <--> Image
- Rufus
- Create bootable USB drives the easy way
- Rufus can format a USB drive in the following partition schemes/formats
- MBR
- GPR
- Super Floppy Disk
- How to create bootable USB drive for Windows 11 with Rufus (2025) - Pureinfotech
- Rufus lets you create a bootable Windows 11 USB for supported and unsupported hardware. Also, it offers the option to download the ISO file.
- Create a bootable Windows USB drive with modifications.
- How to Use Rufus: A Complete Guide | UUByte
- Rufus is a popular free software for creating bootable USB. Do you know how to use it? This is a complete guide for using Rufus.
- Rufus is best known for its ability to create bootable USB drive by burning ISO image to USB. However, it's more than that. In fact, you can use Rufus to create a non-bootable BIOS or UEFI device with GPT or Super Floppy Disk partition scheme. Also, you can format USB device as NTFS, FAT32, or UDF, adjust the volume label, and set your own cluster size.
- Do you plan to add USB → ISO creation support? - FAQ · pbatard/rufus Wiki · GitHub
- i.e. Do you plan to allow a feature that can reverse what Rufus does when converting a bootable ISO to bootale USB, so that a bootable ISO can be created back again?
- This was added in Rufus 4.10. If you show the advanced drive properties, and you have a compatible USB or VHD drive selected, then you can click the "save" icon next to it to save the drive content to an ISO.
- Also note that you can already use Rufus to create a VHD/VHDX image anyway (see the relevant entry in this FAQ), which, in most cases, is probably what you are really after. Rufus will happily open and write
.vhd/.vhdximages just like it can open.isoimages.
- ISO to USB
- ISO to USB is a free and small software that can burn the ISO image file directly to the USB drives, these USB drives include USB flash drives, memory sticks and other USB storage devices, it also supports to create a bootable USB disk with Windows operating systems.
- The ISO image file is a popular image of the CD/DVD discs, an ISO file can include all the content on the disc, this software can easily burn these ISO files to a USB flash disk, makes it easy to carry and use.
- This software currently only support Windows bootable disk, can work with both BOOTMGR and NTLDR boot mode, can create USB disk with FAT, FAT32, exFAT or NTFS file system. (When you are making a bootable USB disk, suggest you choose the FAT32 file system.)
- balenaEtcher - Flash OS images to SD cards & USB drives
- A cross-platform tool to flash OS images onto SD cards and USB drives safely and easily. Free and open source for makers around the world.
- EaseUS Todo Backup
- This software can create a bootable USB drive and put ISO on USB drives. It also helps in creating an image of a USB drive and putting ISO on USB drives.
- An easy-to-use free data backup software for Windows 11/10 users to back up photos, music, videos, documents, system, etc. for PC users.
Builders
- Windows Media Creator
- How to Create Bootable USB Flash Drive to Install Windows 10 | Windows 10 Forums - This tutorial will show you how to create a bootable USB flash drive that can be used to install Windows 10 with UEFI or Legacy BIOS.
- Create Windows 11 Bootable USB Installation Media | Windows 11 Forum
- This tutorial will show you how to create a bootable USB flash drive used to install Windows 11 with UEFI support.
- You can use a Windows 11 installation USB flash drive to clean install, upgrade, reset, or repair Windows 11.
- The installation USB can also be used as a recovery drive to boot to boot to WinRE (aka: advanced startup).
Converters
- IMG to ISO
- IMG to ISO is a free small software utility, as its name suggests, it can convert the IMG image files into the ISO image files.
- The IMG is an disk image file format, it be used by some virtual drive software, Its file extension is generally .img or .ima. The ISO format seems to be more popular than IMG format now, So, if you want to convert your IMG files into ISO files, this little software just helps you.
- The ISO format file that is created by this program can conform to the standard ISO-9660 format. You can also use this software to open *.ima files
Tutorials
Extracting Boot Sector from ISOs
- Extracting boot sectors from Windows ISOs | BetaArchive
- Bootsector is not stored in the files, but in the image itself...
- How to manually extyract the boot sector:
- Download and install 7-ZIP 9.20 from: http://www.7-zip.org/
- Open a bootable Windows 2000/XP ISO file with 7-ZIP.
- There is a folder named [BOOT].
- Go in into [BOOT].
- The boot sector file is named
"Bootable_NoEmulation.img". - Extract this bootsector.
- Rename
Bootable_NoEmulation.imgtoBOOTSECT.BIN - Copy your Windows Whistler PE CD to your hard disk e.g.
"C:\WINPE" - Place
BOOTSECT.BINin the folder"C:\WINPE\I386". - Then use a application that will create your bootable ISO file.
- Extracting floppy boot image from ISO with dd? | GRC Public Forums
- I know there are utilities that can extract the boot image from a CD ISO which can then be used to create a boot floppy or another bootable CD ISO. Anyone know if the differences in the boot header for a bootable FreeDOS floppy image, CD ISO or USB ISO is the sector number where the boot code is located?
- That being said, on Windows I have used 7-zip to extract the boot file. 7-zip shows it in a special folder called "[BOOT]".
If you install 7-zip on Linux (p7zip-full) you can use the 7z command to extract the file:7z e isofile.iso '[BOOT]'
- Mentions balenaEtcher for making USB drives.
- How to Extract Boot Sector Information from a Bootable DVD | Tom's Hardware Forum
- Use UltraISO with these instructions to extract the .BIF file.
- The bootable disc has a .BIF file i.e. boot information file which is responsible for booting the disc from a removable storage. Every bootable disk, thus, has a .BIF file that makes it bootable. The difference between a normal installation disk and a boot time installation disk lies mainly in the boot information sector.
- Boot Image Extractor - How to extract boot image from CD/DVD? | WinISO - WinISO is a powerful ISO Extractor, which can extract not only ISO image file but extract the boot image file if you desired.
Create a Bootable USB
- How to Create a Bootable USB Drive Without Using Any Software : 3 Steps - Instructables
- To create a bootable USB drive manually, we will use the command prompt (diskpart) as a Windows default program.
- Here are step by step to create a bootable USB drive as the Windows installation media.
- How To Create Bootable Windows 10 ISO From Files/Folders
- Use this guide if you have Windows 10/8.1/7 installation files and want to create a bootable ISO image file using those files.
- Shows how to use ImgBurn to make a bootable disks, also shows emulation types: None, Floppy disk, Hard Disk.
- ImgBurn
Bootable USB to ISO
- How to Convert Bootable USB to an ISO Image (Tutorial) - YouTube
- In this tutorial video, I'll show you How to Convert Bootable USB to an ISO image. So, if you've been wondering how to create an ISO image file from files and folders, this video is for you as I'll take you through the entire process step-by-step.
- AnyBurn, ImgBurn
- 2 Timeless Ways to Convert Bootable USB Drive to ISO
- Due to some reason, you need to convert bootable USB to ISO. Then you can refer to the methods offered in this post to complete the operation.
- ImgBurn, AnyBurn
- How to Convert Bootable USB to ISO (windows 10/11)
- You created a bootable USB of Windows 11, 10, or even 8.1 after downloading it. Then you deleted the ISO file to make space on the partition since we have the bootable. Now you want to create another bootable but the original ISO is missing. No worries as you can convert bootable USB to ISO.
- ImgBurn
- 2 Free Ways to Convert Bootable USB to ISO on Windows 10
- How to convert bootable USB to ISO in Windows 10? Here you can know how to easily create ISO file from a bootable USB for free.
- Sometimes you may need to create an ISO file from bootable USB for some purpose. Here this article will show you how to easily convert bootable USB to ISO on Windows 10 with 2 ways for free.
- ShapeISO, AnyBurn
- How to Convert Bootable USB to ISO
- Converting your bootable USB to an ISO can save you from these headaches. If you delete the original ISO after making the bootable USB, you will have to redownload it later. It’s easy to convert a bootable USB to ISO on Windows; here are the two best ways to do it.
- AnyBurn, ImgBurn
- How to Create ISO Image from USB with USB to ISO
- What is an ISO file? Are you looking for a way to create ISO image from USB? This article will tell how to create an ISO from USB drives on Windows 11/10/8/7.
- EaseUS Todo Backup, Rufus, DISM
- Make Bootable ISO Image from a Bootable USB Drive
- Learn how you can create a bootable ISO image using a bootable USB drive (with Windows installation files on it) very easily.
- Extract the
.BIFfrom an existing Bootable ISO and use that. - PowerISO
DiskGenius focused
- Create an .iso out of a bootable USB stick? | Ventoy Forum
- e.g. the software DiskGenius (https://www.diskgenius.com) can only create a bootable USB stick (UEFI and BIOS), but not an
.isothat I could use with Ventoy directly. - Just copy the
boot.wimfile to the Ventoy USB disk and boot to theboot.wimdirectly from Ventoy - no need to make an ISO. You will need to add Wimboot Plugin too. - Plugin.wimboot . Ventoy - Ventoy use this plugin to boot WIM files (Legacy BIOS + UEFI).
- e.g. the software DiskGenius (https://www.diskgenius.com) can only create a bootable USB stick (UEFI and BIOS), but not an
- Recommendations for bootable ISOs to add to Ventoy | Windows 11 Forum
- Q: I have not yet discovered an easy way to convert a bootable USB drive to a bootable ISO. Many utilities that claim to do this are getting long in the tooth - i.e 2012 or 2016 and I'd like to use more recent apps.
- A: There are a few methods and techniques on this thread so I will just summarise them.
- oscdimg (Page 1)
oscdimg.exe -m -o -u2 -udfver102 -bootdata:2#p0,e,bd:\iso_files\boot\etfsboot.com#pEF,e,bd:\iso_files\efi\microsoft\boot\efisys.bin d:\iso_files d:\14986PROx64.iso becomes oscdimg.exe -m -o -u2 -udfver102 -bootdata:2#p0,e,bE:\boot\etfsboot.com#pEF,e,bE:\efi\microsoft\boot\efisys.bin E:\ C:\users\myname\myiso.iso You can create a one line batch file to do above.
- You could use cdimage, oscdimg or mkisofs which are command line tools, Or you can use, Lancer, which has a GUI (Page 1)
- Copy the DiskGenius WIM to the Ventoy disk and boot from that. (Page 1)
- Windows-isomaker_x64_x86_sha256.zip (Page 1)
- isomaker.zip (Page 1)
- mkisofs Linux (Page 1)
sudo mkisofs -o /path/to/image. iso /dev/sdb
- replacing /path/to/image. iso with the desired location and name of your ISO file and /dev/sdb with the device name of your USB drive.
- isomaker-DISKGENIUS.zip (Page 2)
- Lancer _x64 wont work for the unusual construction of diskgenius boot media.
- I have done a special one for diskgenius.
- Instructions
- Copy and paste the diskgenius usb stick to a hard drive.
- Rt click the usb stick and select copy. Rt click on a hard drive partition and select paste.
- So you have a folder e.g. C:\DISKGENIUS ( it will have the same name as the usb stick)
- then run the .cmd file and browse to C:\DISKGENIUS
- Do not browse to a sub folder inside C:\DISKGENIUS
- I made a diskgenius usb stick and tested the above .
- Boot from the WIM (Page 2)
- You really only need to copy the file
Boot.wimfrom the folderDiskGenius - Boot(and optionally rename the file to something like, e.g.,DiskGenius 5.5.1.1508 x64.wimto make it easier for you to see what exactly this one is) to the root of the VENTOY partition that's on your USB flash drive. Aside from this, you also need to make sure that you have installed the Wimboot plugin for Ventoy before you boot from the USB flash drive. (For this, you need to create a new folder namedventoyin the root of the VENTOY partition, and then copy the fileventoy_wimboot.imginto this folder like has been explained here.)
- You really only need to copy the file
- Use an existing Bootable ISO (Page 3)
- Using something like the free anyburn, edit a known working iso file (e.g. your macrium iso file ).
- Replace the \sources\boot.wim in the known working iso with the boot.wim from your diskgenius usb stick.
- Then save the iso as a new name, e.g. diskgenius.iso
- NB: I have not tried this.
- oscdimg (Page 1)
Disk Image Handling
Glossary
- P2V
- (Physical-to-Virtual) conversion
- P2V converts a physical server's operating system, applications, and data into a virtual machine format (like VMDK).
- V2V
- (Virtual-to-Virtual) conversion
- the process of migrating a virtual machine (VM) from one virtualization platform to another.
- Fixed Disk / "Thick" Provisions
- These disk images are a set size and are never changed. They are roughly the size of the disk defined in the image.
- Dynamic Disk / Growable / "Thin" Provisioned / "Sparse" Provisioned
- The disk image file size can change and is not directly related to the size of the defined virtual disk it holds.
- OVA/OVF
- These are not disk images, but a standard to allow moving of virtual machines between platforms.
- Deploy and Export OVF and OVA Templates
- You can export virtual machines, virtual appliances, and vApps in Open Virtual Format (OVF) and Open Virtual Appliance (OVA). You can then deploy the OVF or OVA template in the same environment or in a different environment.
- How To Convert Virtual Machines Between VirtualBox and VMware
- Migrating to another virtual machine program can be intimidating.
- If you use an ova extension, then all of the files will be combined into one Open Virtualization Format Archive.
- If you use an ovf extensions, several files will be written separately.
- Super Floppy
- This is the term given to a type of USB formating where it has the following features:
- No MBR
- No Partition Table
- 1 Partition that takes the whole of the drive
- The term "super floppy" can be a bit ambiguous, but generally, when people refer to a "super floppy" in the context of USB drives, they often mean a removable drive (like a USB flash drive) that does not have partitions, behaving more like a traditional floppy disk. Some older disk management utilities, like Acronis Disk Director, might label such drives as "Super Floppy."
- This is the term given to a type of USB formating where it has the following features:
- Boot Sector
- This can contain MBR or GPT code.
- Boot sector - Wikipedia
- A boot sector is the sector of a persistent data storage device (e.g., hard disk, floppy disk, optical disc, etc.) which contains machine code to be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and then executed by a computer system's built-in firmware (e.g., the BIOS).
- Master Boot Record (MBR)
- The MBR is physically the first sector of a data medium (e.g. hard drive or USB stick), which is used by computers for the booting, or start-up process. The computer must be equipped with a BIOS and a x86 operating system.
- The searches for the active partition and then load the VBR
- The MBR code is OS specific.
- This is placed in the boot sector of a drive
- Volume boot record - Wikipedia
- A master boot record (MBR) is a type of boot sector in the first block of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.
- The MBR holds the information on how the disc's sectors (A.K.A. "blocks") are divided into partitions, each partition notionally containing a file system.
- The MBR also contains executable code to function as a loader for the installed operating system—usually by passing control over to the loader's second stage, or in conjunction with each partition's volume boot record (VBR). This MBR code is usually referred to as a boot loader.
- MBR (Master Boot Record) explained - IONOS UK - The master boot record is a vital piece of code for many PCs to start up. But how does it work, how is it structured and how can it be repaired if necessary?
- What’s in the MBR?
- First 446 bytes: Bootloader code
- Next 64 bytes: Partition table
- Last 2 bytes: Boot signature (should be
0x55AA) - NB: this is first 512 bytes on a physical drive.
- Volume Boot Record (VBR)
- This is where Windows/OS start to load.
- The VBR is a file with a specific file name in a specific location.
- The VBR code is OS specific.
- The VBR for Windows is a file in the root called:
BOOTMGR - Volume boot record - Wikipedia
- A volume boot record (VBR) (also known as a volume boot sector, a partition boot record or a partition boot sector) is a type of boot sector introduced by the IBM Personal Computer.
- The code in volume boot records is invoked either directly by the machine's firmware or indirectly by code in the master boot record or a boot manager. Code in the MBR and VBR is in essence loaded the same way.
- Windows Boot Manager
- Windows Boot Manager - Wikipedia
- The Windows Boot Manager (
BOOTMGR) is the bootloader provided by Microsoft for Windows NT versions starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It is the first program launched by the BIOS or UEFI of the computer and is responsible for loading the rest of Windows. It replaced the NTLDR present in older versions of Windows. - The boot sector or UEFI loads the Windows Boot Manager (a file named
BOOTMGRon either the system or the boot partition), accesses the Boot Configuration Data store and uses the information to load the operating system throughwinload.exeorwinresume.exeon BIOS systems, andwinload.efiandwinresume.efion UEFI systems. - On system with BIOS firmware, the BIOS invokes MBR boot code from a hard disk drive at startup. The MBR boot code and the VBR boot code are OS-specific. In Microsoft Windows, the MBR boot code tries to find an active partition (the MBR is only 512 bytes), then executes the VBR boot code of an active partition. The VBR boot code tries to find and execute the bootmgr file from an active partition.[3]
- On systems with UEFI firmware, UEFI invokes
bootmgfw.efifrom an EFI system partition at startup, starting the Windows Boot Manager.
- The Windows Boot Manager (
- Windows Boot Manager - Wikipedia
- Operating System Boot Loader.
UEFI / MBR Boot Procedure
- Windows MBR Boot Procedure
- MBR is loaded into RAM by the firmware.
- MBR searches for an active partition
- MBR loads the Windows Boot Manager (
BOOTMGR/ VBR) from the active paritition. - Windows Boot Manager now loads the Windows Boot loader from one of these locations:
\windows\system32\winload.exe \windows\system32\boot\winload.exe
- Windows now loads
- Windows EFI Boot Procedure
- UEFI invokes the Windows Boot Manager from an EFI system partition (ESP) at startup,
\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi
- A user can make an OS selection now, or the default OS is loaded. These settings are defined in the BCD.
- Windows Boot Manager now loads the Windows Boot loader from one of these locations.
\windows\system32\winload.efi \windows\system32\boot\winload.efi
- Windows now loads
- UEFI invokes the Windows Boot Manager from an EFI system partition (ESP) at startup,
Links
- UEFI boot: how does that actually work, then? | AdamW on Linux and more - This blog post is aimed at regular everyday folks; it's intended to dispel a few common myths and help regular people understand UEFI a bit better. It is not a low-level fully detailed and 100% technically accurate explanation, and I'm not a professional firmware engineer or anything like that.
- Difference between bootmgr.efi and bootmgfw.efi? - Super User
- Could someone explain the EFI partition file structure please? | Reddit - I'm trying to boot back into PopOS after something went wrong during an update. I need to recreate an EFI boot entry in NVRAM, and am looking for the correct .efi file to point to on the EFI partition.
- 1. Introduction — UEFI Specification 2.10 documentation | UEFI Specification - This Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) Specification describes an interface between the operating system (OS) and the platform firmware. UEFI was preceded by the Extensible Firmware Interface Specification 1.10 (EFI). As a result, some code and certain protocol names retain the EFI designation. Unless otherwise noted, EFI designations in this specification may be assumed to be part of UEFI.
- edk2/MdePkg/Include/Uefi/UefiSpec.h at master · tianocore/edk2 · GitHub - A boot loader code example.
- UEFI vs BIOS: What is the difference between BIOS and UEFI? | TheWindowsClub - A imple and concise answer to this questions.
USB Drives
USB drives:
- behave similiar to Hard Drives (HDD/SSD/NVMe).
- can be partitioned.
- can be made bootable
- access sectors/data via standard LBA methods.
- do not have the HDD demulation that a CD-ROM/ISO as it is not required.
- can use a SuperFloppy format that it allows it to be loaded as a large floppy disk (this is just a specialised partition layout).
- have their Removable Media bit (RMB) set, which is a hardware flag showing the device is removable device. This is used so the OS knows how to correctly handle the drive.
Some BIOSes have a feature where a USB drive can be:
- mounted and then presented as a HDD to older OS.
- mounted as a floppy disk.
Image Formats
- VHD (deprecated)
- (Microsoft Virtual PC Virtual Hard Disk)
- Azure (requires fixed size), Virtual PC,
- Developed by Microsoft
- Does Azure use VHD or VHDX? - Darwin's Data - Azure supports both VHD and VHDX disk formats for virtual machine disks. The choice between VHD and VHDX depends on the specific scenario and requirements.
- VHD should not be used for new systems.
- What is a VHD File? (Unpacking Virtual Hard Disk Mysteries) - Discover how Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) files revolutionize computing by simplifying management of multiple operating systems and enhancing efficiency.
- VHDX
- (Microsoft Hyper-V Virtual Hard Disk)
- Microsoft Hyper-V
- [MS-VHDX]: Virtual Hard Disk v2 (VHDX) File Format | Microsoft Learn - Specifies the Virtual Hard Disk v2 (VHDX) File Format Protocol, the virtual hard disk format that provides a disk-in-a-file abstraction.
- Hyper-V technology overview | Microsoft Learn - Describes what Hyper-V is, how to get it, key features, and common uses. This article includes an overview for Hyper-V in Windows and Windows Server.
- Hyper-V Manager: Is It the Right Tool for Hyper-V Configuration? - Hyper-V Manager is used for creating, configuring and deleting Hyper-V hosts and VMs. Read this blog post to learn more about Hyper-V Manager capabilities.
- Hyper-V Disk Types Explained - BDRSuite
- Hyper-V Disks : Fixed Size, Dynamically Expanding, and Differencing Disks
- In today’s blog post, we’ll discuss what virtual file formats are supported by Hyper-V and their types. We’ll cover in detail, the different types of VHD/VHDX, and how to choose the right one for your business requirements.
- VMDK
- (VMware Virtual Disk File)
- VMware and ESXi
- VDI
- (VirtualBox Virtual Disk File)
- VirtualBox
- QCOW (deprecated)
- KVM type Virtual Machines (old format, deprecated)
- QCOW2
- KVM type Virtual Machines
- HDD,HDS
- (Parallels Desktop Virtual Disk File)
- Parallels
- DD
- These are created by the Linux command
dd. - This is a binary blog, made by copying the RAW bits, and therefore is file system agnostic.
- These are created by the Linux command
- IMG
- (Disk or Partition Image File)
- This binary blog, made by copying the RAW bits, and therefore is file system agnostic.
- IMG (file format) - Wikipedia
- The .img file extension was originally used for floppy disk raw disk images only. A similar file extension,
.ima, is also used to refer to floppy disk image files by some programs. A variant of raw image, calledIMZ, consists of a gzipped version of a raw floppy disk image. These files use the.imzfile extension, and are commonly found in compressed images of floppy disks created by WinImage. - QEMU uses the
.imgfile extension for a raw image of a hard disk drive and calls the format "raw".
- The .img file extension was originally used for floppy disk raw disk images only. A similar file extension,
- An .img file is just a raw disk image, a sector-by-sector copy of a storage device (like a hard drive, SSD, USB stick, etc.). It doesn’t have a special format; it’s literally just the binary contents of a disk.
- .img was not a format invented by dd, it’s just a raw image file — a byte-for-byte copy of a disk.
- IMA
- (Virtual Floppy Disk Drive)
- This is a binary blog, made by copying the RAW bits, and therefore is file system agnostic.
- IMZ
- GZipped (Virtual Floppy Disk Drive)
- RAW
- This is a binary blog, made by copying the RAW bits, and therefore is file system agnostic.
- BIN
- This is a binary blog, made by copying the RAW bits, and therefore is file system agnostic.
- WIM
- Microsoft Windows Image File
- This is used to hold a Windows operating system and various other task.
- This is not strictly a Disk Image file but can behave like one.
- PHVD
- Paragon
- PMFX
- DiskGenius
- E01
- EnCase
- AFF
- (Advance Forensics Format)
- EWF
- (Expert Witness Compression Format)
- FFU
- (Windows Full Flash Update)
- GitHub - rbalsleyMSFT/FFU
- Using Full Flash Update files to speed up Windows Deployment
- Has full YouTube video with timestamps.
- Richard Balsley from Microsoft
- Capture and apply Windows Full Flash Update (FFU) images | Microsoft Learn - Deploy Windows faster on the factory floor by using the Full Flash Update (FFU) image format.
Software
There will be cross over between software functionality and their category.
Conversion (V2V and P2V)
- StarWind V2V Converter
- StarWind V2V / P2V Converter converts (sic!) virtual machines from one format to another, and turns physical machines into VMs as well. It simplifies transition between virtual environments, both public clouds and on-premises, making migration quick and frictionless. With on-the-fly, snapshot-based “direct” VM conversion between hypervisors, StarWind eliminates downtime and the burden of allocating intermediate space, saving valuable time and resources.
- Supports all the major image formats as source and destination.
- StarWind V2V Converter generally does not directly support converting or accessing USB drives as part of its core functionality. While it can convert virtual machine images and physical disks, USB drives are typically handled differently within virtualized environments.
- StarWind V2V Converter Help : Command Line Interface | Starwind - There are two ways for working with StarWind V2V Converter without GUI which is covered here.
- StarWind V2V Converter Overview (Part 5): Converting VMs to QCOW2v3 | Starwind - The StarWind V2V Converter series wraps up with an exciting new feature – QCOW2v3 support! From larger disks to better encryption, see how this format can transform your VM migration workflow Introduction Welcome to the fifth and final article in our StarWind V2V Converter series. In the previous articles, we covered converting virtual machines (VMs) to and from Oracle VirtualBox, oVirt, Proxmox, and explored hot migration from Microsoft Hyper-V to VMware ESXi. Now, we'll delve into an exciting new feature of StarWind V2V Converter: the ability to convert your disk images into the QCOW2v3 format. QCOW2v3 is the latest iteration of the widely used QEMU Copy-On-Write format, offering better performance, improved snapshot capabilities, and more efficient use of storage space. This makes it ideal for virtualization professionals who need a reliable, flexible, and powerful conversion tool for optimized VM migrations. For those who haven't yet tried StarWind V2V Converter, you can download.
- VMware vCenter Converter Standalone
- VMware vCenter Converter is an essential tool for users of VMware Workstation, enabling seamless physical-to-virtual machine conversions. While bundled with VMWare Workstation, it installs independently and supports individual version upgrades, offering flexibility and efficiency for virtualization tasks.
- Is able to reach into an offline virtual machine image and change the drivers in the Windows installation to the ones the VMWare environments need/offer.
- Convert Windows and Linux physical machines or third-party VMs into VMware virtual machines.
- Resize partitions and control disk formats during migration.
- Extremely painful sign up and download procedure, the website is terrible, but at least the software is free.
- Introduction to VMware vCenter Converter Standalone - VMware vCenter Converter Standalone provides an easy-to-use solution that automates the process of creating VMware virtual machines from physical machines (running Windows and Linux) and from other virtual machine formats.
- VMware vCenter Converter Download | filehorse
- VMware vCenter Converter transforms your Windows and Linux-based physical machines and third-party image formats to VMware virtual machines.
- It supports many source physical machines, including Windows and Linux desktop and server editions. It also supports the conversion of third-party virtual machines like Hyper-V and KVM.
- P2V and V2V Conversion: The software allows you to perform both Physical-to-Virtual (P2V) and Virtual-to-Virtual (V2V) conversions, giving you the flexibility to migrate from physical servers to virtual ones or move virtual machines between different hypervisors.
- This page has a good write-up of features.
- This is an alternative download source.
- Migrate machines to VMWare vCenter VMs using standalone converter - Notes_Wiki - VMWare standalone converter can be used for converting physical or virtual machines from different types of physical hardware or hypervisors to VMWare vCenter based VMs. For the conversion use following steps:
- VBoxManage
- This is part of the VirtualBox hypervisor package.
- VBoxManage is the command-line interface to Oracle VM VirtualBox. With it, you can completely control Oracle VM VirtualBox from the command line of your host operating system.
- It also has the ability to convert and manipulate disk images.
- How to Convert Between Fixed and Dynamic Disks in VirtualBox | How-to-Geek - VirtualBox allows you to choose either a dynamically allocated or fixed size disk when creating a new virtual hard disk file.
- Convert a VirtualBox Fixed Disk to a Dynamic or vice versa | TheWindowsClub - When creating a virtual machine, you are asked to select a disk type, you can either go for Fixed Disk or Dynamic Disk. What if you went for a Fixed Disk and later on realized that you need a dynamic one, or vice-versa? Well! You can convert one into another. In this post, we will see how you can convert a VirtualBox Fixed Disk to a Dynamic one or vice-versa.
- Use VBoxManage for Raw to VDI
VBoxManage convertfromraw source.img output.vdi --format VDI
- QEMU disk image utility (qemu-img)
- This is part of the QEMU hypervisor package.
- qemu-img allows you to create, convert and modify images offline. It can handle all image formats supported by QEMU.
- There are many options and are all run from the command line.
- Use qemu-img for Raw to VHDX
qemu-img convert -f raw -O vhdx source.img output.vhdx
- Disk2vhd - Sysinternals | Microsoft Learn
- Disk2vhd simplifies the migration of physical systems into virtual machines.
- Disk2vhd is a utility that creates VHD (Virtual Hard Disk - Microsoft's Virtual Machine disk format) versions of physical disks for use in Microsoft Virtual PC or Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machines (VMs).
- The difference between Disk2vhd and other physical-to-virtual tools is that you can run Disk2vhd on a system that’s online.
- Disk2vhd uses Windows' Volume Snapshot capability, introduced in Windows XP, to create consistent point-in-time snapshots of the volumes you want to include in a conversion.
- You can even have Disk2vhd create the VHDs on local volumes, even ones being converted (though performance is better when the VHD is on a disk different than ones being converted).
- Disk2vhd: Best Guide to Convert Physical to Virtual Machine - EaseUS - Disk2vhd is a utility that converts logical disks into virtual disks in VHD format. In this article, I will explain in detail what is disk2vhd and how it can be used to help us meet our virtualization needs.
- vhdtool.exe / vhdxtool.exe (Microsoft)
- These are old sofwares made by Microsoft and should not be used.
- VhdTool Is Dead, Long Live VhdxTool! | Systola
- KB200004
- This article covers this new tool and explains a few things.
- VhdxTool | Systola
- KB100005
- VhxdTool is a command line utility for Windows for quick creation and resizing of virtual hard disk files (VHDX).
- Convert-VHD (PowerShell) (Hyper-V Management Tools)
- How to Convert from Dynamic VHD/VHDX Disk Format to / from Fixed in Hyper-V | BC Blog
Convert-VHD –Path c:\VM\my-vhdx.vhdx –DestinationPath c:\New-VM\new-vhdx.vhdx –VHDType Dynamic
- Converting Fixed Size VHDs to Dynamic Sized VHDs – The World According to Mitch - You can use the Hyper-V menu or powershell.
- Convert VHD to VHDX | Virtualization file conversions - How to convert VHD to VHDX for better performance and larger disk support using Hyper-V Manager or PowerShell.
- How to convert VHD to VHDX using Hyper-V Manager | TheWindowsClub - If you have a VHD file and want to convert it to VHDX format, you can use Hyper-V Manager. This tutorial will show you how to convert VHD to VHDX using Hyper-V Manager in Windows 11/10.
- CITRIXEN: Convert, Resize, and Optimize VHD and VHDX files with PowerShell
- Convert, Resize, and Optimize VHD and VHDX files with PowerShell.
- This small article covers a lot.
- How to Convert from Dynamic VHD/VHDX Disk Format to / from Fixed in Hyper-V | BC Blog
- Powershell
- Fixed to Dynamic, Dynamic to Fixed
## Fixed --> Dynamic Convert-VHD -Path "D:\Path\To\Fixed-Disk.vhd" -DestinationPath "D:\Path\To\Dynamic-Disk.vhd" -VHDType Dynamic ## Dynamic --> Fixed (For Reference Only) Convert-VHD -Path "D:\Path\To\Disk-dynamic.vhd" -DestinationPath "D:\Path\To\Disk-trimmed-fixed.vhd" -VHDType Fixed
- Fixed to Dynamic, Dynamic to Fixed
- Multiple
- How to Convert VMDK to VHDX (VMWare to Hyper-V)? | TheITBros
- In an environment where different versions of the hypervisor are used, it is often necessary to convert virtual machine files from one format to another. In this article, we will look at how to convert a VMware virtual machine’s VMDK file to Hyper-V (VHDX) format.
- The article covers both PowerShell, Starwind V2V converter and QEMU-img.
- Convert VHD from Dynamic to Fixed | Easy Guide to Convert Dynamic VHD to Fixed | DiskInternals - Easily convert dynamic VHD to fixed or fixed VHD to dynamic with this step-by-step guide ?️. Learn the best tools and methods for hassle-free VHD conversions!
- Ultimate Guide to Converting Virtual Disks with VBoxManage and Other Tools - Learn how to convert VDI, VMDK, VHD, and more with VBoxManage, qemu-img, and other system virtualization tools.
- How to Convert VMDK to VHDX (VMWare to Hyper-V)? | TheITBros
Resizing
- VhdResizer | Softpedia
- A small and straightforward Windows utility designed to help users to shrink or expand the volumes of VHD files. Made in 2007.
- How to Resize a Microsoft Virtual Hard Drive (VHD) File - When you create a Microsoft Virtual Hard Drive either through Virtual PC or Virtual Server, you have to specify the maximum size of the file up front.
- VhdxTool
- VhxdTool is a command line utility for Windows for quick creation and resizing of virtual hard disk files (VHDX).
- This offers similar functionality to a former program vhdtool for Windows Server 2008/R2, but while vhdtool worked with older (VHD) format, vhdxtool works with the new (VHDX) format.
Compacting
- vboxmanage
- wslcompact
- Compacts the size of the ever-growing WSL vhdx images.
- Compacting the size of the ever-growing WSL images · microsoft/WSL · Discussion #9566 · GitHub
- Give the usage commands of the tool.
- Using virtual drives is a great idea. But, ext4 filesystem optimization inside VHDX images is not so well supported by the optimization tools. NTFS partitions are well optimized, but ext4 partitions are not so well optimized, and WSL suffers from this problem.
- Since WSL doesn't provide a good solution for this, I have coded a small utility wslcompact that compacts the WSL partitions.
- Any thoughts on improving the tool would be welcome. However, it would be better if the WSL team releases something similar. A good improvement would be an improvement in the export function, not only making a copy of the VHD file but dumping the contents in a newly created VHD, which would considerably reduce the size of the backup.
- Optimize-VHD (Hyper-V Management Tools)
- Needs Hyper-V to be installed.
Optimize-VHD -Path "Path\To\Your\VHDfile.vhdx" -Mode Full
- Needs Hyper-V to be installed.
- DISKPART
- Always present in Windows.
- Optimize-Vhd doesn't require diskpart, of course, both processes can do more or less the same regarding drive compaction. Diskpart is somehow more convenient as it is readily available in all systems without the need for installing any extra package.
- diskpart | Microsoft Learn - Reference article for the diskpart command interpreter, which helps you manage your computer's drives.
- Compact a VHD file created by Disk Management? - Super User
- You can then complete the compacting using diskpart from a Command Prompt
- Run
diskpart - Select the disk via its path: s
elect vdisk file="<path>" - Attach it as read-only:
attach vdisk readonly - Compact it:
compact vdisk - Upon completion of the compact, detach it again:
detach vdisk
- Run
- You can then complete the compacting using diskpart from a Command Prompt
Image Creation (Disk)
- DiskGenius: Data Recovery, Partition Manager, Backup & Disk Utilities
- This software handles a variety of formats (.vmdk, .vhd, .vhdx, .vdi, .hdd, .img) but is read only in the free version, this means you cannot backup a drive to one of these formats with the free version. There is a proprietary DiskGenius disk image format (.pmfx) you can use for normal disk operations.
- The paid version will also allow you to convert between the various Disk Image formats
- You can also browse the files on disk images.
- DiskImager
- A simple but powerful tool for saving and writing disk images.
- Save raw binary images of any disk as regular files.
- Write disk images to physical disks.
- When writing an image to a disk, supports industry-standard disk image formats (in addition to raw images), including VDI (VirtualBox), VMDK (VMware), E01 (EnCase), and VHDX/VHD (Virtual hard disk).
- MultiDrive
- 100% free disk management software for Windows. Clone, backup, restore, and erase drives with ease.
- Allows you to create IMG of drives and I think also USB Drives.
- dd (Linux)
- This is a low-level command-line utility that copies data from one location to another, byte by byte. It's commonly used to:
- Clone disks or partitions
- Create disk images
- Write ISO or IMG files to USB drives
- How to Make Disk Images in Linux with the DD Command: An Essential Guide for Sysadmins – TheLinuxCode
- Hey there! Do you manage Linux systems and need to make backups or clone disks? If so, the dd command should be part of your essential sysadmin toolkit. In this guide, I‘ll show you how to use dd to create complete disk images in Linux.
- This is very comprehensive.
- How to make disk image with dd on Linux or Unix | nixCraft - Explains how to use the dd command on Linux, macOS (OS X), FreeBSD, and Unix like system to clone hard disk or partitions from the CLI.
- This is a low-level command-line utility that copies data from one location to another, byte by byte. It's commonly used to:
- OSFClone
- OSFClone is a free, open-source utility designed for use with OSForensics. OSFClone is a self-booting solution which lets you create or clone exact, forensic-grade raw disk images.
- OSFClone is a free, self-booting solution which enables you to create or clone exact raw disk images quickly and independent of the installed operating system. In addition to raw disk images, OSFClone also supports imaging drives to the open Advance Forensics Format (AFF), AFF is an open and extensible format to store disk images and associated metadata, and Expert Witness Compression Format (EWF). An open standard enables investigators to quickly and efficiently use their preferred tools for drive analysis.
Image Creation (USB)
Rufus
- Rufus - The Official Website
- Rufus is a small application that creates bootable USB drives, which can then be used to install or run Microsoft Windows, Linux or DOS.
- This app also allows you to create disk image files (VHD/VHDX) of any USB pendrives plugged in.
- Rufus uses DD (or windows equivalent) to image the drive to a VHD/VHDX.
- This creates a "RAW" image as all bits are read `As-Is` and then recorded into the image irrelevant of whether they are files, empty space or random bits.
- Being raw, they are fully equivalent to a block-for-block disk image.
- Rufus produces Fixed (Pre-Allocated) VHD images.
- The image is the same size as the USB drive.
- The file size cannot be reduced because it's size is fixed.
- Reclaiming free space will not reduce the image size.
- Rufus produces Dynamic (Growable) VHDX images
- Because it is made from a raw DD copy, all sectors are used.
- The image is the same size as the USB drive.
- To reclaim free space you need to
- Internally recover the free space from the virtualised drive
- Zero out sectors or
- Mount the image and have a live OS TRIM the drive
- Compacted the disk image.
- Have an external program (file aware) compress the image file by removing all of the references to free thus reducing the VHDX image file size.
- Zero fill the USB drive before use
- This will reduce the noise on the drive and allow for compression, but this is obviously no good for drive that already have data on them.
- Internally recover the free space from the virtualised drive
- Rufus uses DD (or windows equivalent) to image the drive to a VHD/VHDX.
- Commands
- Power keys/Cheat modes - FAQ · pbatard/rufus Wiki · GitHub
Ctrl+L= Show the logCtrl+Z- Zero fill the selected USB drive.
- It writes zeroes into every single sector of the drive.
- This leaves the drive completely blank and unpartitioned.
- Misc
- How do I create a VHD drive to use with Rufus? - FAQ · pbatard/rufus Wiki · GitHub - Here is how you can create a VHD/VHDX to use with Rufus.
- Help, I don't see the ISO download button! - FAQ · pbatard/rufus Wiki · GitHub
- For the ISO download feature to be avaiable, you also need to have 'Check for updates' enabled in the Rufus settings.
- Also, if there was an issue with your network while Rufus launching or if you are running Rufus in an unconnected environment, the ISO download button will not appear.
- Disk Format information
- When you create a VHD(X) with Rufus, it effectively changes media state from removable (USB) to non-removable (HDD) as this is what is defined in the header that Rufus attached to the binary image it has just created.
- This is an AI analysis of the rufus disk mounting process
- Virtual Disk Handling | pbatard/rufus | DeepWiki
- The Virtual Disk Handling system in Rufus provides capabilities for working with virtual disk files and disk images.
- This includes mounting and analyzing VHD/VHDX files, handling Windows Imaging Format (WIM) files, and supporting various compressed disk image formats.
- Virtual disk handling enables Rufus to extract content from these files, analyze their bootability, and use them as sources for creating bootable USB drives.
- Virtual Disk Handling | pbatard/rufus | DeepWiki
- Why does Rufus call a .vhd file a DD Image? - Super User
- Rufus developer here. This is because the save option is only for uncompressed VHD images, and uncompressed VHD images are just the same as DD images with an extra 512 byte footer added.
- So, for all purposes, you can use DD to write the VHD image created by Rufus, and it will work just fine (with either the extra 512 byte footer being ignored as random data, if you use a larger sized disk, or being dropped, if using same exact same size disk).
- Ergo, what Rufus creates when you click the save button is essentially a DD image since it can very much be used as such.
- PS: For those who wonder why Rufus doesn't compress the VHD images it saves this is primarily due to the compression algorithm being used by Microsoft being very poor (IMO) and therefore not worth spending time implementing support for. This is also part of the reason why save as DD image is only available when clicking the advanced options.
- Getting Rufus to output to a disk image file - Super User
- Akeo
- Rufus can create an uncompressed VHD image from whichever drive you have currently selected, which, for all intent and purposes can be used as a regular DD image (because the only difference with a regular DD image is an extra 512-byte footer, which, no matter how much you may think otherwise, will NEVER EVER come in the way of using the
.vhdas a.img). - UPDATE: And recent versions can also create compressed VHDX images, that take less space, and that can work the same way.
- Rufus can create an uncompressed VHD image from whichever drive you have currently selected, which, for all intent and purposes can be used as a regular DD image (because the only difference with a regular DD image is an extra 512-byte footer, which, no matter how much you may think otherwise, will NEVER EVER come in the way of using the
- gronostaj
- Solution 1: Read the image from a prepared flash drive. Win32DiskImager can be used to do this.
- Solution 2: Prepare your own hybrid ISO. Most of modern Linux distros use so called hybrid ISOs. They are valid ISOs that can be burned to a CD/DVD, but at the same time they are valid disk images that can be written to a flash drive. For example you could feed an Ubuntu ISO to Win32DiskImager and have it write it to disk (Rufus may offer this feature for some ISOs, it calls it "dd mode"). Community documentation on ISO customization is ten to thirteen years old, but may still be useful and you'll find many useful guides all over the Internet.
- Akeo
- Make image from disc · Issue #1274 · pbatard/rufus · GitHub
- Aha, then this is my cue to enlighten you:
- An uncompressed is just a DD image with a 512 byte footer added.
- Therefore, because writing that footer (or not) is inconsequential, you can absolutely use the
.vhdthat was created by Rufus as a DD image. - Now, in case you have doubts about those extra 512 bytes potentially causing an issue let me explain that:
- If you are restoring the image to a drive of the exact same size as the one you used to create the VHD, then these 512 bytes will happily be dropped by
dd(At least the Linux version ofdddoesn't care much if you try to write more data that the drive can hold - it'll report it, but it will not have any kind of impact on the data written), leaving you with a 1:1 copy of the original drive. - If you are using a drive that is larger than the one you used to create the VHD, then, even if you are unfortunate enough to have the 512-byte VHD footer fall at the precise location where the GPT backup is located (a few sectors before the end of the drive), then because this is a backup, any modern OS will detect that the backup is corrupted and fix it by duplicating the master, which is located at the beginning of the disk. Oh, and, even when you restore a pure GPT based DD image onto a larger drive, this kind of GPT backup fix needs to happen anyway, since, obviously, the backup GPT from the original image is at the wrong location, and a new backup GPT needs to be created at the right one. In other words, the writing of that 512-byte VHD footer is no different than the case of expecting whatever garbled data one might find at the expected location for the backup GPT when writing a "regular" DD image. And really, even as this is a complete non-issue, the possibility that the VHD footer will fall at the precise location where the backup GPT should go is exceedingly small. Oh, and if your image is using a MBR partition table, then it's even less of an issue, because none of the data up to (size of VHD - 512 bytes) will EVER be seen as accessible from the original image.
- If you are restoring the image to a drive of the exact same size as the one you used to create the VHD, then these 512 bytes will happily be dropped by
- In summary, and I really have to stress this out, for all purposes, an uncompressed VHD image is exactly the same as a DD image. Therefore you can use the Rufus created
.vhdexactly as you would use a standard DD image. There REALLY is no "What if...?" or "But surely..." associated to using an uncompressed.vhdas you would a DD image.
- VHDX Disk image created by Rufus is shown as a Dynamic (Growable) image and not as a fixed (pre-allocated) disk image
- This is correct and is expected behaviour. A VHD image file will always be a fixed sizxe.
- StarWind V2V Converter shows the VHDX image as a Growable Image · Issue #2831 · pbatard/rufus · GitHub
- Hence VHDX is a compressed image format.
- Now, of course, if you have random data all over the disk, the fact that VHDX can compress data does not mean that its size will always be smaller than VHD. But in you have long sections of zeroed data, VHDX will work wonders as a compressed disk image format, hence why Rufus labels it as such.
- Well, using "growable" would imply that Rufus can somehow grow that drive, which it can't, so you have to be very careful about what the terminology you use implies your application might do (yes, even if you are going to reply "Well, it can be grown externally, so it still applies!"). And fixed/dynamic is already used for disks in a completely different context (fixed as opposed to removable, and dynamic disk is used in Windows disk manager and other places) so it would be exceedingly confusing there too.
- Instead, uncompressed and compressed (or "compressable", but we don't want to go into semantics here) does describe pretty exactly the difference between VHD and VHDX as far as Rufus' usage is concerned, so I am not planning to change the terminology because one person thinks some alternative would work better for their specific workflow.
- Why This Happens
- Rufus does not create truly dynamic (growable) disks. Instead, it writes raw, fully allocated (fixed-size) disk images, even when saving to
.vhdxformat. But:- Rufus doesn't explicitly write the full VHDX metadata headers the same way Hyper-V or Windows Disk Management does.
- This can cause third-party tools like StarWind to misinterpret the image format or default to "growable" in their interface or assumptions.
- Rufus does not create truly dynamic (growable) disks. Instead, it writes raw, fully allocated (fixed-size) disk images, even when saving to
- Evidence & Explanation
- StarWind is designed to work with officially structured VHDX files (including all metadata).
- Rufus writes uncompressed, flat VHDX files but doesn’t necessarily populate all optional VHDX metadata fields.
- StarWind may detect the structure or size mismatch and label it as "growable" (which usually means "dynamic")—even if it's not actually dynamic.
- How to Check What It Really Is
- You can confirm the truth using:
- PowerShell
Get-VHD -Path "C:\path\to\your.vhdx"
- Look for VHDType: Fixed or Dynamic
- vhdxinfo (from libvhdi)
vhdxinfo mydisk.vhdx
- It will show you
type: fixedortype: dynamicexplicitly.
- It will show you
- Workaround or Fix
- If you want the VHDX to be 100% standards-compliant and recognized as "fixed" by all tools (including StarWind), do this:
- Mount the Rufus-generated VHDX in Windows.
- Create a new fixed-size VHDX using:
New-VHD -Path "C:\fixed-compliant.vhdx" -SizeBytes 10GB -Fixed
- Use
ddorxcopyto clone contents to the new disk.
- This gives you a 100% spec-compliant VHDX that should show as "fixed" in all tools.
- If you want the VHDX to be 100% standards-compliant and recognized as "fixed" by all tools (including StarWind), do this:
Others
- ImageUSB (PassMark)
- ImageUSB is an effective tool for writing an image to multiple USB Flash Drives for mass duplication and creating images of thoese drives.
- ImageUSB is a free utility which lets you write an image concurrently to multiple USB Flash Drives. Capable of creating exact bit-level copies of USB Flash Drive (UFDs), ImageUSB is an extremely effective tool for the mass duplication of UFDs.ImageUSB also supports writing of an ISO file byte by byte directly to an USB drive (*). ImageUSB can also be used to install OSFClone to a USB Drive for use with PassMark OSForensics™.
- Unlike other USB duplication tools, ImageUSB can preserve all unused and slack space during the cloning process, including the Master Boot Record (MBR). ImageUSB can perform flawless mass duplications of all UFD images, including bootable UFDs.
- ImageUSB includes functionality to Zero a USB Flash Drive. This will replace the contents of the entire drive with 0s. Or alternatively to just Zero the MBR and/or GPT entries that exists on the drive. In addition, imageUSB has the ability to reformat even hard to format drives and reclaim any disk space that may be lost previously.
- (*) CD ISO images use a different file systems compared to USB drives. So the direct imaging of ISO9660, Joliet or UDF file system, from a CD, to a USB drive, might not allow the USB drive to function in all operating systems. A reformat can recover the drive however. As of V1.5, imageUSB now supports extraction of ISO contents onto USB Drive.
- Warning: Due to the forensic nature of image duplication by ImageUSB, please ensure that you select UFDs with a storage size similar to the image you wish to duplicate. For example, if a 2GB image is copied to an 8GB USB Flash Drive, the drive will only be able to use two out of the eight gigabytes of storage space. In this scenario, users will need to reformat the UFD in order to access the rest of the storage space.
- How to Create an Image of Your USB Drive | How-To Geek - You can backup your USB drive by creating a saved image. You can even take that image and clone multiple USB sticks. This guide shows you how to create an image of your USB drive.
- USB Image Tool – alex's coding playground
- USB Image Tool can create images of USB flash drives, SD cards and any other devices that are mounted as USB storage drives.
- It can create an exact byte copy of these devices in raw and compressed image formats and also restores or write images on the device.
- USB Image Tool works with any device, that implements the USB Mass Storage protocol. This includes flash drives, card readers/SD cards and a lot of other devices like digicams, cell phones and mobile music players.
- USBImager
- A really simple GUI application that writes compressed disk images to USB drives
and creates backups. Available platforms: Windows, MacOSX and Linux. Its interface is as simple as it gets, totally bloat-free.
- A really simple GUI application that writes compressed disk images to USB drives
- UltraISO
- This can write images to USB so I am guessing it can make them aswell.
Disk Image Repair software
- VMFS Recovery™ - repair VMDK, VMDK recovery tool. ESX/ESXi recovery | DiskInternals - VMFS Recovery™ repairs VMDK files stored in Virtual Machine images and compatible with WMware® VMFS, vSphere, ESX, ESXi Server, VirtualPC, VirtualBox and other. VMFS Recovery™ recovers data from corrupt or deleted VM images.
- VDI Repair Tool for Virtual Disk Image Recovery - SysInfo - To repair corrupt VDI file, VDI Repair tool is the best solution one can have. Get free VDI recovery tool to restore Virtual disk image data from corrupt VDI files.
- VHD Recovery Tool to Recover Deleted, Corrupted VHD File Free - VHD Recovery Tool is a best Virtual File Recovery software to recover damaged VHD file. It repairs corrupt VHD file and recover VHD data in their original form.
- Smart Virtual Disk recovery solution- restore corrupt & formatted VHD files. - Virtual disk recovery '' VHD recovery tool ''is made to restore corrupt VHD files. Get the best VHD recovery tool online to recover your corrupt and formatted VHD files.
- Virtual Disk Recovery Tool to Recover Data from Corrupt Disk Image File - Aryson Virtual Disk Recovery Software permits you to repair and restore all types of corrupted Virtual Machine VMware Files including all databases.
Other Software
- sDelete (Secure Delete)
- SDelete - Sysinternals | Microsoft Learn - Securely overwrite your sensitive files and cleanse your free space of previously deleted files using this DoD-compliant secure delete program.
- How to use the command 'sdelete' (with examples) - Secure deletion is an essential part of data management and protection, particularly when it involves sensitive information. The command-line tool ‘sdelete’ offers a robust solution by permanently erasing files, directories, or entire volumes, thus ensuring that data cannot be recovered. Developed by Sysinternals, ‘sdelete’ employs advanced algorithms to overwrite data, mitigating the risk of unauthorized data access. Below we explore various use cases, each tailored to different secure deletion needs.
- Meet Sdelete, the obscure Microsoft tool that wipes data for good | PCWorld - Sdelete, short for Secure Delete, is a powerful but little-known tool from Microsoft's Sysinternals suite that permanently wipes files and folders by overwriting data.
- How to use SDelete to ensure deleted data is gone for good | TechTarget - Standard delete functions aren't good enough to guarantee data is gone for good. Learn how to use SDelete to ensure your information is removed permanently.
Mounting and Managing Images (in Windows)
- Windows
- It can mount WIM, VHD and VHDX natively.
- You can use 7zip to open WIM files.
- Mount-WindowsImage (Dism) | Microsoft Learn - Mounts a Windows image in a WIM or VHD file to a directory on the local computer.
- How To Mount and Update Windows Image Files (WIM) | KC's Blog
- Using Microsoft’s own Windows Image Files (WIM) format, it’s also easy to mount to not only read but update files in the image file
- Example
## Mount WIM DISM /Mount-Wim /WimFile:"d:\boot.wim" /index:1 /MountDir:"d:\chicken" ## Make changes # Unmount WIM (Discarding Changes): DISM /unmount-wim /MountDir:"d:\chicken" /discard # Unmount WIM (Keeping Changes): DISM /unmount-wim /MountDir:"d:\chicken" /commit
- Arsenal Image Mounter
- Arsenal Image Mounter mounts the contents of disk images as complete disks in Windows.
- FTK Imager - Forensic Data Imaging and Preview Solution | Exterro
- A free data preview and imaging tool used to acquire electronic evidence in a forensically sound manner by creating copies of computer data without making changes to the original evidence.
- With FTK Imager, you can create forensic images of local hard drives, CDs and DVDs, thumb drives or other USB devices.
- Mount an image for a read-only view that leverages Windows® File Explorer to see the content of the image exactly as the user saw it on the original drive.
- OSFMount - Mount Disk Images & Create RAM Drives
- The free OSFMount tool mounts raw disk image files in mulitple formats. You can also create RAM drives. Formats supported include img, dd, E01, VHD, ISO & bin
- Instructions
- Step 1 of 4: Just select your disk image, do not mount as ram disk
- Step 2 of 4: Mount entire image as virtual disk
- Step 3 of 4: Skipped by the software, must be something to do with partition detection.
- Step 4 of 4:
- Read-only drive: Optional, but readonly keeps the original image clean
- Write mode: Write cache
- Drive emulation: Physical Disk Emulation = we need this for the boot sector
- Drive type: HDD
- NB:
- In Starwind, your virtual disk will be listed as real disk called
osfdisk - If you mount as FDD (possible a super floppy mode) Starwind will not see the drive.
- In Starwind, your virtual disk will be listed as real disk called
- OSFMount - What is the difference between logical and physical drive emulation modes:
- In OSFMount, the difference between logical and physical drive emulation lies in how the mounted image is presented to the operating system:
- Logical Drive Emulation
- What it is: Mounts a partition within a disk image as a drive.
- Use case: When you're only interested in accessing a specific partition (e.g., a file system like NTFS or FAT32).
- Example: Mounting just the C: partition from a full disk image.
- Visible as: A standard drive letter in Windows (e.g., D:, E:).
- No boot sector or MBR is emulated—just the file system content.
- Faster and simpler for common use cases like extracting files.
- Physical Drive Emulation
- What it is: Mounts the entire image as if it were a real physical disk, including the MBR, partition table, and all partitions.
- Use case: When you need to work with the full disk structure (e.g., for forensic analysis or imaging software that requires MBR access).
- Visible as: A physical disk (not a drive letter), usually accessed via disk management tools or forensic software.
- Can emulate multiple partitions, raw sectors, boot records, etc.
- Slower and more resource-intensive, but gives low-level access.
- Logical Drive Emulation
- Forum
- OSFMount decides automatically whether to use physical or logical emulation based on the presence of a partition table in the image.
- OSFMount shall automatically mount using Physical Drive or Logical emulation based on whether the image file contains a partition table or not
- Another forum post clarifies the difference in practical terms:
- Logical emulation: mounts only the file system as a volume — you get a drive letter but no low-level disk access..
- Physical emulation: mounts the entire disk, including all sectors and partitions — useful for low-level forensic or VM boot tasks
- In OSFMount, the difference between logical and physical drive emulation lies in how the mounted image is presented to the operating system:
- VMware Workstation / Player
- This has inbuilt functionality to mount
.vmdkimage files - How to Open VMware VMDK Files in Windows 10/11 and 8.1/7 - Sysprobs
- Do you want to know how to open VMware VMDK files in Windows 10/11 or 8.1/7? Here is the simple guide without any 3rd party tools.
- This has inbuilt functionality to mount
- VMware/VMDK Additional
- 4 Ways to Mount a VMDK Image File in Windows | KC's Blog - If you have a VMDK file that hosts one or more VM partitions, here are 4 ways to get it mounted in Windows as a disk drive.
VMware Workstation vmware-mount.exe X: “C:\Temp\TestVM.vmdk”
- Exact Steps to Map VMware Disk to Windows Disk
- For some reason, you may want to mount VMware disk to Windows disk. If so, take a look at this post where 3 available methods are offered.
- Mount VMware Disk to Windows Disk via VMware Workstation
- Mount VMware Disk to Windows Disk via Disk Mount Utility
- Mount VMware Disk to Windows Disk via vSphere Disk Development Kit
- For some reason, you may want to mount VMware disk to Windows disk. If so, take a look at this post where 3 available methods are offered.
- How to Open VMDK File in Windows 11
- This guide shows you how to open a VMDK (Virtual Machine Disk) file in Windows 11 and access the contents in it using VMware Workstation or 7-Zip file archiver.
- 4 Ways to Mount a VMDK Image File in Windows | KC's Blog - If you have a VMDK file that hosts one or more VM partitions, here are 4 ways to get it mounted in Windows as a disk drive.
- Image Mounter | Paragon Software Group
- Image Mounter helps IT pros and forensic experts mounting raw images as well as virtual drives.
- Mount RAW images and a plethora of virtual disk images
- Mount disks on the physical level with all partitions
- Auto-mount partitions in familiar OS formats
- Leverage cross-platform compatibility delivered by the Paragon technology.
- The preview version of Image Mounter by Paragon Software is available free of charge!
- VMFS Recovery | DiskInternals
- This is primarily a image recovery utility but can mount VMDK image files.
- WinMount - Compress & Mount RAR ZIP CD DVD HDD images (this is very old)
- Winmount is a powerful windows utility which is dedicated to managing files and disks impressively and conveniently.
- It's a compression tool, also a virtual disk tool ( Mount RAR ZIP MOU and CD DVD HDD images as virtual disk/folder ).
- Supported formats:MOU, RAR, ZIP, 7Z, CAB, ARJ, ISO, GZ, BZ2, TAR, WIM, ISO, BIN, BWT, MDS/MDF, NRG, IMG, ISZ, CUE, CCD, APE, FLAC, WV, VHD, VDI, VMDK.
- DAEMON Tools Lite: The most personal application for disc imaging yet - DAEMON-Tools.cc
- A well-known solution that allows you to mount, copy and create an image. It works with the most popular types of virtual discs.
- DAEMON Tools Lite allows you to mount all known types of disc image files and emulates up to 4 DT + SCSI + HDD devices.
- It enables you to create images of your optical discs and access them via well-organized catalogue.
- Simple VHD Manager v1.5
- A portable freeware which helps VHD users simplify some of these operations:
- You can attach and detach VHD/VHDX/ISO files via drag and drop
- You can permanently attach a virtual hard disk in Windows 11 – 10 – 8,1 – 8 and Windows 7
- You can easily add and/or remove VHD/VHDX/ISO files to the boot menu
- A portable freeware which helps VHD users simplify some of these operations:
- Mount and Unmount a VHD File in Windows Explorer via a Right-Click
- Virtualization has become an incredibly powerful and flexible way to deploy environments. So much in fact that Microsoft has integrated the ability to attach virtual hard drive (VHD) files as physical disks in the Windows Disk Management tool.
- This process is easy enough to do manually but if you attach VHD files often then we have a solution which enables you to mount and unmount VHD files with a single click.
- This article has batch scripts you can attach to the context menu to allow easy use of the right click feature.
Best Practices
- Fixed vs Dynamic disks - Microsoft Q&A - Hi Can anyone point me to a link that shows the correct official guidance from Microsoft as to if fixed or dynamic VHD's or VHDX's should be used in a production enviroment? Thanks
Tutorials
- Create from Scratch
- Windows Disk Management
- How do I create a VHD drive from scratch to use with Rufus? - FAQ · pbatard/rufus Wiki · GitHub - Create a VHD/VHDX imageusing windows in-built Disk Management.
- Control Panel --> Administrative Tools --> Computer management --> Storage --> Disk Management (or however you get there)
- On newer versions of Windows you cannot click on the drives as shwon here. Look under the Actions menu and you will find:
- Create VHD
- Attach VHD
- How to create virtual drive (VHD, VHDX, Dev Drive) on Windows 11 - Pureinfotech - The Settings app on Windows 11 now allows you to create and attach virtual drives, and in this guide, you will learn how.
- Free and Powerful VHD Resizer Download - AOMEI Partition Assistant - This article focuses on VHD Resizer. First you’ll be told what VHD is and its features, and then an amazing VHD resizer will be recommended.
- How to create and set up new VHD or VHDX File in Windows 11/10 | TheWindowsClub - Today, we will see how to create and set up (initialized and formatted) a new VHD and VHDX virtual hard disk file in Windows 11/10 using Disk Management. But before we begin, we will see what is a VHD and VHDX.
- How do I create a VHD drive from scratch to use with Rufus? - FAQ · pbatard/rufus Wiki · GitHub - Create a VHD/VHDX imageusing windows in-built Disk Management.
- Windows Disk Management
- Export/Import Virtual Machines
- How To Convert Virtual Machines Between VirtualBox and VMware - Migrating to another virtual machine program can be intimidating. if you already have your virtual machines set up they way you like them, you don’t necessarily have to install them from scratch – you can migrate your existing virtual machines.
- Migrate Proxmox VMs to VMware with StarWind V2V Converter • Nolabnoparty - StarWind V2V Converter is a free tool used to convert VMs from one format to another bidirectionally and physical machines to VMs.
- Shrinking and Compacting
- How to Shrink and Compact VHDX Files in Hyper-V? | Vinchin Backup
- This article serves as a comprehensive tutorial on managing VHDX disk space in Microsoft Hyper-V environments.
- It differentiates between shrinking and compacting VHDX files, outlines the advantages of the VHDX format over the older VHD, and provides detailed steps to perform both shrink and compact operations using both Hyper-V Manager and PowerShell commands.
- How to Shrink and Compact Virtual Hard Disks in Hyper-V | TheWindowsClub - In this post, we will see how to shrink and compact hard disks in Hyper-V. This allows you to make room for the hard disks if they are too big for your physical computer. Since Hyper-V hard disks are usually dynamic in nature, it is crucial to shrink and compact virtual hard disks in Hyper-V.
- How to Shrink the Virtual Disk of a Linux Distro in WSL | by bonguides.com | Medium - When you delete files or free up space in your WSL distribution, the virtual disk doesn’t automatically shrink. To reclaim this unused space, you need to compact the virtual disk (VHDX) file.
- Diskpart
- Open PowerShell (Terminal) as administrator then type diskpart and press Enter
- Use the following command, replacing the path with the actual location of your VHDX file to select the VHDX file.
select vdisk file=""
- Once the disk is selected, run the below command within the DiskPart prompt to shirk the disk. This will reclaim the unused space in your VHD file. You should see a message indicating that the disk has been successfully compacted
compact vdisk
- After the process is complete, you can check the size of the VHD file to confirm that it has been reduced.
- Hyper-V
- Open PowerShell as administrator, then navigate to the location of the VHD file
- Run the following command to compact the VHD file:
Optimize-VHD -Path .ext4.vhdx full
- You can monitor the processing status on the screen. After completion, verify the virtual disk size to confirm functionality.
- WSLCOMPACT
- Install it using the below PowerShell commands:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser iwr -useb https://raw.githubusercontent.com/okibcn/wslcompact/main/setup | iex
- Run the wslcompact command to see the current size and estimated size of all WSL instances.
- Run the below command to compact the disk and apply the change to the VHD file.
wslcompact -c ubuntu
- If the tool is no longer needed, to remove the utility, close all your PowerShell instances, open a fresh one, and type:
Remove-Item "$($env:PSModulePath.split(';')[0])/WslCompact" -Recurse -Force
- Install it using the below PowerShell commands:
- Diskpart
- Shrink and Compact Virtual Hard Disks In Hyper-V (Guide) - If your Hyper-V environment starts running low on disk space, find out how to shrink and compact virtual hard disks in this step-by-step guide.
- How to Shrink and Compact Virtual Hard Disks in Hyper-V - TechDirectArchive
- Master the process of shrinking and compacting your Hyper-V virtual hard disks to save space and enhance virtual machine efficiency.
- Different method iusing: Hyper-V Manager, PowerShell, Resize-VHD
- WSL2 on Windows 11 - Virtual Disk vhdx is 200GB now | Reddit
- Release VHDX unused space:
Open Powershell and run the following: wsl --shutdown diskpart select vdisk file="path-to-your-virtual-disk\ext4.vhdx" attach vdisk readonly compact vdisk detach vdisk exit
- Release VHDX unused space:
- How to Compact/Shrink a WSL2 Virtual Disk – Stephen Rees-Carter
- You can use the diskpart tool to compact a VHDX. This allows you to shrink a WSL2 virtual disk file, reclaiming disk space. I went from 100GB to 15GB.
- How to Compact a WSL2 VHDX Virtual Disk | mycodde.blogspot.com - I was struggling to compact my WSL VHDX disk, it has hardly 10 GB data but it was showing 72 GB in size.
- How to Shrink and Compact VHDX Files in Hyper-V? | Vinchin Backup
- Resizing
- How to Resize a VHD File or VHDX | DiskInternals - Learn how to resize VHD or VHDX files easily in Hyper-V or without it! Follow step-by-step methods using Hyper-V Manager, PowerShell, or Diskpart.
- Resize-VHD (Hyper-V) | Microsoft Learn - Use this topic (Resizes a virtual hard disk) to help manage Windows and Windows Server technologies with Windows PowerShell.
- Starwind V2V Converter
- Starwind V2V Converter - Ultimate Free P2V & V2V Conversion tool - This article explains the detailed feaures about Starwind V2V Converter and how to perform V2V & P2V conversion using Starwind V2V Converter
- VMware vCenter Converter Standalone
- Convert Physical Linux Server to VMware - P2V Vmware - In this topic, we will see how to convert a physical Linux server to a VMware VM. To make this conversion, I used VMware vCenter Converter Standalone.
- QEMU
- QEMU also supports various other image file formats for compatibility with older QEMU versions or other hypervisors, including VMDK, VDI, VHD (vpc), VHDX, qcow1 and QED. For a full list of supported formats see qemu-img --help. For a more detailed description of these formats, see the QEMU block drivers reference documentation.
- Converting images with qemu-img convert · GitHub - Converting images with qemu-img convert.
- How to use the command qemu-img (with examples)
- qemu-img is a versatile command-line utility designed to create and manipulate virtual HDD images for Quick Emulator (QEMU).
- This tool is particularly useful for handling tasks such as creating new disk images, converting between different virtual disk formats, resizing existing disk images, and more.
- Use Qemu-img to Manage and Convert Different Virtual Disks | Vinchin Backup - This post describes what is qemu-img and how to use this qemu disk image utility to create, resize, and convert virtual disk for VM management and migration.
- Converting a Physical disk to a Virtual disk with Qemu’s qemu-img on Windows | Virtually Fun - Give you the commands to convert a physical drive into a virtual disk and also gives the full list of support image files in QEMU.
- VBoxManage
- Converting disks (vboxmanage clonemedium)
- Convert VMDK to VirtualBox VDI and compact disk - How to convert the vmdk to a VDI file and then compact it.
## Convert VBoxManage clonemedium disk --format VDI [drive]:[\path_to_file\sourceFile.vmdk] [drive]:[\path-to\destinationFile.vdi] ## Compact VBoxManage modifyhd --compact "[drive]:\[path_to_image_file]\[name_of_image_file].vdi"
- Convert VMDK to VirtualBox VDI and compact disk - How to convert the vmdk to a VDI file and then compact it.
- resize VDI image size
VBoxManage modifyhd "[drive]:\[path_to_image_file]\[name_of_image_file].vdi" --resize 81920
- RAW Disk handling
- vboxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk - Bing Search
- The
VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdkcommand in VirtualBox allows you to create a virtual disk that maps to a physical disk or partition. This is useful for accessing a physical disk directly from a virtual machine. - Example
- To create a virtual disk that maps to an entire physical disk on a Windows host, use the following command:
VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\path\to\file.vmdk" -rawdisk \\.\PhysicalDrive0
- This command creates a
.vmdkfile that represents the physical diskPhysicalDrive0
- To create a virtual disk that maps to an entire physical disk on a Windows host, use the following command:
- Accessing Specific Partitions
- You can also map specific partitions of a physical disk. For example, to map partitions 1 and 5 of
/dev/sdaon a Linux host:VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename /path/to/file.vmdk -rawdisk /dev/sda -partitions 1,5
- This creates a
.vmdkfile that provides access to partitions 1 and 5 of/dev/sda
- You can also map specific partitions of a physical disk. For example, to map partitions 1 and 5 of
- Important Considerations
- Permissions: Ensure you have the necessary read/write permissions for the physical disk.
- Data Safety: Incorrect use can lead to data loss. Avoid accessing the same partition from both the host and guest simultaneously.
- Platform Differences: The device specification varies by platform (e.g.,
\\.\PhysicalDrive0for Windows,/dev/sdafor Linux).
- Using
VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk, you can effectively utilize physical disks within your VirtualBox VMs, providing flexibility and direct access to hardware resources. - Learn more
- The
- Example Commands
vboxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\Users\Public\Documents\VirtualBox\Raw Disk Images\spinrite.vmdk" -rawdisk "\\.\PhysicalDrive2" vboxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename "C:\rawdisks\spinrite.vmdk" -rawdisk "\\.\PhysicalDrive2"
- Use physical harddisk in Virtual Box - Straight forward instructions - Super User - Today, I managed to boot from physical drives. This achievement required....
- vboxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk - Bing Search
- Converting disks (vboxmanage clonemedium)
- How to Read VHDX Metadata (e.g., virtual size, block size)
- PowerShell
- Run:
Get-VHD -Path "C:\path\to\your.vhdx"- This returns
- VHD type (Fixed/Dynamic)
- Size
- Logical sector size
- Physical sector size
- This returns
- Note: Only works on Windows with Hyper-V features installed.
- Run:
- Use vhdxinfo from libvhdi (Linux/macOS/Windows)
- Install libvhdi tools:
- On Linux:
sudo apt install libvhdi-utils - On macOS (via brew):
brew install libvhdi - On Windows: Download libvhdi
- On Linux:
- Run:
vhdxinfo yourfile.vhdx- This will show:
- Header info
- Log GUIDs
- Virtual disk size
- Block size
- Parent locator (if differencing disk)
- This will show:
- Install libvhdi tools:
- Parse the VHDX File Manually (Hex or Script)
- You can parse the structure using a hex editor or script:
- Look for the magic header at offset 0:
00000000 76 68 64 78 66 69 6c 65 # "vhdxfile"
- Read region table at
0x20000, which lists metadata regions. - Use the region table to find:
- Virtual disk size
- Block size
- Logical/physical sector size
- GUIDs, versioning
- Look for the magic header at offset 0:
- You'd need to follow the Microsoft VHDX Specification to decode it fully.
- You can parse the structure using a hex editor or script:
- PowerShell
- TRIM'ing VHD(X) files
- Optimize-VHD (Hyper-V) | Microsoft Learn
- Optimizes the allocation of space used by virtual hard disk files, except for fixed virtual hard disks.
- Optimize-Volume (Storage) | Microsoft Learn
- Optimizes a volume.
- The Optimize-Volume cmdlet optimizes a volume, performing defragmentation, trim, slab consolidation, and storage tier processing. If no parameter is specified, then the default operation will be performed per the drive type as follows:
- HDD, Fixed VHD, Storage Space. -Analyze -Defrag.
- Tiered Storage Space. -TierOptimize.
- SSD with TRIM support. -Retrim.
- Storage Space (Thinly provisioned), SAN Virtual Disk (Thinly provisioned), Dynamic VHD, Differencing VHD. -Analyze -SlabConsolidate -Retrim.
- SSD without TRIM support, Removable FAT, Unknown. No operation.
- Multiple VHD/VHDx Optimization using PowerShell Workflows
- Optimize multiple VHD/VHDx files using PowerShell Workflows.
- After about 5 minutes of investigation I came up with this simple PowerShell command:
Get-VM | Where { $\_.State -eq 'Off' } | Get-VMHardDiskDrive | Optimize-VHD -Mode Full - It basically performs a full optimization on all VHD/VHDx files attached to all Virtual Machines that are in the Off state on the host the command is run on. This does the job quite well but has a few annoyances:
- The optimization is performed in series.
- Running guests won’t be optimized.
- The command only works on VMs on the host the command is run on.
- Optimize-VHD (Hyper-V) | Microsoft Learn
Reducing a VHDX Disk Image Size (Pre-created)
- I have not have much success with it.
- VHD images cannot be compressed or have their size reduced.
- Mount your drive image
- Windows Native (GUI)
- Right click on the drive image and select mount.
- or through `Disk Management`: Action --> Attach VHD
- Windows Native (diskpart)
- Select the disk via its path:
select vdisk file="<PathToYourDesktop>\DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.vhdx"
- Select the disk via its path:
- OSFMount
- Windows Native (GUI)
- Clear free space
- Run
sdeleteto zero out unused space on the image's volume - This might not be required if Starwind only sees files and not RAW data.
- Run
- Convert the image with StarWind V2V / P2V Converter
- Select the location of the image to convert: P2V
- Select physical data to convert: Physical Disk
- Select physical disk to convert: Virtual Disk
- Select the location of the destination image: Local file
- Select the destination image format: VHD/VHDX
- Select option for VHD/VHDX image format: VHDX growable image
- Ignore `Activate windows Repair Mode`
- Set destination filename:
<PathToYourDesktop>\DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.vhdx - Click `Convert`
- Compact the Dynamic disk image to reduce space
- This might be required to recover the free space.
- Unmount your drive image
- Window Native (GUI)
- You can unmount by right clicking on the drive and selecting Eject.
- or through `Disk Management`: Right click on the drive you want to unmount and select, Detach VHD.
- Windows Native (diskpart)
- run the command: detach vdisk
- Window Native (GUI)
Convert and Compact an Offline VHD/VHDX Fixed Disk Image to a Dynamic Disk Image
- TRIM is the process of the OS telling a SSD/NVMe drive to release the sector as it is no longer used, these drives do not actually zero fill the sectors to prevent uneeded writes, but in the future when the sector is read, the drive will supply back all Zeros.
- In a Fixed Disk Image, an unused sector is denoted by being all Zeros.
- In a Dynamic Disk Image, an empty unused sector is either all Zeros or is juts not referenced at all, in either case, all Zeros will be returned.
- If the Disk Image files is part of an online system, the OS it is running can perform TRIM on the drives and volumes to "Zero out" unused sectors.
Instructions
VHD and VHDX are interchangeable for these commands.
- Mount the Disk image
Mount-VHD -Path "D:\Path\To\Fixed-Disk.vhdx" -ReadOnly Or Mount through the GUI (Disk Management, Right Click)
-ReadOnly: This should protect the volume being written to by the OS, but not this command. I am not 100% on this.
- Zero out free space (inside the VHDX) (TRIM)
- You need to fill the free space with zeros so the compacting process knows it’s unused.
- Use sdelete from Sysinternals:
sdelete64.exe -z X:
- Replace
X:with the drive letter assigned to the mounted VHD. - -
z: This flag instructs ‘sdelete’ to write zeros over the available free space, a less intensive option than multiple passes and suitable for non-critical data. - This is needed because when a full RAW image of a drive is done, all bits are stored into the image, irrespective of whether that sector is holding any data.
- Unmount the VHDX
-
Dismount-VHD -Path "D:\Path\To\Fixed-Disk.vhdx" Or Unmount through the GUI (Disk Management, Right Click)
-
- Convert the Fixed VHDX to Dynamic.
- Powershell
Convert-VHD -Path "D:\Path\To\Fixed-Disk.vhd" -DestinationPath "D:\Path\To\Dynamic-Disk.vhd" -VHDType Dynamic
- Use StarWind V2V / P2V Converter to convert the Fixed disk to a Dynamic disk
- This process actually generates a copy of the disk image.
- Powershell
- Compact the Dynamic VHDX.
- Using Powershell
Optimize-VHD -Path "D:\Path\To\Dynamic-Disk.vhdx" -Mode Full
- Using Diskpart
diskpart select vdisk file="D:\Path\To\Dynamic-Disk.vhdx" attach vdisk readonly compact vdisk detach vdisk exit
readonly: This should protect the volume being written to by the OS, but not this command. I am not 100% on this.
- Using Powershell
- Done
Running Trim in a live OS
- Virtual Drive TRIM - VergeOS Docs - How to regain space on a virtual SSD
- After importing a virtual machine from another hypervisor, sometimes the free space available inside the virtual machine does not match the free space reported to the VergeOS platform.
- This discrepancy is often due to the virtual disk being thick-provisioned from the VM source, making VergeOS unaware of the unused disk space.
- To resolve this, a TRIM/UNMAP operation needs to be performed on the virtual disk from within the virtual machine.
- Trimming a Windows Drive
Optimize-Volume -DriveLetter YourDriveLetter -ReTrim -Verbose Optimize-Volume -DriveLetter E -ReTrim -Verbose
- Trimming a Linux Drive
## Check TRIM Timer/Schedule Status: sudo systemctl status fstrim.timer ## Check TRIM Service Status: sudo systemctl status fstrim If TRIM is enabled, an operation will run at the next scheduled time. If TRIM is not enabled, you can ## Run a manual TRIM using: sudo fstrim -av ## Info It is recommended to enable automatic TRIM to ensure that data usage is reflected accurately between VergeOS and the guest OS. ## To enable automatic TRIM, run: sudo systemctl enable fstrim.timer
Repairing Disk Images
- How to Repair Corrupted VHD File in Windows - Virtualization - Spiceworks Community - We all know that data is vulnerable in every form. This also allows to VHD(Virtual Hard Disk). When it comes to data loss, it becomes a critical situation for the users like us and it creates chaos inside us”. So in this handout, I’ll cover the VHD(Virtual Hard Disk) File, reasons for VHD Corruption and the way to repair or recover corrupt VHD.
- Corrupt VDI File: How to Fix and Recover Virtual Disk Data Effectively | DiskInternals - Troubleshoot a corrupt VDI file ? and recover lost data with expert methods. Use DiskInternals VDI Recovery™ for fast and reliable results. Safeguard your virtual machines today!
- Repair VHDX and Recover Corrupted/Unreadable VHD or VHDX Files in Windows 10 – EaseUS - This page provides the best VHD file recovery software and methods to help you effectively repair corrupted or unreadable VHD/VHDX and restore lost files in Windows 10 with simple clicks. Follow to see how to fix and repair your corrupted VHD disk partition without losing any data.
- 6 Methods to Fix VHD/VHDX file is Corrupted and Unreadable Error - VHD/VHDX file format which is similar to a hard drive is also prone to get corrupted and sometimes unreadable. The difference between VHDX and the physical hard drive is that VHDX is a virtual machine environment. The VHD/VHDX files getting corrupted or unreadable is a common problem and not easy to fix.
- Repair-VHD PowerShell: Step-by-Step Guide (3 Essential Steps to Fix VHD) | DiskInternals - Learn to repair VHD files using PowerShell ?️ with our comprehensive guide. Follow these steps to restore your virtual disks effectively!
- How to Repair VHD File: A Complete Guide to Recover Corrupted Virtual Disk Files - Virtual Disk Recovery Blogs - VHD Files are often prone to corruption which led to serious damage of your files and folders. So here read about how to repair vhd file manually.
- Free Methods to Repair Corrupted and Unreadable VHD Files (Aryson) - Free methods to repair corrupted and unreadable VHD files. Restore your virtual machines and recover data with our easy-to-follow guide.
Partition Types
- Partition type - Wikipedia
- Partition types: List of partition identifiers for PCs - Below a list of the known partition IDs (system indicators) of the various operating systems, file systems, boot managers, etc.
Makes your USB drive appear as a Hard drive and not removable Media
Is htis best ehre or antoher article
TL;DR = Might not be possible any more, and if it is, it is not worth the hassle.
- Flip the Removable Media bit (RMB) on the drive itself
- The Lexar BootIt utility was designed to "flip the removable media bit" on certain USB flash drives, making them appear as fixed (hard) disks to Windows. This was a niche utility and often highly specific to particular flash drive controllers. It's largely outdated and generally not recommended due to potential instability and the possibility of bricking your USB drive.
The "removable media bit" is often a hardware-level setting within the USB drive's controller firmware. So, if a utility like Lexar BootIt doesn't work for your specific drive, there's often no generic software alternative that can reliably change this "bit." - Flip Your Bit USB Utility To Make Local Drive | getusb.info
- BootIt is a Lexar based utility to flip the Removable Media Bit setting of a USB drive. What this means, is you can take a Lexar drive (and many other brands) and make it appear as a Local Drive on your PC rather than Removable Storage.
- Removable USB Flash Drive as Local HDD in Windows | Windows OS Hub
- In this article we’ll show you how to make a USB flash drive or an SD card to be identified in the Windows as a common local hard disk.
- Probably, you may ask why it’s necessary? The matter is that by default Windows identifies all the USB flash drives and SD cards as removable drives that can’t be split into several partitions with the built-in Windows tools.
- And even if you partition the USB flash drive into two or more volumes using third-party utilities (say, in Linux), only the first partition will be available in Windows. Windows supports multiple partitions only for hard disk drives identified as local (i.e. non-removable).
- Windows recognizes USB flash drives as removable devices due to the presence of a special descriptor bit RMB (removable media bit) on each of the devices. If the system determines that RMB=1 when polling the connected device using StorageDeviceProperty function, it concludes that this device is a removable drive. Thus, in order to convert the USB-flash to the hard disk it is enough to modify this descriptor.
- Software covered
- Lexar BootIt
- Hitachi filter driver
- How to make a disk drive "removable" - Windows 10 Forums
- Make USB Removable -> Fixed Disk / Applications & Desktop Environments / Arch Linux Forums - TL;DR : How do you "flip the bit" of a USB Drive to make it be seen by Windows as a "Removable" or "Fixed Disk" under Arch, or really any Linux distro? I can't seem to find any Unix instructions, only Windows apps.
- Removable USB Flash Drive as Local HDD in Windows | Windows OS Hub - In this article we’ll show you how to make a USB flash drive or an SD card to be identified in the Windows as a common local hard disk.
- The Lexar BootIt utility was designed to "flip the removable media bit" on certain USB flash drives, making them appear as fixed (hard) disks to Windows. This was a niche utility and often highly specific to particular flash drive controllers. It's largely outdated and generally not recommended due to potential instability and the possibility of bricking your USB drive.
- Windows Registry
- The mode cannot be changed in the Windows registry.
My DiskGenius Notes
My DiskGenius Notes
General
- Docs
- How to Use DiskGenius – Online User Guide
- This is detailed user guide for DiskGenius. Follow these tutorials and you'll know how to recover lost data, resize partition, backup data, wipe hard drive, etc.
- There is a large PDF manual you can download.
- Useful and Free Manuals of PartitionGuru – (DiskGenius has replaced this) - Free tutorial of PartitionGuru on how to recover lost data and partition, resize partition, clone hard drive, permanent file deletion, convert GPT to MBR, etc.
- How to Use DiskGenius – Online User Guide
- Misc
- When you mount a drive in Windows either using the GUI or diskpart, the image will be mounted as a physical drive.
- Windows and OSFMouint will mount an image whether is is a normal HDD style or a "Super Floppy" (FDD) style image.
- Windows will not fall back to a logical volume emulation if a VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) image file is corrupted—even slightly.
- can 7zip open VHD files?
- The partition table is not inherently protected—it's just stored in a specific location on the USB drive. While it can’t be easily changed by average users without intent or privilege, it can be accessed, overwritten, or corrupted by software that has sufficient access.
- All VHDs (and other image formats) created with DiskGenius, are fixed-size containers from the outset, made via sector-level cloning.
- The `Convert Boot Mode` options have moved here:
- Disk --> Convert Boot Mode -->
- Convert To USB-ZIP Bootable Mode
- Convert To USB-FDD Bootable Mode
- Convert To HDD mode
- Disk --> Convert Boot Mode -->
- If a Volume's `File System` type is display in Red
- This means it is set as the drive's active partition.
- It should also be accompanied by an `Attribute` of
A.
- When you format a USB disk, windows formats it in "Super "loppy format. These can can be booted by a legacy BIOS, but these are not a bootable hard drive.
- Making a USB drive "bootable" adds in an MBR which includes a partition table.
- Windows when loading a USB checks for both a partition table and then if this is not present searches for a partition (Super Floppy) allowing for both types of USB to load in Windows.
- License
- Q: The lifetime license, is this forever or is it linked to a major release of your software? Once licensed will the software work forever or is it time limited?
- A: After the license is activated, it is bound to the computer and hardware and is permanently activated.
- View SSD-nVME transfer mode
- Disk --> View S.M.A.R.T. Information --> Transfer Mode: PCIe 3.0 x4 | PCIe 4.0 x4
Make the DiskGenius Bootable WinPE USB
DiskGenius supports to making a bootable USB version based on Windows PE so that you can recover lost data, manage disk or backup data when system cannot boot.
- When you create your USB drive I think the build process uses your PC for the drivers and the WinPE files, so the resulting data size on the USB drive will change depending on your system (Win10 = 1GB, Win11 = 2GB)
- I don't know if the DiskGenius USB drives are tied to the PC they were created on.
Format the USB drive
Although DiskGenius can use a USB drive in either the "Supper Floppy" (FDD) or Hard drive mode (HDD) it is easier to work with a HDD version where it has an MBR and Partition table like a traditional hard drive.
When you format a USB drive in Windows the "Super Floppy" format is used by default. I am not sure what happens when you use Windows to format a USB drive taht has a partition table, perhaps ot leaves it alone.
- Format your USB in Rufus in MBR format
- Boot selection:
Non bootable - Partition scheme:
MBR - Target system:
BIOS or UEFI - Volume label:
DISKGENIUS(or whatever you want) - File system:
FAT32 - Cluster size:
Default(this might vary depending on the size of the USB drive)
- Boot selection:
- Set the partition active
- This is not required because DiskGenius does this when it makes the USB a WinPE drive.
Write the WinPE USB
This is non-destructive process, so if there were files on the USB before, they should still be there after the creation of the WinPE environment.
- Create WinPE Bootable USB Drive - DiskGenius
- Open DiskGenius
- Tools --> Create WinPE Bootable USB Drive of DiskGenius.
- Insert the USB you just formatted above if not still pugged in.
- Make sure the right USB drive is selected
- It is easier just to have one USB drive connected to prevent mistakes.
- Click OK button from the pop-up window.
- If you get a message about the drive is mounted, just let DiskGenius unmount the drive
- Wait for a couple of seconds and the bootable disk will be created.
- Click OK button after the bootable disk is created successfully.
- NB: The WinPE files and folders are hidden
Booting DiskGenius from Ventoy
- To boot DiskGenius from Ventoy, we need to generate the DiskGenius WinPE Bootable USB Drive and image it.
- Ventoy allows the use of several different image formats, all with their own strengths.
VHD/VHDX (Recommended)
Method 1 - Disk Image of the USB (Recommended)
- I would recommend getting a 2GB USB drive to keep the image size down and reduce the number of steps required.
- (Win10 WinPE = 550mb)
- (Win11 WinPe = 1GB+)
- The size difference between the images created by these formats is minimal.
- Only use VHDX
- Zero fill the USB drive (optional)
- Use
Alt-Zin Rufus to zero a physical drive.
- NB:
- If you have random data all over the disk, the fact that VHDX can compress data does not mean that its size will always be smaller than VHD.
- If you have long sections of zeroed data, VHDX will work wonders as a compressed disk image format, hence why Rufus labels it as such.
- Do not assume a brand new USB drive is empty for the purposes of imaging.
- After each use, you need to zero fill the drive again to return it to an optimal condition for the purposes of compression.
- If you do not zero fill the drive then the size of the image can be any size up to the capacity of the USB drive.
- Use
- Aquire the Image
- Connect the DiskGenius USB drive
- Image with Rufus to get an Fixed Disk Image (VHDX) of the USB drive
- Create a VHDX image, save it to your desktop and call it:
DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.vhdx
- Create a VHDX image, save it to your desktop and call it:
- Disconnect the DiskGenius USB drive (optional)
- Prepare the Image
- Nothing to do
- Configure Ventoy
- Connect the Ventoy USB drive
- Copy
DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.vhdxto your ventoy images partition. - Install the Ventoy Windows VHD Boot Plugin
- Plugin.WinVhdBoot . Ventoy
- Ventoy uses this plugin to boot VHD(x) files with Windows 7+ in it.
- Both Legacy BIOS and UEFI are supported. Both fixed and dynamic VHD(x) are supported.
- In UEFI mode, only 64 bit Windows is supported, 32 bit is NOT supported.
- Plugin.WinVhdBoot . Ventoy
- Done
- Boot from your Ventoy USB and check it loads.
Method 2 - Manually Create VHDX
- Create the VHDX (there are probably other ways)
- Open up `Disk Management`
- Run:
diskmgmt.msc
- Run:
- Action --> Create VHD
- Use these settings:
- Location:
C:\Users\quantunwarp\Desktop\DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.vhdx - Virtual hard disk size:
2GB - Virtual hard disk format:
VHDX - Virtual hard disk type:
Dynamically expanding (Recommended)
- Location:
- Use these settings:
- Once created, the drive is automatically mounted but needs to be initialised like any new disk.
- In `Disk Mangement` Right click on the new drive and select
Initialise Disk - Use the
MBRpartition style
- In `Disk Mangement` Right click on the new drive and select
- Create a FAT32 partition
- Right click on the drive and select New Simple Volume and follow the wizard.
- Use these settings:
- File System:
FAT32 - Allocation unit size:
Default - Volume Label:
Disk Genius - Perform a quick format.
- File System:
- Set the partition active
- Use DiskGenius to set the partition active
- Open up `Disk Management`
- Prepare the Image
- Mount the VHDX disk image.
- Connect the DiskGenius USB drive.
- Show hidden files
- Copy all files on the USB drive to the VHDX volume.
- Hide all files again
- Unmount/Detach the Disk Image.
- Configure Ventoy
- Connect the Ventoy USB drive
- Copy
DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.vhdxto your ventoy images partition. - Install the Ventoy Windows VHD Boot Plugin
- Plugin.WinVhdBoot . Ventoy
- Ventoy uses this plugin to boot VHD(x) files with Windows 7+ in it.
- Both Legacy BIOS and UEFI are supported. Both fixed and dynamic VHD(x) are supported.
- In UEFI mode, only 64 bit Windows is supported, 32 bit is NOT supported.
- Plugin.WinVhdBoot . Ventoy
- Done
- Boot from your Ventoy USB and check it loads.
WIM
- This only works when using EFI/UEFI boot environments.
- If you try and boot the WIM when using MBR/CSM/Legacy, it will start to load and then a black screen will overlay the Ventoy loader and it will crash.
- Aquire the Image
- Connect the DiskGenius USB drive.
- Show hidden files.
- Copy the following file to your desktop:
...\DiskGenius - Boot\boot.wim - Disconnect the DiskGenius USB drive (optional)
- Prepare the Image
- Rename
boot.wimto something human readable likeDiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.wim
- Rename
- Configure Ventoy
- Connect the Ventoy USB drive
- Copy
DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.vhdxto your ventoy images partition. - Install the Ventoy Wimboot Plugin
- Plugin.wimboot . Ventoy
- Use this plugin to boot WIM files (Legacy BIOS + UEFI)
- Use Windows native bootloader (Legacy + UEFI): etfsboot.com + bootx64.efi directly extracted from Windows ISO file
- For Reference (not used)
- WIMBOOT Mode | Ventoy
- WIMBOOT mode is an alternative for booting official Windows ISO.
- Do I need to install the plugin? Is WIM support now native?
- WIMBOOT Mode | Ventoy
- Plugin.wimboot . Ventoy
- Done
- Boot from your Ventoy USB and check it loads.
ISO
- This is a very trick and time consuming option and is not really needed
- Try and find and ISO already done, and then use this.
method 1 get a windows disk and swap out the contents, keeping the boot sector
- Aquire the Image
- Connect the DiskGenius USB drive
- ..............
- Prepare the Image
- ...........
- Configure Ventoy
- Connect the Ventoy USB drive
- Copy
DiskGenius v6.0.1.1645.isoto your ventoy images partition.
- Done
- Boot from your Ventoy USB and check it loads.
Troubleshooting
How to check if your USB is configured as "Super Floppy" or a traditional Hard drive (HDD)
There are a couple of methods outlined below.
- diskpart
- Run the following commands (swap # for the number assigned to your USB disk):
diskpart list disk select disk # detail disk
- This should give an output as follows:
Microsoft DiskPart version 10.0.26100.1150 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. On computer: WIN11PC DISKPART> list disk Disk ### Status Size Free Dyn Gpt -------- ------------- ------- ------- --- --- Disk 0 Online 1863 GB 4096 KB * Disk 1 Online 7651 MB 0 B DISKPART> select disk 1 Disk 1 is now the selected disk. DISKPART> detail disk General USB Flash Disk USB Device Disk ID: 6F20736B Type : USB Status : Online Path : 0 Target : 0 LUN ID : 0 Location Path : UNAVAILABLE Current Read-only State : No Read-only : No Boot Disk : No Pagefile Disk : No Hibernation File Disk : No Crashdump Disk : No Clustered Disk : No Volume ### Ltr Label Fs Type Size Status Info ---------- --- ----------- ----- ---------- ------- --------- -------- Volume 5 E PICTURES FAT32 Removable 7651 MB Healthy DISKPART> list partition Partition ### Type Size Offset ------------- ---------------- ------- ------- * Partition 1 Primary 14 GB 0 B DISKPART> select partition 1 There is no partition selected. DISKPART>
- As you can see, Disk 1 (the USB):
- It is not a GPT based disk.
- Has no free space, meaning that all the space has been assigned to partitions.
- It is not a "Boot Disk".
- Has only 1 Volume/Partition, which is not bootable.
- When you try and select the partition, diskpart returns the error,
There is no partition selected., indicating it has an error accessing the partition table, which do not exist on "Super Floppy" USB drives.
- This is a "Super Floppy" USB drive, or the partition table is corrupted.
- Run the following commands (swap # for the number assigned to your USB disk):
- DiskGenius
- This images shows you a 16GB "Super Floppy" USB drive
- Basic/RAW = This means there is no MBR or Partition Table.
- FAT32 (FDD) = This is a FAT32 partition, but has not been defined in a partition table.
- MBR Signature: 00000000 = No MBR is defined.
- Partition Table Style: NONE = No partition table.
- Volume/Partition is not marked as active.
- In the drive tree, there is a floppy icon instead of a HDD.
- This images shows you a 16GB "Super Floppy" USB drive
- OSFMount
- Does not show partitions in "Step 2 of 4" as shown below, and "Mount partitions as virtual disks" is greyed out.
- This indicates a "Super Floppy" or corrupt disk image.
- There is no valid partition table for OSFMount to read.
- If the Volume gets mounted in windows then the Image is not corrupt and the drive image is that of a "Super Floppy".
- I have an image that when i mount as a physical disk shows not partitions in OSFMount but windows mounts a volume form this drive?
- This behavior can be confusing, but it usually comes down to how Windows interprets disk images versus how OSFMount handles physical vs logical mounting.
- Your Situation:
- You mount an image in OSFMount as a physical disk.
- OSFMount shows no partitions in its interface.
- Windows still assigns a drive letter and allows you to access a volume from that disk.
- Likely Explanation:
- Even though OSFMount is mounting the image as a physical drive, it may not parse or display the partitions correctly, especially if:
- The partition table is non-standard or corrupt.
- The image is just a raw partition, not a full disk with MBR/GPT.
- OSFMount has trouble recognizing certain filesystems or partition layouts.
- The image has a "superfloppy" format — a single partition image without an MBR (common in some forensic images or disk clones).
- Yet Windows is often more lenient:
- It scans all volumes and can mount a recognizable file system (e.g., NTFS or FAT32), even if the partition table is missing or broken.
- Windows may treat the image like a full partition, even though OSFMount expects a structured physical disk.
- Even though OSFMount is mounting the image as a physical drive, it may not parse or display the partitions correctly, especially if:
- What You Can Do:
- Try mounting the image as a logical drive instead of physical:
- In OSFMount, choose: Mount as drive letter (logical drive)
- Select the image file and choose offset 0 (or auto-detect).
- This usually works well if the image is a raw partition.
- Use disk utilities to inspect the structure:
- Tools like FTK Imager, WinHex, or HxD can help determine if the image has an MBR, GPT, or just a raw file system.
- You can also check in Disk Management (diskmgmt.msc) how Windows sees the mounted image (does it show a healthy volume or an unallocated disk?).
- Check the image format:
- If it’s from forensic software (like EnCase or dd), it might be a raw partition or use non-standard formatting.
- Try mounting the image as a logical drive instead of physical:
- Quick Test
- If you suspect it's a partition image (not a full disk), here’s a trick:
- Open it in OSFMount.
- Mount it as a logical drive with Offset = 0 and file system type = "Auto-detect".
- If it mounts and shows files, it’s just a partition, not a full disk with an MBR.
- If you suspect it's a partition image (not a full disk), here’s a trick:
- Does not show partitions in "Step 2 of 4" as shown below, and "Mount partitions as virtual disks" is greyed out.
When you Mount a DiskGenius USB Disk Image as a hard drive in Windows you get this error
- TL;DR this error is caused by the source USB formatted as a "Super Floppy"
- Starwind P2V does not support "Super Floppy" for live copying as it expects a partition table.
- A USB drive can be formatted as a traditional hard drive (HDD) or in a "Super Floppy" format akin to a traditional floppy disk (FDD).
- "Super Floppy" does not have a MBR or a Partition Table which is what Starwind is looking for when copying from the mounted Disk image.
- Starwind wiil not present/see Removable Media disks or their Volumes, only hard disks. This is intentianal by the software developers.
Scenario
- You used a large USB drive for your DiskGenius WinPE and as a consequence the image is very large even though most of the space is empty.
- You mounted the drive image using either Windows Native or OSFMount. (in this example we has used OSFMount)
- The drive has successfully mounted
- You open Starwind V2V to convert your large USB Fixed size disk image to a growable VHDX image which will create a much smaller image file
- After going through the wizard, you click on convert and almost immediately you get the following error.
Error
Log File
7/21 16:24:49.493 2b68 Facility ???INFO: CV2V_ConverterApp::InitInstance: SetDllDirectory: C:\Program Files\StarWind V2V Converter\lib 7/21 16:24:49.493 2b68 Facility ???INFO: CV2V_ConverterApp::InitInstance: File Version: 9.0.1.757 7/21 16:24:49.508 2b68 Facility ???INFO: CV2V_ConverterApp::InitInstance: Load language IDR_XML_ENGLISH 7/21 16:24:49.508 2b68 Facility ???INFO: CV2V_ConverterApp::InitInstance: Set current language English 7/21 16:24:49.508 2b68 Facility ???INFO: CPS_V2V_Converter::CPS_V2V_Converter: Version MajorVersion 10, MinorVersion 0, BuildNumber 19045 7/21 16:24:49.508 2b68 Facility ???INFO: WrapperHyperV::WrapperHyperV: LoadLibrary C:\Windows\system32\wbem\wmiutils.dll - 94cb0000 7/21 16:24:49.508 2b68 Facility ???INFO: WrapperHyperV::WrapperHyperV: LoadLibrary C:\Windows\system32\wbem\wmiutils.dll - 94cb0000 7/21 16:24:53.723 2b68 Facility ???INFO: ICPPage::OnWizardNext: SetActivePage - eSynchronization 7/21 16:24:57.926 2b68 Facility ???INFO: ICPPage::OnWizardNext: SetActivePage - eAzureConnectionTo 7/21 16:25:06.162 2b68 Facility ???INFO: ICPPage::OnWizardNext: SetActivePage - eLocationTo 7/21 16:25:09.053 2b68 Facility ???INFO: ICPPage::OnWizardNext: SetActivePage - eFormat 7/21 16:25:12.381 2b68 Facility ???INFO: ICPPage::OnWizardNext: SetActivePage - eOptionsHyperV 7/21 16:25:17.914 2b68 Facility ???INFO: ICPPage::OnWizardNext: SetActivePage - eConverting 7/21 16:25:43.043 2b68 Facility ???INFO: CPPOutputFile::onNext: Out path: C:\Users\quantumwarp\Desktop\DiskGenius-Dynamic.vhdx, Out format 11 7/21 16:25:43.043 2b68 Facility ???INFO: ICPPage::OnWizardNext: SetActivePage - eHYPERVConnectionTo 7/21 16:25:43.043 1788 Facility ???INFO: CPPConverting::Convert: InConvertType: 2, OutConvertType: 4 7/21 16:25:43.043 1788 Facility ???INFO: CPPConverting::ConvertDisks: pathInput: 1, pathOutput: C:\Users\quantumwarp\Desktop\DiskGenius-Dynamic.vhdx 7/21 16:25:43.043 1788 Facility ???INFO: P2V::CreateInputImage: path 1 7/21 16:25:43.043 1788 Facility ???INFO: P2V::CreateInputImage: Size 1 - 15518924800, BytesPerSector - 512 7/21 16:25:48.090 1788 Facility ???INFO: CPPConverting::ConvertDisks: CreateInputImage: 0 7/21 16:25:48.090 1788 Facility ???INFO: CPPConverting::ConvertDisks: CreateOutputImage: 0 7/21 16:25:48.090 1788 Facility ???ERROR: CPPConverting::ConvertImage: Read 3 7/21 16:32:00.054 1788 Facility ???ERROR: CPPConverting::ConvertDisks: ConvertImage - 2 7/21 16:32:00.054 1788 Facility ???ERROR: CPPConverting::Convert: FAILED
Log Explained
Here's what the log tells us:
- StarWind V2V Converter Version:
9.0.1.757- This is a relatively recent version, so it's unlikely to be a bug in an old release. - Conversion Type:
InConvertType: 2- This indicates a Physical Disk source.OutConvertType: 4- This indicates a Hyper-V (VHDX) destination.- This confirms that StarWind V2V Converter sees the OSFMounted IMG as a physical disk, which is good.
- Source Disk Identification:
pathInput: 1andSize 1 - 15518924800, BytesPerSector - 512pathInput: 1likely refers to the "Disk 1" as seen by Windows Disk Management. This corresponds to the virtual disk presented by OSFMount.- The size
15,518,924,800 bytes(approx 14.45 GB) andBytesPerSector - 512are correctly identified by the converter from the virtual disk.
- Failure Point:
CPPConverting::ConvertDisks: CreateInputImage: 0- This line means StarWind successfully initialized the connection to the source disk.CPPConverting::ConvertDisks: CreateOutputImage: 0- This line means StarWind successfully initialized the connection to the destination VHDX file.CPPConverting::ConvertImage: Read 3- This is the critical error. It happens immediately after the input and output images are created, right at the point where StarWind tries to read the actual data from the source disk. This confirms a low-level read error from the OSFMounted virtual disk.- The subsequent errors (
ConvertImage - 2, FAILED) are a direct consequence of this initial read failure.
- Conclusion from the log
- The log strongly indicates that the issue is not with StarWind V2V Converter itself, nor with the destination drive or VHDX creation. The problem lies squarely with StarWind's ability to read data from the virtual disk presented by OSFMount, which is derived from your disk image file created from your DiskGenius USB drive.
- Rufus can write raw ISO or DD images that may not have a typical partition table or disk signature that StarWind expects. This can cause problems when it tries to interpret sectors and fails.
- Additional
- This following error (not in the example above) shows an issue with the drive (VHD or physical) not being able to read sectors. If it is a physical drive then this indicates the drive is failing.
10/21 12:55:57.929 2764 Facility ???WARNING: P2V::getBuffer: ReadFile - 23. Data error (cyclic redundancy check). 10/21 12:55:57.929 2764 Facility ???ERROR: CPPConverting::ConvertImage: Read 3 10/21 13:03:16.650 2764 Facility ???ERROR: CPPConverting::Convert: FAILED
- This following error (not in the example above) shows an issue with the drive (VHD or physical) not being able to read sectors. If it is a physical drive then this indicates the drive is failing.
Cause
After in-depth research I can clarify the error is not cause by:
- Rufus or DiskImager: these apps just create a binary image of the disk and change nothing. Any errors or issues of the drive are blindly transferred to the disk image.
- Windows 10 or Windows 11: Apart from the size of the
boot.wimthere is no difference (Win10 = 550mb)(Win11 = 1GB). - Windows Native and OSFormat disk image mounting: These were mounting the disk image correctly and giving a 1:1 representation of the imaged USB drive.
- The disk image being mounted as "Read-Only": This does not interfer with the conversion as it is used as a source only.
- The size/capacity of the USB drive: None of the software has any size limits, certainly none that have been reached.
- Cluster Size / Allocation Unit Size: I tried both 4096 and 8192 and those made no difference. 8192 seems to be the default allocation size for 16GB USB drives.
- Trying different locations for the source and destination files made no difference.
- VHD, VHDX and IMG disk image formats all worked as expected.
- I got no Windows Defender errors, so in this case it was not the AV causing issues.
- Encryption on the drive can cause issues but these drive had none so can be ruled out.
What I have tried
- Zero filling the USB before reformatting = When I formatted with Windows, it just created a "Super Floppy" USB drive because this is how Windows formats them.
- I check the USB drive for errors by doing a full surface scan, it found no errors.
- I checked the FAT32 file system with chkdsk which found no errors.
Solutions
- Always use Dynamic/Growable disk image files where possible to keep space used down.
- Always use MBR/HDD style formatting on your USB drives where possible.
- Use a HDD/MBR Style USB drive to begin with or make one:
- Using Rufus, convert the USB drive into bootable USB, with a single FAT32 partition (HDD format), and of course the partiontion will be marked as `Active`.
- Then use DiskGenius to make it a WinPE.
- This way ensures the USB drive and any images created from it will work in Starwind P2V as there is a partition table present.
- This USB drive will is NOT a "Super Floppy".
- Use the original disk image as is.
- You can keep the image size down by using a smaller USB drive (Win10 = 1GB, Win11 = 2GB).
- Use DiskGenius Pro to make a direct VHD/VHDX image from the USB drive
- This is the same as using Rufus to create the disk image.
- All disk images created by DiskGenius are of the Fixed size type.
- Build your own VDH/VDHX image
- Manually create a VHD/VHDX image on your PC (MBR, Single 2GB FAT32 partition)
- Mount the VHD/VHDX drive image
- Set the partition as `Active`.
- Then manually copy all of the files from the USB drive into the new partition ion the drive image.
WinPE - Low Resolution
- TL;DR = UEFI GOP (Graphics Output Protocol) sets the screen resolution before WinPE when using EFI on my lenovo (resolution seems to be set at 800x600 and cannot be changed)
- Solution = Boot in legacy mode and then change the resolution in DiskGenius if needed: View --> Set screen resolution (Options: 1920x1080, 1024x768). This was on my Lenovo laptop.
- Notes
- Using a different boot loader like Grub which can be used to see what resolutions the GOP provides.
- My Lenovo on EFI returns a resolution of 800x600 but when I use CSM/Legacy I get 1024x768 and 1920x1080 which I can then swap between with the DiskGenius menu in the WinPE environment.
- For most users on modern UEFI systems — the hard limit is 1024x768.
- Some people say showing the boot logo helps increase screen resolution (not tested).
- DiskGenius resolution in the BCD is 1024x768
- Resolutions available will vary from PC to PC, Laptop to Laptop, and can also vary depending on the the boot method (Legacy BIOS / UEFI) used.
In DiskGenius
In the WinPE environment created by DiskGenius, you can change the screen resolution according to the following, if your hardware supports it.
Notes
When trying to change the resolution of my screen when using DiskGenius on my Lenonvo laptop.
- Various Options summary
- Legacy Boot = allows me to change res in WinPE
- setres = no
- qres = 2005, didnt work
- powershell = no powershell to use
- unattended.xml = doesn't work
- Modify the WinPE Image Before Boot (Recommended):
- This is the most reliable method for setting the desired resolution. You do this by customizing the boot.wim file that makes up your WinPE environment.
- You can create an unattend.xml file with display settings and place it in the root of your WinPE ISO or USB. This file will be processed during the WinPE startup phase.
- Here's an example of the unattend.xml snippet for setting resolution:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <unattend xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:unattend"> <settings pass="windowsPE"> <component name="Microsoft-Windows-Setup" processorArchitecture="amd64" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" language="neutral" versionScope="nonSxS" xmlns:wcm="http://schemas.microsoft.com/WMIConfig/2002/State" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> <Display> <ColorDepth>32</ColorDepth> <HorizontalResolution>1920</HorizontalResolution> <RefreshRate>60</RefreshRate> <VerticalResolution>1080</VerticalResolution> </Display> </component> </settings> </unattend>
- Modify the WinPE Image Before Boot (Recommended):
- bcdedit / graphicsresolution
- I made sure I was working on the WinPE drive: X: eg:
X:\bcdedit /store D:\boot\BCD /set {globalsettings} graphicsresolution 1280x1024 - Works
bcdedit /store "d:\boot\BCD" /set {bootmgr} graphicsresolution "800x600" bcdedit /store "d:\boot\BCD" /set {bootmgr} graphicsresolution "1024x768" - Not Working
bcdedit /store "d:\boot\BCD" /set {bootmgr} graphicsresolution "1280x768" bcdedit /store "d:\boot\BCD" /set {bootmgr} graphicsresolution "1280x1024" - Reason
- Most UEFI firmware initializes the screen at 1024x768 or lower.
graphicsresolutionis backed by the boot graphics adapter using VESA BIOS Extensions (VBE) or UEFI GOP (Graphics Output Protocol).- Changing that during early boot (before Windows loads its display drivers) is not officially supported past that limit.
- For most users on modern UEFI systems — the hard limit is 1024x768.
- I made sure I was working on the WinPE drive: X: eg:
- Standards
- GOP - OSDev Wiki
- This is the new standard for UEFI that superseded VESA (BIOS) and UGA (EFI 1.0).
- It has basically the same functions as VESA, you can query the modes, set the modes.
- It also provides an efficient BitBlitter function, which you can't use from your OS unfortunately.
- GOP is an EFI Boot Time Service, meaning you can't access it after you call ExitBootServices(). However, the framebuffer provided by GOP persists, so you can continue to use it for graphics output in your OS.
- GOP - OSDev Wiki
- BCD
- BCDEdit Command-Line Options | Microsoft Learn - BCDEdit is a command-line tool for managing Boot Configuration Data (BCD).
- Other Testing
- WinPE Screen Resolution and DPI scaling on UEFI firmware | mistyprojects.co.uk
- This article is based on observations on screen resolution and DPI scaling in WinPE.
- Screen resolution can be changed from a running WinPE booted on BIOS firmware.
- Changing the screen resolution on UEFI firmware is not so simple. Settings in unnatend.xml appear to be ignored and the screen resolution is fixed. Based on available information screen resolution appears to be set based on Graphics Output Protocal (GOP) mode. Once WinPE is booted, the resolution cannot be changed.
- Setting the resolution in the BCD
bcdedit.exe /set {globalsettings} graphicsresolution 800x600 bcdedit.exe /set {globalsettings} graphicsresolution 1024x600 bcdedit.exe /set {globalsettings} graphicsresolution 1024x768 - Attempting to use an unsupported resolution (unsupported by bcdedit.exe - not the hardware) resulted in the following output:
C:\windows\system32>bcdedit.exe /set {globalsettings} graphicsresolution 1920x1080 The integer data is not valid as specified. Run "bcdedit /?" for command line assistance. The parameter is incorrect. - The highestmode option is also supported in bcdedit.exe. This option will enable boot applications to use the highest graphical mode detected by the firmware
bcdedit.exe /set {globalsettings} highestmode on - To find supported resolutions, use the
graphicsmode --infocommand on the GRUB4UEFI commandline.
- WinPE Screen Resolution and DPI scaling on UEFI firmware | mistyprojects.co.uk
- unattend.xml
- How to Change Screen Resolution in Windows PE 4 and 5 | Password Recovery
- To set screen resolution in WinPE, simply put an answer file named unattend.xml file in the root of the WinPE ISO image with the following content.
- This articel has an example file.
- How to Change Screen Resolution in Windows PE 4 and 5 | Password Recovery
- Ventoy
- [issue]: Low resolution gfx mode booting various ISOs · Issue #3019 · ventoy/Ventoy · GitHub
- Could be an issue with Secure Boot and Lenovos
- Check what resolutions are avaiable in UEFI and Legacy: F5 --> Resolution Configuration
- Rebuild your venoty USB from scratch can help get rid of this resolution issue.
- Can i set the GOP resolution with Ventoy?
- Yes, Ventoy offers options to influence the display resolution, including in UEFI mode, but it's important to understand the nuances, especially regarding GOP.
- Ventoy's approach to resolution:
- Ventoy Menu Resolution: Ventoy itself, at its boot menu, tries to set a resolution. You can typically access this by pressing F5 (Tools) --> Resolution Configuration from the Ventoy main menu. This allows you to choose from resolutions detected by your system's firmware.
- In UEFI mode, these options are often limited to the resolutions exposed by the GOP (Graphics Output Protocol) of your motherboard/graphics card. Common options might include 1024x768, 1280x1024, 1920x1080, and sometimes others, but it depends on your hardware's firmware.
- While Ventoy can request a specific resolution from the firmware, the ultimate support depends on what your system's GOP actually offers.
- ISO Boot Resolution (Post-Ventoy): This is where it gets tricky, especially with WinPE.
- Ventoy's role ends once it hands off control to the ISO: So, while Ventoy might display its menu at a certain resolution, the operating system (like WinPE or a Linux distro) inside the ISO will then take over display control.
- WinPE and UEFI GOP: As discussed before, WinPE in UEFI mode often defaults to a generic resolution (e.g., 800x600) because it relies on the basic GOP. It doesn't load full display drivers by default.
- Ventoy's "Secure Boot Support" and Resolution Issues: There have been reports (as seen in search results) that enabling "Secure Boot Support" in Ventoy, especially with certain Lenovo UEFI firmware, can lead to WinPE ISOs being stuck at a low 800x600 resolution in UEFI mode. Some users found success by disabling secure boot support in Ventoy's installation options, even if Secure Boot is still enabled in the BIOS itself. This suggests a potential conflict or a more restrictive GOP mode being enforced when Ventoy's secure boot components are active.
- Ventoy Menu Resolution: Ventoy itself, at its boot menu, tries to set a resolution. You can typically access this by pressing F5 (Tools) --> Resolution Configuration from the Ventoy main menu. This allows you to choose from resolutions detected by your system's firmware.
- How to try and set resolution with Ventoy in UEFI:
- During Ventoy Installation/Update:
- When you run Ventoy2Disk.exe (on Windows) to install or update Ventoy on your USB drive, go to Option and consider unchecking "Secure Boot Support." This has reportedly helped some users with low resolution issues for WinPE in UEFI.
- Backup your ISOs first, as clearing or reinstalling Ventoy will wipe the USB drive.
- From the Ventoy Boot Menu (before booting the ISO):
- Boot your Ventoy USB drive.
- When the Ventoy main menu appears, press F5 (Tools).
- Select Resolution Configuration.
- Choose the desired resolution from the list of available modes. Ventoy will attempt to set this resolution for its menu.
- Then, proceed to boot your DiskGenius WinPE ISO.
- During Ventoy Installation/Update:
- Important points to remember:
- This won't guarantee WinPE will stay at that resolution. Even if Ventoy's menu appears in a higher resolution, WinPE might revert to a lower one once it boots if it doesn't have the necessary display drivers loaded internally.
- Integrating drivers into WinPE is still the most robust solution for UEFI. While Ventoy can set the initial GOP mode, for WinPE to utilize higher resolutions and display options, it truly needs the proper display drivers embedded within its
boot.wimfile. - Check Ventoy's Official Documentation: Always refer to the official Ventoy documentation (ventoy.net) for the most up-to-date information and advanced configuration options (e.g.,
ventoy.jsonfor persistent settings).
- [issue]: Low resolution gfx mode booting various ISOs · Issue #3019 · ventoy/Ventoy · GitHub
- Software to change Resolution
- Articles
- Software
- Powershell
- QRes @ Sourceforge - QuickRes allows you to change color depth and screen resolution without restarting the machine.
QRes.exe /x:800 /y:600
- NirCmd - Windows command line tool - NirCmd is a small utility that allows you to do many useful tasks from command-line, including changing the dsplay resolution.
- NirCmd Command Reference - setdisplay - No meta description
nircmd.exe setdisplay 1024 768 24
- NirCmd Command Reference - setdisplay - No meta description
- SetRes - MajorGeeks - With SetRes you can set the screen resolution, colour depth and refresh rate from the command line or a shortcut.
- ChangeScreenResolution - Change your screen resolution from the command line in Windows
- Misc
- Problem with resolution of Windows Boot Manager - Microsoft Q&A - Is there anyone know that how to take the default resolution back to Windows Boot Manager?
- Low Resolution Boot Screen Issue & Suggested Fix | Windows 11 Forum
- This is simply an aesthetic bother but I can't stand when my 4K PC monitor boot screen looks like it's 480p
- Someone understood and offered this fix
- Yes you can:
bcdedit /deletevalue "{globalsettings}" highestmode reboot - That picture you posted has zero to do with Windows and everything to do with the BIOS/UEFI loading screen.
- If it was as simple as running the above command from within Windows to edit the BIOS loading screen (or any bios settings for that matter, then we would all be in a world of trouble and at the mercy of any and all nasties that managed infect Windows.
- When i boot of diskgenius WinPE bootable USB, the screen resolution is too low. The option to change screen resolution is missing
- When booting a DiskGenius WinPE bootable USB, experiencing low screen resolution and missing resolution options is a common issue. This often stems from WinPE's minimalistic nature, as it typically uses generic display drivers that might not fully support your display's native resolution or advanced graphics settings.
- Here's what you should consider:
- WinPE and Display Drivers: WinPE images generally do not include a full set of display drivers. They rely on basic drivers for compatibility across a wide range of hardware. This means advanced display features, including the ability to change resolution, might be limited or unavailable.
- UEFI vs. Legacy Boot: The behavior of WinPE regarding screen resolution can differ between UEFI and Legacy BIOS boot modes. In some UEFI environments, the screen resolution is determined by the Graphics Output Protocol (GOP) and might be fixed once WinPE boots.
- Integrating Drivers: For specific hardware, it might be possible to integrate display drivers into the WinPE image itself. This is an advanced process and typically involves using tools from the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK) to customize the boot.wim file. However, even with integrated drivers, some users report issues.
- GOP
- Changing the Graphics Output Protocol (GOP) resolution directly in UEFI is a complex topic, and it's not something you typically "change" in the same way you would adjust display settings in a running operating system. Here's a breakdown of what GOP is and why it's so difficult to modify:
- What is GOP?
- The Graphics Output Protocol (GOP) is a core part of UEFI firmware. It's designed to replace the older Video BIOS (VBIOS) found in legacy BIOS systems. Essentially, GOP provides a standardized way for the UEFI firmware and early boot processes to display graphics on your screen before the operating system's full graphics drivers load.
- Key characteristics of GOP:
- Pre-OS Display: It's responsible for displaying the manufacturer's logo, BIOS/UEFI setup screens, and early boot messages.
- Driver Replacement: It replaces the need for a separate VBIOS by providing a protocol that UEFI applications can use to draw directly to a hardware frame buffer.
- Integrated into VBIOS/Firmware: The GOP driver itself is usually embedded within the graphics card's VBIOS (Video BIOS) or the motherboard's UEFI firmware.
- Why is it difficult to change GOP resolution?
- Firmware-Dependent: The available GOP resolutions are determined by your motherboard's UEFI firmware and your graphics card's VBIOS. These are often hardcoded and limited to a few standard resolutions (e.g., 800x600, 1024x768).
- Generic Drivers: WinPE, being a minimal environment, relies on these generic GOP modes. It doesn't load a full suite of display drivers that would allow for dynamic resolution changes.
- No User Interface: There's typically no user-friendly interface within the UEFI firmware itself to change the active GOP resolution directly. You might find a setting to switch between "UEFI" and "CSM" (Compatibility Support Module, which enables legacy BIOS features), but not to pick a specific GOP resolution.
- Security and Stability: Modifying the underlying firmware (VBIOS or motherboard UEFI) to force a different GOP resolution carries significant risks, including potentially bricking your hardware if done incorrectly.
